Equalization (proof)

Equalization is a mathematical analysis of static load-sharing (also called load-distributing) 2-point anchor systems.
Derivation
Consider the node, where the two anchor legs join with the main line. At this node, the sum of all forces in the x-direction must equal zero since the system is in mechanical equilibrium.
-
(1)
The net force in the y-direction must also sum to zero.
-
(2)
Substitute from equation (1) into equation (2) and factor out .
Solve for and simplify.
Use a trigonometric identity to simplify more and arrive at our final solution for .
-
(3)
Then use from equation (3) and substitute into (1) to solve for
-
(4)
Symmetrical Anchor - Special Case
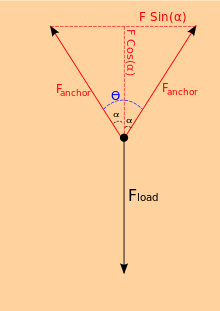
Let us now analyze a specific case in which the two anchors are "symmetrical" along the y-axis.
Start by noticing and are the same. Let us start from equation (4) and substitute for and simplify.
And using another trigonometric identity we can simplify the denominator.
Note that is half of the angle between the two anchor points. To express the force at each anchor using the entire angle , we substitute .
References
- "Non-Load Sharing Anchors." Ratref. Web. 11 February 2012. <http://ratref.com/content/non-load-sharing-anchors>.