Android-x86
 | |
|
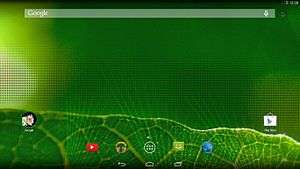
Screenshot of Android-x86 4.4 KitKat, showing the homescreen | |
| OS family | Android |
|---|---|
| Working state | Active |
| Source model | Open source |
| Latest release | 6.0-r1[1] / September 13, 2016 |
| Latest preview | 6.0-rc2 (or "Remix OS for PC - Android M rc2 (version: 3.0.201)" / August 15, 2016 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (modified Linux kernel) |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Official website |
www |
Android-x86 is an unofficial initiative to port Google's Android mobile operating system to run on devices powered by AMD and Intel x86 processors, rather than RISC-based ARM chips.
The project began as a series of patches to the Android source code to enable Android to run on various netbooks, tablets and ultra-mobile PC.
Chih-Wei Huang and Yi Sun originated the project in 2009. Yi Sun then quit due to personal affairs. Chih-Wei Huang is the current project maintainer, that has collaborated with Jide technology (that makes Remix OS), prior to joining that company.
Overview
The OS is based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) with some modifications and improvements. Some components are developed by the project which allow it to run on PC architecture. For instance, some low-level components are replaced to better suit the platform, such as the kernel and HALs. The OS enables Open GL ES hardware acceleration if supported GPUs are detected, including Intel GMA, AMD's Radeon and Nvidia's chipsets (Nouveau). Without supported GPUs the OS can also run in non-accelerated mode via software rendering.
Like a normal Linux distribution, the project releases prebuilt ISO images which can run under live mode or install to the harddisks of the target devices. Since the 4.4-r2 the project also releases efi_img[2] which could be used to create a live USB which is bootable from UEFI devices.
The following components are developed from scratch or derived from other open source projects:
Android-IA
A related project, Android-IA[3] has been produced by Intel that will run on newer UEFI devices. The Android-IA project states that its intention is to drive Android support and innovation on Intel Architecture in addition to providing a venue for collaboration.[3] Android-IA re-used the drm_gralloc graphics HAL module from Android-x86 in order to support Intel HD Graphics hardware. The Android-IA project provides a FAQ[4] with more detailed information. The project has since been discontinued.
Remix OS
Jide Technologies announced Remix OS, a currently closed-source derivative of Android-x86 designed for use on conventional PCs, is partnering with Chih-Wei Huang, the main developer of Android-x86. Remix OS's first beta was made available on March 1, 2016.[5]
Another similar operating system for computers based on Android-x86 is Phoenix OS,[6] which when installed has an option to Dual Boot with Windows 10.
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.android-x86.org/releases/releasenote-6-0-r1
- ↑ "Android-x86 Release 4.4". android-x86@sourceforge. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Home". Android on Intel Architecture. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ "FAQ". Android on Intel Architecture. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ http://forum.xda-developers.com/remix/remix-os/announcement-release-remix-os-pc-beta-t3326362
- ↑ http://www.phoenixos.com
External links
- android-x86.org, official site