Crossbite
| Crossbite | |
|---|---|
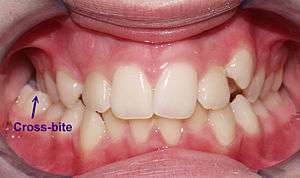 | |
| Unilateral Posterior Crossbite. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | gastroenterology |
| ICD-10 | K07.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 524.27 |
Crossbite is a form of malocclusion where a tooth (or teeth) has a more buccal or lingual position (that is, the tooth is either closer to the cheek or to the tongue) than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower dental arch. In other words, crossbite is a lateral misalignment of the dental arches.
Terminology and classification
Crossbite can involve a single tooth or a group of teeth. It can be classified in anterior or posterior and bilateral or unilateral.
An anterior cross bite can be referred as negative overjet, and is typical of class III skeletal relations (prognathism).
Posterior crossbite is often correlated to a narrow maxilla and upper dental arch. A posterior cross-bite can be unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral cross-bite often determines a lateral shift of the mandibular position, which can become structural if left untreated for a long time during growth, leading to skeletal asymmetries. There are 3 types of crossbite : simple anterior, functional anterior, and skeletal anterior
Posterior crossbite is also known as "reverse articulation".[1]
Treatment
There are several therapies that can be used to correct a cross bite: braces, 'Z' spring or cantilever spring, quad helix, removable plates, clear aligner therapy, or a Delaire mask. The correct therapy should be decided by the orthodontist depending on the type and severity of the crossbite.
References
- ↑ Rickne C. Scheid; Julian B. Woelfel (2007). Woelfel's dental anatomy: its relevance to dentistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 379–. ISBN 978-0-7817-6860-3. Retrieved 22 April 2010.