Dutch East Indies campaign
| Dutch East Indies campaign | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Pacific Theatre of World War II | |||||||
 Japanese forces land on Java. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
148,000 troops[1] 33 warships[4]41 submarines[5] 234 aircraft[2] |
52 warships[6][7] 18 submarines[5] 50,000 troops[8] 331 aircraft | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
2,384 killed 100,000+ captured[9] | 671 killed[10] | ||||||
The Dutch East Indies campaign of 1941–42 was the conquest of the Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) by forces from the Empire of Japan in the early days of the Pacific Campaign of World War II. Forces from the Allies attempted unsuccessfully to defend the islands. The East Indies were targeted by the Japanese for their rich oil resources which would become a vital asset during the war. The campaign and subsequent three and a half year Japanese occupation was also a major factor in the end of Dutch colonial rule in the region.
Background
The East Indies was one of Japan's primary targets if and when it went to war because the colony possessed abundant valuable resources, the most important of which were its rubber plantations and oil fields;[11][12] the colony was the fourth-largest exporter of oil in the world, behind the U.S., Iran, and Romania.[12][A 1] The oil made the islands enormously important to the Japanese (see below), so they sought to secure the supply for themselves. They sent four fleet carriers and a light carrier along with the four fast battleships of the Kongō class, 13 heavy cruisers and many light cruisers and destroyers to support their amphibious assaults in addition to conducting raids on cities, naval units and shipping in both that area and around the Indian Ocean.[13]
Access to oil was one of the linchpins of the Japanese war effort, as Japan has no native source of oil;[14] it could not even produce enough to meet even 10% of its needs,[12] even with the extraction of oil shale in Manchuria using the Fushun process.[15] Japan quickly lost 93 percent of its oil supply after President Franklin D. Roosevelt issued an executive order on 26 July 1941 which froze all of Japan's U.S. assets and embargoed all oil exports to Japan.[16] In addition, the Dutch government in exile, at the urging of the Allies and with the support of Queen Wilhelmina, broke its economic treaty with Japan and joined the embargo in August.[14] Japan's military and economic reserves included only a year and a half's worth of oil.[12] As a U.S. declaration of war against Japan was feared if the latter took the East Indies, the Japanese planned to eliminate the U.S. Pacific Fleet, allowing them to overtake the islands; this led to the attack on Pearl Harbor.[17][18]
Declarations of war
In late November, the East Indies government began preparing for war: ships of the Royal Netherlands Navy were sent to sea and the KNIL Air Force was mobilised.[19] On 4 December, three days after having decided on a policy of war against America, Britain and the Netherlands, the Japanese government decided instead to "treat the Netherlands as a quasi enemy until actual hostilities ... occur."[20][21] This was in the hopes that the Dutch would not preemptively destroy oil installations before the Japanese were ready to invade.[20] On 8 December 1941, in a public proclamation, the Netherlands declared war on Japan.[22] By 7:00 a.m. on the day of the attack, the East Indies government had warned merchantmen at sea to make for the nearest port. At that hour, the governor general made a public announcement over the radio that the Netherlands "accepts the challenge and takes up arms against the Japanese Empire."[19] Instructions had been telegraphed to the embassy in Tokyo at 2:30 a.m., even before news of the attack on Pearl Harbor had reached the Dutch government in London at 4:00. The instructions were only received on the evening of the next day, and the declaration of war was finally handed to the Japanese foreign minister, Shigenori Tōgō, by the Dutch ambassador, J. C. Pabst, on the morning of 10 December.[19] The Swedish ambassador agreed to handle Dutch interests for the duration of the conflict.
The Dutch declaration did not alter the Japanese decision, and the latter's declaration of war did not come until 11 January 1942.[20] When Japan was charged with waging a "war of aggression" before the International Military Tribunal for the Far East in 1946, it was argued that her attitude towards the Netherlands proved otherwise, since the Dutch had declared war first. The tribunal rejected this, on the grounds that Japan's sole intention was "to give less time to the Netherlands for destroying oil wells."[20] They found that the Netherlands' declaration was in self-defence.[21]
Campaign
General Hisaichi Terauchi, commander of the Southern Expeditionary Army Group, began the campaign with attacks against Borneo: on 17 December, Japanese forces successfully landed on Miri, an oil production centre in northern Sarawak, with support from a battleship, an aircraft carrier, three cruisers and four destroyers.[23]
Initially, the Japanese forces launched air strikes on key areas and gained air superiority. Following the airstrikes, landings were made at several locations targeting airfields and other important points in the area. In addition to the landings at Miri, the Japanese forces made landings at Seria, Kuching, Jesselton and Sandakan between 15 December 1941 and 19 January 1942. After these main objectives in Borneo were completed, the Japanese forces planned a three-pronged assault southward using three forces named Eastern Force, Center Force and Western Force. The aim of this assault was to capture the oil resources in the East Indies. The Eastern Force was to advance from Jolo and Davao and move on to capture Celebes, Amboina and Timor, while protecting the Center Force's flank. The Center Force was to capture oil fields and airfields in Tarakan Island and Balikpapan. Both these forces would support the Western Force, which was to attack and capture the oil refineries and airfields in Palembang. The Japanese forces launched the assault on 11 January and landed at Tarakan.[24]
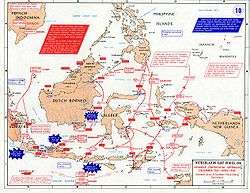
To coordinate the fight against the Japanese, the American, British, Dutch, and Australian forces combined all available land and sea forces under the American-British-Dutch-Australian Command (ABDACOM or ABDA) banner. This command was activated on 15 January 1942, with the overall commander being British Field Marshal Sir Archibald Wavell.[25] The command structure had the American Army Air Force Lieutenant General George Brett as deputy commander, the British Lieutenant General Henry Royds Pownall as chief of staff; under them were the American Admiral Thomas C. Hart as naval commander, the Dutch Lieutenant General Hein ter Poorten as ground forces commander, and the British Air Chief Marshal Sir Richard Peirse as the air commander.[26] Although the forces were combined, they had differing priorities: the British believed the defense of the territory of Singapore and the eastern entrances to the Indian Ocean (the route to British Ceylon and British India) to be paramount, the Americans and Australians did not want a total penetration of Southwest Asia that would deprive them of bases necessary for any serious counterattack, and the Dutch considered Java and Sumatra, their "second homeland where [they] had been trading and living for over three centuries", to be the most important place to defend.[27]
Even the combined forces could not stop or even slow the Japanese advance due to their much greater numbers; to face the Japanese attacking naval forces, the ABDA command had a conglomerate of ships drawn from any available units, which included the U.S. Asiatic Fleet (fresh from the fall of the Philippines), a few British and Australian surface ships, and Dutch units that had previously been stationed in the East Indies. Major forces included two seaplane tenders (USS Langley and Childs), two heavy cruisers (USS Houston and HMS Exeter), seven light cruisers (HNLMS De Ruyter, Java and Tromp, USS Marblehead and Boise, HMAS Hobart and Perth), 22 destroyers, and, perhaps their greatest strength, 25 American and 16 Dutch submarines. Being based on Java, these ships had to take on the central and western prongs of the three-headed Japanese assault; the central force's combat ships, the light carrier Ryūjō, the seaplane tenders Sanyo Maru and Sanuki Maru, three light cruisers and 16 destroyers, while the western force contained five heavy cruisers, and seven destroyers. In addition, four fleet carriers (Akagi, Kaga, Hiryū and Sōryū) and the four Kongō-class battleships.[7]
The manner of the Japanese advance resembled the insidious yet irresistible clutching of multiple tentacles. Like some vast octopus it relied on strangling many small points rather than concentration on a vital organ. No one arm attempted to meet the entire strength of the ABDA fleet. Each fastened on a small portion of the enemy and, by crippling him locally, finished by killing the entire animal. [...] The Japanese spread their tentacles cautiously, never extending beyond the range of land-based aircraft unless they had carrier support. The distance of each advance was determined by the radius of fighter planes under their control. This range was generally less than 400 miles, but the Japanese made these short hops in surprisingly rapid succession. Amphibious operations, preceded by air strikes and covered by air power developed with terrifying regularity. Before the Allies had consolidated a new position, they were confronted with a system of air bases from which enemy aircraft operated on their front, flanks and even rear.[28]
The Japanese forces were using Tarakan airfield as a forward airbase by 17 January, and Balikpapan was also captured a week later. However, the Dutch garrisons had destroyed the oil fields before they were captured by the Japanese in both cases. Several Japanese vessels were destroyed or damaged due to naval and air counterattacks from the Allied forces, but the defending Dutch battalions were overrun by the Japanese forces. By 28 January, the Japanese had taken control of the airfields at Balikpapan, and their aircraft were operating from them.[24] By the end of January, Japanese forces had captured parts of the Celebes and Dutch Borneo.[29] By February, Japanese forces had landed on Sumatra and encouraged a revolt in Aceh.[29]
Most of the naval components of the allied force were crushed in the battles of Java Sea, Sunda Strait and Second Java Sea;[14][30] the only American ship larger than a destroyer to survive was the old cruiser Marblehead.[31] In addition, the land forces on the islands were quickly overwhelmed and most major resistance was overcome within two months of the initial assaults, although a guerrilla campaign in Timor was successfully waged for a time.[14][30] The ABDA command was dissolved at about 01:00 on 1 March, less than two months after its inception, by Admiral Conrad Emil Lambert Helfrich, Governor-General of the East Indies.[32]
Allied operations in Indonesia (except Sumatra) were later controlled by the South West Pacific Area command, under General Douglas MacArthur.
Aftermath
Allied forces did not attempt to retake the islands of Java, Sumatra, Timor, or Bali during the war. Japanese forces on those islands surrendered at the conclusion of World War II. Most of the Japanese military personnel and civilian colonial administrators were repatriated to Japan following the war, except for several hundred who were detained for investigations of war crimes, for which some were later put on trial. About 1,000 Japanese soldiers deserted from their units and assimilated into local communities. Many of these soldiers provided assistance to Indonesian Republican forces during the Indonesian National Revolution.[33]
Battles of the campaign
- Battle of Borneo (1941–42)
- Battle of Manado (1942)
- Battle of Tarakan (1942)
- Battle of Balikpapan (1942)
- Battle of Ambon (1942)
- Battle of Palembang (1942)
- Battle of Makassar Strait
- Battle of Badung Strait (1942)
- Battle of the Java Sea (1942)
- Second Battle of the Java Sea (1942)
- Battle of Sunda Strait (1942)
- Battle of Java (1942)
- Battle of Timor (1942-43)
Notes
- ↑ The statistics given are for 1935. The top five oil exporters that year were, in order, the United States, with 6,958 kt, Persia (Iran), with 6,860 kt, Romania, with 6,221 kt, the Dutch East Indies, with 5,139 kt, and the Soviet Union, with 3,369 kt. See: The Way to Pearl Harbor: US vs Japan, accessed 27 February 2009. Full citation given below.
References
- ↑ Does not include naval personnel
- 1 2 3 "Chapter 10: Loss of the Netherlands East Indies". The Army Air Forces in World War II: Vol. 1 – Plans & Early Operations. HyperWar. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ↑ George McTurnan Kahin and Adrian Kahin, Subversion as Foreign Policy, New York: The New Press, 1995 (ISBN 1565842448), Pp 22
- ↑ Morison (1948), pp. 158, 271–273, 293 and 311
- 1 2 "Submarine War in the Dutch East Indies (1941-1942)". Dutch East Indies Campaign website. 1999–2000. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ↑ Morison (1948), pp. 274– 276, 296, 384
- 1 2 Morison (1948), pp. 275–276
- ↑ Groen (2010), pp. 12
- ↑ "WORLD WAR II: THE DEFENSIVE PHASE", US Army Center Of Military History, p. 87
- ↑ Francis Pike, "Hirohito's War: The Pacific War, 1941-1945", 2015, p. 309.
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 280
- 1 2 3 4 Arima, Yuichi (December 2003). "The Way to Pearl Harbor: US vs Japan". ICE Case Studies Number 118. American University. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ↑ Morison (1948), pp. 274–276, 296, 384
- 1 2 3 4 "The Netherlands East Indies and the Pacific War". Allies in Adversity; Australian and the Dutch in the Pacific War. Australian War Memorial. 1997–2009. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ↑ Dyni, John R. (2006). "Geology and Resources of Some World Oil-Shale" (PDF). Deposits Scientific Investigations Report 2005–5294. U.S. Department of the Interior. U.S. Geological Survey: 13. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ↑ Worth Jr. (1995), pp. 4 and 66
- ↑ "Pearl Harbor Raid, 7 December 1941". Naval Historical Center. Department of the Navy. 7 October 2000. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ↑ Reynolds, Paul (20 April 2004). "Oil and conflict - a natural mix". BBC News. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- 1 2 3 Hubertus Johannes van Mook (1944), The Netherlands Indies and Japan: Their Relations, 1940–1941 (London: G. Allen & Unwin), pp. 106–07 and nn.
- 1 2 3 4 Ken'ichi Goto (2003), Tensions of Empire: Japan and Southeast Asia in the Colonial and Postcolonial World, ed. Paul H. Kratoska (Singapore: Singapore University Press), p. 52.
- 1 2 Gabrielle Kirk McDonald and Olivia Swaak-Goldman, edd. (2000), Substantive and Procedural Aspects of International Criminal Law: The Experience of International and National Courts, Volume II, Part 1 (The Hague: Kluwer Law International), pp. 764–65.
- ↑ "The Kingdom of the Netherlands Declares War with Japan", Inter-Allied Review, Inter-Allied Review via Pearl Harbour History Associates Inc. hosted at ibiblio, December 15, 1941, retrieved 2009-10-04
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 191
- 1 2 Bradley, John N.; Bradley, John H.; Buell, Thomas B.; Griess,Thomas E.; Dice, Jack W. (2002). The Second World War. Square One Publishers. p. 85. ISBN 0757001629. Retrieved March 29, 2009.
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 277
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 278
- ↑ Morison (1948), pp. 281–282
- ↑ Morison (1948), pp. 292–293
- 1 2 Vickers, Adrian. (2005) A History of Modern Indonesia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p86-87
- 1 2 "Japanese conquest". Allies in Adversity; Australian and the Dutch in the Pacific War. Australian War Memorial. 1997–2009. Retrieved 27 February 2009.
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 375
- ↑ Morison (1948), p. 377
- ↑ Tjandraningsih, Christine, (Kyodo News), "Japanese recounts role fighting to free Indonesia", Japan Times, Sep 9, 2009, p. 3.
Bibliography
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (1948). The Rising Sun in the Pacific; 1931 – April 1942. History of United States Naval Operations in World War II. Boston: Little, Brown. OCLC 7361008.
- Post, Peter; Frederick, William H.; Heidebrinki, Iris; Sato, Shigeru, eds. (2010). "The War in the Pacific". The Encyclopedia of Indonesia in the Pacific War. Leiden: BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-16866-4.
Further reading
- Klemen, L. "The Netherlands East Indies 1941-1942".
- Burton, John (2006). Fortnight of Infamy: The Collapse of Allied Airpower West of Pearl Harbor. US Naval Institute Press. ISBN 159114096X.
- Cull, Brian (2004). Hurricanes Over Singapore: RAF, RNZAF and NEI Fighters in Action Against the Japanese Over the Island and the Netherlands East Indies, 1942. Grub Street Publishing. ISBN 978-1904010807.
- Cull, Brian (2008). Buffaloes over Singapore: RAF, RAAF, RNZAF and Dutch Brewster Fighters in Action Over Malaya and the East Indies 1941-1942. Grub Street Publishing. ISBN 978-1904010326.
- Drea, Edward J. (1998). In the Service of the Emperor: Essays on the Imperial Japanese Army. Nebraska: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-1708-0.
- Kelly, Terence (2008). Hurricanes Versus Zeros: Air Battles over Singapore, Sumatra and Java. Pen and Sword. ISBN 978-1844156221.
- Krancher, Jan A. (2003). The Defining Years of the Dutch East Indies, 1942-1949: Survivors Accounts of Japanese Invasion and Enslavement of Europeans and the Revolution That Created Free Indonesia. McFarland & Company. ISBN 978-0786417070.
- Shores, Christopher (2002). Bloody Shambles: Volume One: The Drift to War to the Fall of Singapore. London: Grub Street Publishing. ISBN 094881750X.
- Shores, Christopher (2009). Bloody Shambles: Volume Two: The Complete Account of the Air War in the Far East, from the Defence of Sumatra to the Fall of Burma, 1942. London: Grub Street Publishing. ISBN 0948817674.
- Womack, Tom (2006). Dutch Naval Air Force Against Japan: The Defense of the Netherlands East Indies, 1941-1942. McFarland & Company. ISBN 978-0786423651.