Farm Forestry Toolbox

The Farm Forestry Toolbox is a collection of computer programs, referred to as 'Tools', intended to be used by farm forest owners and managers to aid decision making. The Toolbox includes a set of simple 'Hand Tools'; conversation of measurements and map co-ordinates; measuring the volume of stacked logs, slope, basal area; and a survey tool. A second set of more complex tools or 'Power Tools'; are used to estimate site productivity (growth rate), volume and value of wood grown for individual trees, at the coupe or stand level and forest estate level.
The Toolbox was included in the 2009 CSIRO publication Agroforestry for Natural Resource Management.[1]
The Toolbox Inventory tool is recognised in the A Standard for Valuing Commercial Forests in Australia,[2] as a suitable tool to undertake inventory for the purposes of the Standard.
A Workshop - The Farm Forestry Toolbox - Australia's most versatile and widely used forestry software, was conducted as part of the 8th Australia and the New Zealand Institute of Forestry (ANZIF) Conference (2015).[3]
Background
Farm Forestry is a term used in Australia to describe the use of private land to grow wood products and provide a number of other ecosystem services. Private land is land registered under Torrens title and leasehold land, usually leased from the government. Farm Forestry is defined as 'establishment and/or management of trees or forests on agricultural landscapes for commercial, aesthetic and/or environmental reasons [4] The term 'Farm Forestry', as used in Australia, encompasses Afforestation, Agroforestry, Analog forestry, Buffer strip, Plantation, Reforestation, Riparian-zone restoration, Silvopasture and Windbreak.
Support for Farm Forestry is provided by both the Australian Government [5] and State governments. In 2005 the Australian government released a Farm Forestry - National Action Statement.[6]
Governments have provided grants, funded research, provided advice (extension) and tax incentives to encourage landowners to adopt Farm Forestry.[7]
Rationale
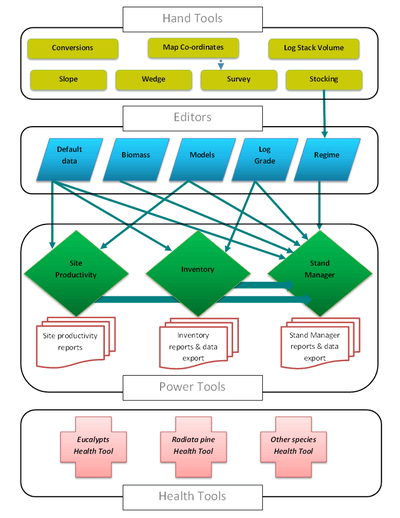
The 'Tools' were initially developed to make routine tasks easier. For example, using the 'Stocking Tool' it is possible to calculated the number of trees required, given a row and in-row spacing, and area to be planted.
The 'Health Tool' has a similar approach. A user can diagnose tree health problems using the Toolbox, replacing the need to use reference texts, or having to enlist the assistance of a forest health expert.
Forest researchers have developed a number growth models, but these models are often difficult to access and use. The Toolbox was developed to ensure that growth models were available to farm forestry owners and managers, able to be used to inform decision making, and provide a link between the growth models outputs and financial modelling tools.
The 'Stand Manager' is more complex and used to calculate net present value, internal rates of return, and wood and product yield. This Tool is used to explore management scenarios, and the resultant financial return and wood yield. A user of the 'Stand Manger' is required to create log grade sets (log specifications), regimes (sequence of events over the life of the rotation detailing events, including timing and costs/returns), as input data. This Tool can also use the output from 'Site Productivity' and 'Inventory' tools.
Users can 'customise' the Toolbox by using the 'Editors' and/or manual input of key data, such as growth rate. This means the Toolbox can be used for any type of planted forest (windbreak or shelterbelt, agroforestry, woodlot, or plantation), and can be used for existing planted forest or an area being considered for planting.
Extensive user support is available for the Toolbox, with Manuals and Workbooks provided. In addition to 'On Screen Help', 'Help' panels are displayed in many Tools. A series of 'Video Help' Camtasia Studio files provides instruction on the use of the Tools. The Toolbox includes in the 'Editors' sample Log Grade sets, Regimes and Biomass sets, that a user can modify.
Development
Dr Andy Warner, then an employee of Private Forests Tasmania, conceived the concept of the Farm Forestry Toolbox in 1996.[8] He obtained funding support for, and managed, the development of versions 1 to 5.[9] Originally the Toolbox was promoted as a User Friendly PC Tree Modelling Package (versions 1 and 2). Dr Warner also conducted training courses around Australia and overseas. Now living in Thailand, he continues to support the ongoing development and promotion of the current Toolbox for wider use internationally.
Adrian Goodwin,[10] initially as an employee of Forestry Tasmania and since 2003 as principal consultant of Bushlogic, is responsible for most of the concepts and code, and continues to expand the functionality of the Toolbox package. He has presented the Toolbox to forest growers, foresters and educators in Australia and overseas.[3][11]
Farm Forestry Toolbox version 5
In 2008, Toolbox was completely re-written in VB.NET 2005 implementing .NET Framework 2. This has resulted in an improved user interface, and provided an opportunity to streamline code.
Version 5 of the Toolbox is sensitive to international currency and date formatting. It is possible to set defaults for anywhere in the world and select any currency. Non-English help and instructions can be displayed by populating appropriately named folders with translated .RTF files. The Toolbox developers are in the process of “internationalising” some of the Toolbox programs so that all labels and headings can be translated to non-English.
A number of enhancements were made to Version 5.1,[12][13] and labelled as Farm Forestry Toolbox Version 5.1 - Carbon Ready. These enhancements allow a user to model biomass components and explore changes in accumulation of biomass due to climate change and changes in growth rates for planted forests. Carbon planting regimes were developed and modifications to the 'Stand Manager' allows a user to explore options to use planted forests for carbon storage.
The Toolbox is able to be used for a wide range of plantation species in Australia,[9][14] including mallee oil [15] and sandalwood.[16] It is also suitable for inventory in teak plantations in Southeast Asia.
Version 5 contains 50 taper models, 15 empirical growth models, and 4 process-based growth models (3 parameterisations of AGGRO [17] and an adaption of 3PG [18] for oil mallee). AGGRO calibrations for P.radiata and E.nitens are currently unavailable and awaiting re-calibration.
It is reported that the Toolbox is being used in universities in Germany, Thailand, Portugal, Ireland, Spain and Australia.[19]
Recent version history for Version 5.3
| Version | Version Date |
|---|---|
| 5.3.5 | August 2014 |
| 5.3.6 | September 2014 |
| 5.3.7i | June 2015 |
| 5.3.8 | December 2015 |
| 5.3.8b | February 2016 |
Farm Forestry Toolbox Versions
Version history
| Details | Version 1 | Version 2.0 to 2.8 | Version 3.0 to 3.12 | Version 4.0 to 4.9 | Version 5.0 to 5.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Released/launched | March 1999 [20] | 2000 [21] | 2001 [22] | 2003 [23][24] | 2008 (5.3 released October 2012) |
| Release name | Helping Treegrower Help Themselves | An aid to growing trees on farms | An aid to growing trees on farms | An aid to growing trees on farms | An aid to successfully growing trees on farms. |
| Operating System | Microsoft Windows 95, 98 or NT | No change | No change | No change | Microsoft Windows XP onwards. VB.NET 2005 implementing .NET Framework 2. |
Stages of development for "Hand Tools"
| Hand Tools | Version 1 | Version 2.0 to 2.8 | Version 3.0 to 3.12 | Version 4.0 to 4.9 | Version 5.0 to 5.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator | The standard Microsoft Windows Calculator | No change | Deleted | ||
| Conversions | Converts common standard units of measurement including area, length, volume, weight and slope. | Updated with more conversations | No change | Updated with more conversations | No change |
| Log Stack Volume | Estimates volume and weight of an individual log or a stack of logs. Calculates and presents a statistical report for a stack of logs. Output can be saved and printed. | No change | No change | No change | No change |
| Plot Area | Determines the area of rectangular, pseudo- rectangular, and circular plots. | No change | No change | No change | Deleted |
| Map-Coordinates | Not available | Not available | Converts geographic and map grid coordinates on various datums. | No change | Updated - Works globally. |
| Slope | Calculates vertical, horizontal and slope length using angle units (degrees or percent) | No change | No change | No change | No charge |
| Stocking | Calculates the number of trees per hectare using the distance between trees and between rows. It can also account for grazing bays. | No change | No change | No change | Updated - replaced by a planting design tool which links to planting event(s) in the Regime editor. |
| Survey | Not available | Not available | Calculates the map area, using bearings and distances, either from a traverse or by GPS. | Updated – able to annotate maps and print at different scales and import/export files to GIS | Updated - Allows an image (scanned aerial photo or map) to be added to the background of a map. Boundaries can then be over-drawn and areas and distances estimated. The tool is now more efficient, and can import larger shape files more quickly. |
| Wedge Calibration | Not available | Calibrates angle gauge instruments used to measure basal area. | No change | No change | No change |
Stages of development for "Power Tools"
| Power Tools | Version 1 | Version 2.0 to 2.8 | Version 3.0 to 3.12 | Version 4.0 to 4.9 | Version 5.0 to 5.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Productivity (for Plantations) | Estimates, for selected species, growth over time using Site Quality Index (MDH - mean dominant height & Age) or ProMod. | Updated | No change | No change | Updated – The ProMod model replaced by AGGRO, the physiological model also used in Stand Manager. AGGRO is calibrated for E. globulus, E. nitens, and P. radiata. Site and climate data required. Toolbox provides default climate data for most Australian regions in which commercial plantations can be grown. |
| Tree and Log Volume | Estimate volume (and value) of any log in a standing tree, including the entire stem. It also provides information about the shape of a log; for instance, its diameter (under bark) at a certain height, or vice versa. The tool can be used to work out the length of the merchantable log. | Replaced by Inventory Tool | |||
| Inventory Tool | Not available | A tool that allows quality assessments of single trees or plots. Log grades to be specified and value specified by user. Output can be saved and printed. | No change | No change | Updated – able to estimate wood volume and log grades in a single tree, a plot of trees or the whole forest. The tool displays information graphically and has import and export data function. 30 additional taper models for species from Australia. |
| Management Tool | Not available | Tracks income and expenditure over the rotation of your forest to calculate NPV and IRR. You can save and print the output. | Replaced by Stand Manager | ||
| Stand Manager | Not available | Not available | Uses costs and income (actual or predicted) to calculate returns over a rotation. Allows a user to test management options. Output can be saved and printed. | No change | Updated – Inclusion of a physiological growth model (AGGRO) with parameterisations for Eucalyptus globulus, Eucalyptus nitens, and Pinus radiata. Ten additional empirical growth models for species planted in Australia. All scenario runs summarized in the Session Log, and scenario data can be recovered from both the Session Log. Users able to simulate an income stream from carbon credits with Carbon Inventory events. |
Stages of development for "Other Tools"
| Other Tools | Version 1 | Version 2.0 to 2.8 | Version 3.0 to 3.12 | Version 4.0 to 4.9 | Version 5.0 to 5.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default Data Editor | Not available | Used to define some system-wide default values. | No change | No change | Updated - Finance tab had been removed. The setting of interest rates and scope now takes place in the financial base event in each regime. Biomass tab added: Stem wood can now be given a dollar value per tonne for biomass evaluation. |
| Log Grade Editor | Not available | Used to define log grade specifications. | No change | No change | Updated - Grades can be defined with preferred length and overcut allowance. Log assorts can be directed to maximise preferred product volumes, or total value. |
| Regime Editor | Not available | Used to construct a sequence of forest operations/events. | No change | No change | Updated – Regimes are now of two types, Forest used for growing trees, or NPV & IRR used purely for financial analysis without forest growth and harvesting. Adding a Planting event to a 1st rotation automatically adds compulsory Financial Base and Clear-felling events. The Planting event facilitates complex planting designs and area exclusions. The Financial Base event sets the date to which future cost and revenues are discounted, and the interest rate to be used for NPV calculations. Event dates set to the day rather than the year and can be set as a date or age. Event costs can be set as a rate ($/ha), or a fixed cost. Biomass removal (roots, branches etc.) is now dictated by the cutting event (thinning, clear-felling etc.) rather than the Stand Manager. Regimes apply to both Empirical and Process-based (physiological) models. |
| Health Keys. Three separate keys - Eucalypt Health Key, Pine Health Key and Other Species Health Key | Not available | Not available | A key to assist in the identification of health problems in plantation grown trees. The 'Health Tool' is an expert system for the major commercial eucalyptus plantation species used in southern Australia (Eucalyptus globulus & Eucalyptus nitens) and major commercial exotic pine species Pinus radiata. | Updated [25] | Key revamped and changes made to operation. This Tool is designed to allow the addition of other keys. |
Contribution to Toolbox from researchers and others
The Toolbox is a means of ensuring research output is made available for forest owners and managers. The following summaries the contribution from researchers and others, and the organizations they worked for when the contribution was made [26] Available as part of the Toolbox download.
3PG-FFT - (in Site Productivity and Stand Manager) - developed by Joe Landsberg and Richard Waring [17] with additional contributions by Peter Sands and CSIRO.
AGGRO - (in Site Productivity and Stand Manager) - developed by Michael Battaglia of Ensis and CRC-Forestry with support for the Joint Venture Agro-Forestry Program (Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation/Land & Water Australia/Forest Wood Products Research Development Corporation/Murray Darling Basin Commission (Authority) - joint venture) (Project CPF-1A).
Biometric Models - Developed and programmed by Adrian Goodwin; Eric Keady (Forestry Plantations Queensland); Steve Candy (Forestry Tasmania); Jerry Vanclay (Southern Cross University); Yue Wang and Thomas Baker (School of Forest and Ecosystem Science, University of Melbourne) with the support of the Forests and Wood Products Research and Development Corporation and the Department of Primary Industries (Victoria); and Justin Wong (Department of Sustainability and Environment Victoria).
Forest Health Keys - Software concept and original programming by Tim Osborn (Forestry Tasmania). Keys prepared by Tim Wardlaw (Forestry Tasmania). Additional unpublished information, advice and comment were provided by the following specialists: Dick Bashford, Jane Elek, Andrew Walsh, Paul Adams (Forestry Tasmania); David de Little, Tim Hingston (Gunns Ltd); Dugald Close, Phil Smethurst, Clare McArthur, Caroline Mohammed, Geoff Allen, Marina Hurley (Cooperative Research Centre for Sustainable Production Forestry); Andy Warner. Unless otherwise acknowledged, photographs used in keys were taken by staff of Forestry Tasmania. Robyn Doyle provided many photographs taken specifically for use in this key.
Specialised models and data - Oil Mallee Production - Based on a concept by Alan Herbert, Senior Economist with AgWest and using growth models developed by John Bartle, Manager of the Farm Forestry Unit at Department of Conservation and Land Management (Western Australia); and Adrian Goodwin. Data provided by Kim Brooksbank (AgWest, Farm Forestry and Revegetation group), Dan Wildy (University of Western Australia) and the Future Farm Industries Cooperative Research Centre. Sandalwood Production - Data provided by Kim Brooksbank.
Citation of literature where Farm Forestry Toolbox used to model outcomes
The Toolbox has been used to model financial and wood yield and results reported in peer reviewed publications, thesis, and reports and proceedings.
Peer reviewed publications
- Battaglia, Michael. and Sands, Peter. J., 1997. Modelling site productivity of Eucalyptus globulus in response to climate and site factors. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 24 (6): 831 - 850.[27]
- Kube, P. D., & Raymond, C. A., 2005. Breeding to Minimise the Effects of Collapse in Eucalyptus nitens Sawn Timber. Forest Genetics 12(1):23-24, 2005.[28]
- Wood M.J., McLarin M.L., Volker P.W, and Syme M., 2009. Management of eucalypt plantations for profitable sawlog production in Tasmania, Australia. Tasforests Vol. 18 p 117 November 2009.[29]
Thesis
- Baral, H. Ecosystem Goods and Services in Production Landscapes in South-Eastern Australia".[30] Submitted in total fulfillment of the requirements of the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, Department of Forest and Ecosystem Science, Melbourne School of Land and Environment, The University of Melbourne. October 2013.
- Smith, A., The Development of Strategies for the Management and Research of Foliar Pathogens on Eucalypt Plantations: Using Mycosphaerellaas a Case Study.[31] Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, School of Agricultural Science, University of Tasmania, and CRC for Forestry and Ensis Forest Biosecurity and Protection, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. June 2006.
- Kube, P.D, Genetic Improvement of Wood Properties of Eucalyptus nitens - Breeding to improve solid wood and pulp properties..[32] Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, University of Tasmania. April 2005
- Candy, S. G., Predictive Models for Integrated Pest Management of the Leaf Beetle Chrysophtharta bimaculata in Eucalyptus nitens Plantations in Tasmania.[33] Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy, University of Tasmania, and Cooperative Research Centre for Sustainable Production Forestry, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. December 1999.
- Warner, A.J. Development and Evaluation of Teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) Taper Equations in Northern Thailand. Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy. Faculty of Forestry, Kasetsart University. Bangkok, Thailand. 2016.
Reports and conference proceedings
- 2002
- Osborn, T., and Warner, A., 2002.[34] A Tree Health Diagnostic Tool for Farm Forestry Toolbox 4. Australian Forest Grower, Vol. 25, No. 3, Spring 2002: 16.
- Wood, M.J., Volker, P.W. and Syme, M. (2002).[35] Eucalyptus plantations for sawlog production in Tasmania, Australia: optimising thinning regimes. Forestry Tasmania, Division of Forest Research and Development, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
- 2004
- Greave, B., Dutkowski, G., & McRae, T., 2004.[36] Breeding Objectives for 'Eucalyptus globulus' for products other than Kraft pulp. IUFRO Conference - Eucalyptus in a changing world. Aveiro, Portugal 11–15 October 2015.
- Freudenberger D., Cawsey, E.M., Stol, J., & West, P.W., 2004.[37] Sustainable firewood supply in the Murray-Darling Basin. CSIRO: Canberra.
- Wardlaw, T., 2004.[38] The impact of a single epidemic of Mycosphaerella leaf blight on the growth of Eucalyptus globulus. Division of Forest Research and Development, Technical Report 15/2004, Forestry Tasmania, Hobart.
- Warner, A., 2004.[39] Farm-Level Blackwood Experience: Tasmanian Observations in Blackwood Management: Learning from New Zealand. Proceedings of an International Workshop, Rotorua, New Zealand, 22 November 2002. Edited by A.G. Brown. A report for the RIRDC/Land & Water Australia/FWPRDC/MDBC Joint Venture Agroforestry Program July 2004. RIRDC Publication No 04/086.
- 2005
- Finnigan, J., and Poulton, R., 2005.[40] Commercial tree growing options with the Tasmanian NAP region : a computer based strategic investigation. Australian Forest Growers and Private Forests Tasmania, 2005
- Volker, P., W., Greaves, B., & Wood, M,.[41] Silvicultural Management of Eucalypt Plantation for Solid Wood and Engineered Wood Products - Experience from Tasmania, Australia in Plantation Eucalyptus: Challenge in Product Development: Proceedings of the International Conference on Plantation Eucalyptus, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China, November 28 - December 1, 2005. Science Pres, Beijing. Editors Li Xiuwei, Liu Jing, Gai Yu, Li Feng. Chinese Research Institute of Wood Industry, China Eucalyptus Research Center.
- 2008
- Dickenson, I. 2008.[42] Balancing the three-legged stool: a Case Study of Forest Conversion and Conservation in Biodiversity: Integrating Conservation and Production - Case Studies from Australian farms, forests and fisheries. Edited by. Lefroy, T. Baily, K. Unwin, G & Norton, T. CSIRO Publishing.
- 2009
- Baral, H., Kasel, S., Keenan, R., Fox, J., and Stork, N., 2009.[43] GIS - based classification, mapping and valuation of ecosystem services in production landscapes: A case study of the Green Triangle region of south-eastern Australia. In: Forestry: a climate of change, Thistlethwaite, R., Lamb, D.,and Haines, R. (eds). pp. 64 –71. Proc. IFA Conference. Caloundra, Queensland, Australia, 6–10 September 2009.
- 2010
- Livingston, S., 2010.[44] Wood Production Options: Case Studies for Carbon Plantations – Extending R&D to best management practices for carbon sequestration, wood production and new investment opportunities on private land in Tasmania. Funding from the Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry under its Forest Industries Climate Change Research Fund program.
- 2011
- Morgan, H., 2011.[45] Benefits of Restoring Skyline Tier Scamander Plantation, Tasmania. June 2011. Author Helen Morgan, Bushways Environmental Services – Tasmania. Prepared for The North East Bioregional Network -
- Wardlaw, T., 2011.[46] Managing Biotic Risk in Developing a Eucalypt Resource: Learning from Australia and Elsewhere. Wood Technology Research Centre, Marlboro Research Centre, New Zealand. 2011, p 105 – 124.
- 2012
- May, B., M.,Bulinski, J., Goodwin,.A & Macleod, S.[47] Tasmanian Forest Carbon Study
- pitt&sherry. 2012 [48]Potential Timber Production Estimate from the Tasmanian Private Plantation Estate. Prepared for: Independent Verification Group. Prepared by: pitt&sherry and Esk Mapping & GIS Services for February 2012.
- 2013
- Sohn, J., McElhinny, C., Hilbig,. E., Grove, S., and Bauhus, J., 2013.[49] A Simplified Inventory Approach for Estimating Carbon in Coarse Woody Debris in High Biomass Forests. Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania, Volume 147, 2013 p 15-23.
- 2014
- Chan, H., 2014 [50]A Case Study Using the Farm Forestry Toolbox to Determine Timber Volumes, Values and Financial Outcomes for Farm Forests. Presented at the Australian Forest Growers, National Farm Forestry Conference in Lismore, NSW. October 2014
See also
References
- ↑ Edited by Ian Nuberg, Brendan George and Rowan Reid (2009). Agroforestry for Natural Resource Management. Canberra: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643092242.
- ↑ Technical Editors ; Leech, Jerry and Ferguson, Ian (2012). A Standard for Valuing Commercial Forests in Australia. Version 2.1, July 2012. (PDF). Canberra: Association of Consulting Foresters of Australia, Division of the Institute of Foresters of Australia.
- 1 2 "The Farm Forestry Toolbox - Australia's most versatile and widely used forestry software". 8th Australia and the New Zealand Institute of Forestry (ANZIF) Conference (2015). Institute of Foresters of Australia and the New Zealand Institute of Forestry. 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Australia's State of Forests Report 2013 (PDF). Canberra: ABARES. 2013. p. 403. ISBN 978-1-74323-169-2.
- ↑ "Farm forestry management strategies". Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ "Farm Forestry - National Action Statement" (PDF). Australian Government - Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry. August 2005. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Farm Forestry Area and Resources in Australia. Canbarre: Rural Industries Research Development Corporation. 2008. ISBN 1741516927.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 1997-1998 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 1998.
- 1 2 Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2007-2008 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2008.
- ↑ "ResearchGate". Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ "Scientific cultivation and green development to enhance the sustainability of eucalypt plantations". Pre-Conference Workshop at the 2015 IUFRO Eucalypt Conference 2015. IUFRO. October 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2010-2011 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2011.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2011-2012 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2012.
- ↑ Warner, A (2007). "Farm Forestry Toolbox Version 5.0: Helping Australian growers to manage their trees". Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Barton, A (1999). "The Oil Mallee Project: A Multifaceted Industrial Ecology Case Study". Journal of Industrial Ecology. 3 (2–3): 161–176.
- ↑ "Indian Sandalwood Plantations in Australia". Tropical Forest Services (TFS) Ltd. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- 1 2 Hensken F.L., Battaglia M. & Ottenschlaeger M.L. (2008). Silvicultural Design Support for Farm Forestry (PDF). Canberra: Rural Industries Research Development Corporation.
- ↑ Landsberg J.J. & Warning R.H. (1997). "A generalised model of forest productivity using simplified concepts of radiation-use, carbon balance and partitioning" (PDF). Forest Ecology and Management. 95: 209–228.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2013-2014 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2014.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 1998-1999 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 1999.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 1999-2000 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2000.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2000-2001 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2001.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2002-2003 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2003.
- ↑ Private Forests Tasmania Annual Report 2003-2004 (PDF). Hobart: Private Forests Tasmania. 2004.
- ↑ Osborn, Tim & Warner, Andy (2002). "A Tree Health Diagnostic Tool for Farm Forestry Toolbox 4". Australian Forest Grower. 25 (3).
- ↑ Farm Forestry Toolbox Versions 5.2 Manual. Private Forests Tasmania. 2011.
- ↑ Battaglia, Michael; Sands, Peter (1997). "Modelling site productivity of Eucalyptus globulus in response to climate and site factors". Australian Journal of Plant Physiology. 24 (6): 831 to 850. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Kube, Peter D; Raymond, Carolyn A. (2005). "Breeding to minimise the effects of collapse in Eucalyptus nitens sawn timber". Forest Genetics. 12 (1): 23–34. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Wood, M.J.; McLarin, M.L.; Volker, P.W.; Syme, M (2009). "Management of eucalypt plantations for profitable sawlog production in Tasmania, Australia" (PDF). Tasforests. 18: 117. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Baral, Himlal (2013). Ecosystem goods and services in production landscapes in south-eastern Australia. Melbourne: Department of Forest and Ecosystem Science, Melbourne School of Land and Environment. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Smith, AH (2006). The development of strategies for the management and research of foliar pathogens on Eucalypt plantations : using Mycosphaerella as a case study. Hobart: University of Tasmania. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Genetic Improvement of Wood Properties of Eucalyptus nitens - Breeding to improve solid wood and pulp properties. http://eprints.utas.edu.au/20603/
- ↑ Candy, SG (2000). Predictive models for integrated pest management of the leaf beetle Chrysophtharta bimaculata in Eucalyptus nitens plantations in Tasmania. Hobart: University of Tasmania. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Osborn, Tim; Warner, Andy (2002). "A Tree Health Diagnostic Tool for Farm Forestry Toolbox 4". Australian Forest Grower. 25 (3): 16. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Wood, M.J.; Volker, P.W.; Syme, M. (2002). Eucalyptus plantations for sawlog production in Tasmania, Australia: optimising thinning regimes. Hobart, Tasmania, Australia: Forestry Tasmania, Division of Forest Research and Development. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Greave, Bruce; Dutkowski, Greg; McRae, Tony (2004). Breeding Objectives for 'Eucalyptus globulus' for products other than Kraft pulp. IUFRO Conference - Eucalyptus in a changing world. Aveiro, Portugal 11–15 October 2015.
- ↑ Freudenberger, David; Cawsey, E. Margaret; Stol, Jacqui; West, P.W. (2004). Sustainable firewood supply in the Murray-Darling Basin (PDF). Canberra: CSIRO. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Wardlaw, Tim (2004). * Wardlaw, T., 2004. The impact of a single epidemic of Mycosphaerella leaf blight on the growth of Eucalyptus globulus (PDF). Hobart, Tasmania: Division of Forest Research and Development Technical Report 15/2004. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Warner, Andy (2002). Farm-Level Blackwood Experience: Tasmanian Observations (PDF). Canberra: Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation. pp. 52–57. ISBN 0642587965. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Finnigan, Julie; Poulton, Rebecca (2005). Commercial tree growing options with the Tasmanian NAP region : a computer based strategic investigation. Australian Forest Growers and Private Forests Tasmania. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Volker, Peter; Greaves, Bruce; Wood, Michael (2007). Silvicultural Management of Eucalypt Plantation for Solid Wood and Engineered Wood Products - Experience from Tasmania, Australia - (PDF). pp. 1–9. ISBN 9787030193995. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Dickenson, Ian (2008). Balancing the three-legged stool: a Case Study of Forest Conversion and Conservation in Biodiversity: Integrating Conservation and Production - Case Studies from Australian farms, forests and fisheries. Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643098664. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Baral, H; Kasel, S; Keenan, R; Fox, J; Stork, N (2009). GIS - based classification, mapping and valuation of ecosystem services in production landscapes: A case study of the Green Triangle region of south-eastern Australia (PDF). Institute of Foresters of Australia. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Livingston, S (2010). Wood Production Options: Case Studies for Carbon Plantations – Extending R&D to best management practices for carbon sequestration, wood production and new investment opportunities on private land in Tasmania (PDF). Launceston, Tasmania: Private Forests Tasmania. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Morgan, Helen (2011). Benefits of Restoring Skyline Tier Scamander Plantation, Tasmania (PDF). he North East Bioregional Network. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Wardlaw, Tim (2011). Managing Biotic Risk in Developing a Eucalypt Resource: Learning from Australia and Elsewhere (PDF). New Zealand: Wood Technology Research Centre, Marlboro Research Centre. pp. 105–124. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ May, Barrie; Bulinski, James; Goodwin, Adrian; Macleod, Stuart (2012). Tasmanian Forest Carbon (PDF). CO2 Australia Limited. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Potential Timber Production Estimate from the Tasmanian Private Plantation Estate (PDF). pitt&sherry. 2012. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Sohn, Julia; McElhinny, Chris; Grove, Simon; Hilbig, Eva; Bauhus, Jürgen (2013). "A Simplified Inventory Approach for Estimating Carbon in Coarse Woody Debris in High Biomass Forests". Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania. 147. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Chan, Henry (2014). A Case Study Using the Farm Forestry Toolbox to Determine Timber Volumes, Values and Financial Outcomes for Farm Forests (PDF). Private Forests Tasmania. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
External links
- Farm Forestry Toolbox
- International Union of Forest Research Organisations
- Australian Agroforestry Foundation
- Australian Forest Growers