Eagle syndrome
| Eagle syndrome | |
|---|---|
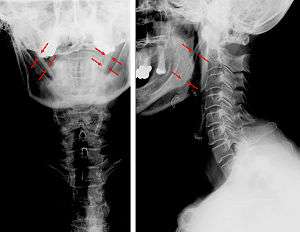 | |
| Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of cervical spine showing ossification of the stylohyoid ligament on both sides | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| DiseasesDB | 33542 |
| eMedicine | article/1447247 |
Eagle syndrome (also termed stylohyoid syndrome[1] styloid syndrome,[2] styloid-stylohyoid syndrome,[2] or styloid–carotid artery syndrome)[3] is a rare condition characterized by sudden, sharp nerve-like pain in the jaw bone and joint, back of the throat, and base of the tongue, triggered by swallowing, moving the jaw, or turning the neck.[1] Named for the doctor who first described it in 1937, the condition is caused by an elongated or misshapen styloid process, the slender, pointed piece of bone just below the ear, and/or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament, which interferes with the functioning of neighboring regions in the body, giving rise to pain.
Signs and symptoms
Possible symptoms include:
- Sharp, shooting pain in the jaw, back of the throat, base of the tongue,[1] ears, neck, and/or face[4]
- Difficulty swallowing[4]
- Sensation of having a foreign object in throat[4]
- Pain from chewing, swallowing, turning the neck, or touching the back of the throat[5]
- Ringing or buzzing in the ears
Classic eagle syndrome is present on only one side, however, rarely, it may be present on both sides.[4]
In vascular eagle syndrome, the elongated styloid process comes in contact with the internal carotid artery below the skull. In these cases, turning the head can cause compression of the artery or a tear inside the blood vessel, which restricts blood flow and can potentially lead to a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.[4]
Cause
The cause of the condition is unknown.
Diagnosis
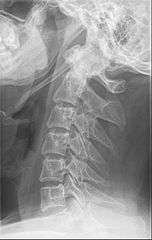 Radiograph, lateral view showing elongated stylohyoid process and stylohyoid ligament ossification
Radiograph, lateral view showing elongated stylohyoid process and stylohyoid ligament ossification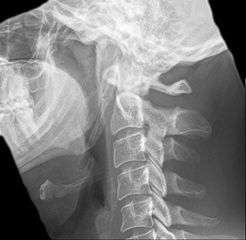 Radiograph, lateral view showing joint-like formation in ossified stylohyoid ligament
Radiograph, lateral view showing joint-like formation in ossified stylohyoid ligament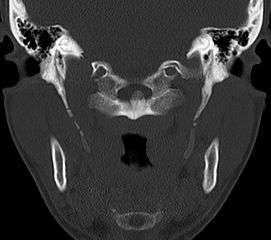 CT scan, coronal section showing bilateral extended styloid process and stylohyoid ligament ossification (incidental finding)
CT scan, coronal section showing bilateral extended styloid process and stylohyoid ligament ossification (incidental finding) 3D-reconstructed CT scan showing bilateral stylohyoid ligament ossification
3D-reconstructed CT scan showing bilateral stylohyoid ligament ossification- 3D reconstructed CT scan showing elongated styloid process (right side)
Diagnosis is suspected when a patient presents with the symptoms of the classic form of "eagle syndrome" e.g. unilateral neck pain, sore throat or tinnitus. Sometimes the tip of the styloid process is palpable in the back of the throat. The diagnosis of the vascular type is more difficult and requires an expert opinion. One should have a high level of suspicion when neurological symptoms occur upon head rotation. Symptoms tend to be worsened on bimanual palpation of the styloid through the tonsillar bed. They may be relieved by infiltration of lidocaine into the tonsillar bed. Because of the proximity of several large vascular structures in this area this procedure should not be considered to be risk free.
Imaging is important and is diagnostic. Visualizing the styloid process on a CT scan with 3D reconstruction is the suggested imaging technique.[6] The enlarged styloid may be visible on an orthopantogram or a lateral soft tissue X ray of the neck.
It is worth noting that the styloid may be enlarged (>30 millimeters in length) in 4% of the population and only a small minority (~4%) of people with enlarged styloids have symptoms.
Treatment
In both the classic and vascular form, the treatment is surgical.[7] A partial styloidectomy is the preferred approach. Repair of a damaged carotid artery is essential in order to prevent further neurological complications. Regrowth of the stylohyoid process and relapse are a common occurrence.[5]
Epidemiology
Approximately 4% of the general population have an elongated styloid process, and of these about 4% give rise to the symptoms of Eagle syndrome.[8] Therefore, the incidence of stylohyoid syndrome may be about 0.16%.[8]
Patients with this syndrome tend to be between 30 and 50 years of age but it has been recorded in teenagers and in patients > 75 years old. It is more common in women, with a male:female ratio ~ 1:2.
History
The condition was first described by American otorhinolaryngologist Watt Weems Eagle in 1937.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 Waldman SD (6 June 2013). Atlas of Uncommon Pain Syndromes. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 35–36. ISBN 1-4557-0999-9.
- 1 2 Bumann A; Lotzmann U (2002). TMJ Disorders and Orofacial Pain: The Role of Dentistry in a Multidisciplinary Diagnostic Approach. Thieme. p. 279. ISBN 978-1-58890-111-8.
- ↑ Hoffmann, E.; Räder, C.; Fuhrmann, H.; Maurer, P. (2013). "Styloid–carotid artery syndrome treated surgically with Piezosurgery: A case report and literature review". Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 41 (2): 162–166. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2012.07.004. PMID 22902881.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kamal, A; Nazir, R; Usman, M; Salam, BU; Sana, F (November 2014). "Eagle syndrome; radiological evaluation and management.". JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association. 64 (11): 1315–7. PMID 25831655.
- 1 2 Scully C (21 July 2014). Scully's Medical Problems in Dentistry. Elsevier Health Sciences UK. ISBN 978-0-7020-5963-6.
- ↑ Karam C, Koussa S (December 2007). "[Eagle syndrome: the role of CT scan with 3D reconstructions]". J Neuroradiol (in French). 34 (5): 344–5. doi:10.1016/j.neurad.2007.08.001. PMID 17997158.
- ↑ Orhan KS, Güldiken Y, Ural HI, Cakmak A (April 2005). "[Elongated styloid process (Eagle's syndrome): literature review and a case report]". Agri (in Turkish). 17 (2): 23–5. PMID 15977090.
- 1 2 3 Petrović, B; Radak, D; Kostić, V; Covicković-Sternić, N (2008). "[Styloid syndrome: a review of literature].". Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo. 136 (11-12): 667–74. PMID 19177834.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eagle syndrome. |