Green Bay, Wisconsin
| Green Bay, Wisconsin | ||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
|
Clockwise from top: Downtown Green Bay, Resch Center, Leo Frigo Memorial Bridge, Brown County Courthouse, Lambeau Field | ||
| ||
| Nickname(s): "Titletown", "Bayland", "Bay City", "Packerland", and "Packer City" | ||
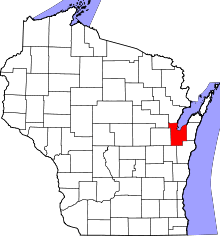
 Location in Brown County and the state of Wisconsin. | ||
 Green Bay, Wisconsin Location in the United States | ||
| Coordinates: 44°30′48″N 88°0′57″W / 44.51333°N 88.01583°WCoordinates: 44°30′48″N 88°0′57″W / 44.51333°N 88.01583°W[1] | ||
| Country | United States | |
| State | Wisconsin | |
| County | Brown | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Jim Schmitt | |
| Area[2] | ||
| • City | 55.96 sq mi (144.94 km2) | |
| • Land | 45.47 sq mi (117.77 km2) | |
| • Water | 10.49 sq mi (27.17 km2) | |
| Elevation | 581 ft (177 m) | |
| Population (2010)[3] | ||
| • City | 104,057 | |
| • Estimate (2015)[4] | 105,207 | |
| • Rank | US: 272nd | |
| • Density | 2,288.5/sq mi (883.6/km2) | |
| • Urban | 206,520 (US: 176th) | |
| • Metro | 312,409 (US: 158th) | |
| Time zone | Central (UTC−6) | |
| • Summer (DST) | CDT (UTC−5) | |
| ZIP code | 54301-08, 54311, 54313, 54324, 54344 | |
| Area code | 920 | |
| FIPS code | 55-31000[5] | |
| GNIS feature ID | 1565801[6] | |
| Website |
greenbaywi | |
Green Bay is a city in and the county seat of Brown County in the U.S. State of Wisconsin,[7] located at the head of Green Bay, a sub-basin of Lake Michigan, at the mouth of the Fox River. It is located 581 feet (177 m) above sea level and 112 miles (180 km) north of Milwaukee. The population was 104,057 at the 2010 census.[5] Green Bay is the third-largest city in the state of Wisconsin, after Milwaukee and Madison, and the third-largest city on the west shore of Lake Michigan, after Chicago and Milwaukee. Green Bay is home to the National Football League team Green Bay Packers.
Green Bay is the principal city of the Green Bay Metropolitan Statistical Area, which covers Brown, Kewaunee, and Oconto counties;[8] the MSA had a combined population of 306,241 at the 2010 census.[5]
Green Bay is an industrial city with several meatpacking plants, paper mills, and a port on Green Bay, an arm of Lake Michigan known locally as "the Bay of Green Bay". Located in Green Bay are the Neville Public Museum, with exhibitions of art, history, and science; the Children's Museum; and the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay.
History
Samuel de Champlain, the founder of New France, commissioned Jean Nicolet to form a peaceful alliance with Indians in the western areas, whose unrest interfered with French fur trade, and to search for a shorter trade route to China through Canada. Nicolet and others had learned from other First Nations of the Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) people, who identified as "People of the Sea", and believed they must reside on or near the Pacific Ocean.[9] Champlain had also heard about natural resources in the area, including fertile soil, forests, and animals. Nicolet began his journey for this new land shortly before winter in 1634.[10] In what later became a French fur-trading route, he sailed up the Ottawa River, through Lake Nipissing and down the French River to Lake Huron, then through the straits of Michilimackinac into Lake Michigan. He is believed to have landed at Red Banks, near the site of the modern-day city of Green Bay, Wisconsin.[11]
From the trading post La Baie des Puants to the town La Baie verte
Nicolet founded a small trading post here in 1634, originally named La Baye or La Baie des Puants (French for "the stinking Bay").[12] From this, Green Bay claims to be one of the oldest European permanent settlements in America, but a 1671 Jesuit mission was the first true European outpost.
When Nicolet arrived in the Green Bay area, he encountered the Menominee, as this was their territory. He also met the Ho-Chunk, also known as the Winnebago, a people who spoke a Sioux language. The Winnebago hunted, fished, and cultivated corn, bean, squash, and tobacco. Wild rice, which they had incorporated as a dietary staple, grew in abundance along the riverbanks. They regularly harvested and cooked this, along with a wide variety of nuts, berries, and edible roots of the woods.[13] The tribe had clearly distinguished gender roles. The men typically hunted and fished for food, and the women processed game and other foods in cooking. They prepared and made clothing from the furs as well as using other parts of animals for tools, cord, etc. Women also had a role in the political process, as no action could be taken without agreement of half of the women. Nicolet stayed with this tribe for about a year, becoming an ally. He helped open up opportunities for trade and commerce with them before returning to Quebec.[13]
A few months after Nicolet returned to Quebec, Champlain died. His death halted other journeys to La Baie Verte (French for "The Green Bay"). Père Claude Allouez sent Nicolas Perrot to La Baie. After this, the French avoided the area for some decades, because of the intensity of First Nations and European conflicts in the east. In 1671, a Jesuit Mission was set up in the area. A fort was added in 1717 and gradually associated development took place. The town was incorporated in 1754. As Great Britain took control of French areas during the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War in some areas of North America, this town came under British control in 1761. The French ceded their North American lands East of the Mississippi River to the British following defeat in 1763.
The first permanent French settlers were Charles de Langlade and his family from Canada, who moved to Green Bay in 1765, becoming the first European-American settlers in today's Wisconsin. Langlade, called the "Founder and Father of Wisconsin", was an Ottawa war chief with a French father. He is credited with planning the ambush of British General Braddock and George Washington in the French and Indian War. The Grignons, Porliers and Lawes, who followed, brought Canadian-French culture with them. Colorful "jack-knife Judge" Reaume dispensed British justice in the territory.[13] These early French settlers set the tone for many who followed.
The British take-over
Green Bay and Lake Winnebago on the 1835 Tourist's Pocket Map of Michigan among the "Mennomonie" villages of Wisconsin Territory
The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-New Englanders and a few African American freedmen, arrived in Wisconsin while it was under British control. Charles Michel de Langlade is generally recognized as the first settler, establishing a trading post at Green Bay in 1745, and moving there permanently in 1764.[14] Settlement began at Prairie du Chien around 1781. The French residents at the trading post in what is now Green Bay, referred to the town as "La Bey", however British fur traders referred to it as "Green Bay", because the water and the shore assumed green tints in early spring. The old French title was gradually dropped, and the British name of "Green Bay" stuck. The region coming under British rule had virtually no adverse effect on the French residents as the British needed the cooperation of the French fur traders and the French fur traders needed the goodwill of the British. During the French occupation of the region licenses for fur trading had been issued scarcely and only to select groups of traders, whereas the British, in an effort to make as much money as possible from the region, issued licenses for fur trading freely, both to British and French residents. The fur trade in what is now Wisconsin reached its height under British rule, and the first self-sustaining farms in the state were established as well. From 1763 to 1780, Green Bay was a prosperous community which produced its own foodstuff, built graceful cottages and held dances and festivities.[15]
After Independence
The Green Bay area was still under British control until the 1783 treaty formally ended the American Revolutionary War. Following the War of 1812, which in part was over disputes related to the border with Canada, the United States built Fort Howard on the Fox River in 1816 to protect its northern border.[13] Doty, Whitney, Arndt, Baird and Martin were among the many British-American settlers whose numbers pushed French culture into the background.[13] As British settlers in the area came to outnumber the French, they referred to the town as "Green Bay" (from the French: Baie Verte).
The Erie Canal was completed in 1825, linking New England with the Great Lakes. This led to the advance of Green Bay as a trading center. The end of the Black Hawk War in 1832 also gave impetus to settlement of the region. Most of the settlers were farmers from New England who began using the Erie Canal to pour into Wisconsin. As more and more New England settlers arrived, Green Bay developed into a trading center for this population.[16]
Built in 1837, the Hazelwood Historic House Museum is on the National Register of Historic Places and is now used as the Brown County Historical Society.[17]
Wisconsin's first newspaper, The Green Bay Intelligencer, was started in 1833 by Albert Ellis and John V. Suydam. The borough of Green Bay was created in 1838 and is the main center of the current city. The borough combined the town of Astoria (a company town of the American Fur Company), with Navarino, platted by Daniel Whitney.[18] Before Wisconsin became a state in 1848, its commerce was based on the fur trade, which became dominated by John Jacob Astor's American Fur Company. After statehood, there was a shift away from fur trading toward lumbering. "For a short time in 1860s and 1870s, iron smelting in charcoal kilns rivaled the timber industry while the port handled increasing amounts of fuel, feed, and lumber. Today's major local industry had its start in 1865 when the first paper mill was built."[13]

By 1850 the town had a population of 1,923. The town was incorporated as the city of Green Bay in 1854. The Green Bay Area Public School District was founded in 1856.[13] Throughout the 1850s, word spread of America's cheap land and good soil, bringing in an influx of Belgian people, German, Scandinavian, Irish and Dutch immigrants, each adding to the culture. The greatest concentration of newcomers came from Belgium. They cleared the land to farm and build their homes.[13]
The railroad arrived in the 1860s. Chicago and Northwestern Railroad companies were formed, which allowed people and products to travel all over the state, increasing business and trade opportunities. The area was able to grow and enrich itself with the use of the river and the plentiful timber resources. This led to the paper industry becoming the major employer in Green Bay, and opened up the port for international trade.[10]
In 1934, President Franklin D. Roosevelt came to Green Bay to honor its tercentenary.[12] By 1950, the city had a population of 52,735. In 1964, the Town of Preble was consolidated with the city of Green Bay.[19]
Geography
Green Bay is located in the northeastern part of Wisconsin at the mouth of the Fox River. Today, Interstate 43 meets U.S. Route 41 in Green Bay, about 90 miles (140 km) north of Milwaukee.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 55.96 square miles (144.94 km2), of which, 45.47 square miles (117.77 km2) is land and 10.49 square miles (27.17 km2) is water.[2]
Climate
Green Bay has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb),[20] with some moderation due to the city's proximity to Lake Michigan. Like other cities with this type of climate, there are four distinct seasons, often with severe or extreme variation between them in terms of temperature and precipitation. Green Bay experiences warm, humid, frequently hot summers and long, cold and snowy winters. The variance in temperature and precipitation between months is severe and often extreme. Tornadoes are rare in the Green Bay area, with the strongest being an F3 tornado that hit the community of Pittsfield on June 26, 1969.[21]
Monthly mean temperatures range from 16.6 °F (−8.6 °C) in January to 69.1 °F (20.6 °C) in July.[22] In July, the warmest month, the average high temperature is 81.2 °F (27.3 °C).[22] There are 6.1 days of 90 °F (32 °C)+ highs, 68 days where the high remains at or below freezing, and 19 days with sub-0 °F (−18 °C) lows annually. From December to February, even during thaws, the temperature rarely reaches 50 °F (10 °C). Extremes have ranged from −36 °F (−38 °C) on January 21, 1888 to 104 °F (40 °C) on July 13, 1936.
The wettest month in Green Bay is August, when 3.77 inches (95.8 mm) of precipitation falls, mostly in the form of rainfall from thunderstorms. The driest month in Green Bay is February, when the majority of precipitation falls as low moisture-content snow due to cold, dry air. On average, 1.01 inches (25.7 mm) of precipitation falls in February.
| Climate data for Green Bay, Wisconsin (Austin Straubel Int'l), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1886–present[lower-alpha 1] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 56 (13) |
61 (16) |
82 (28) |
89 (32) |
99 (37) |
101 (38) |
104 (40) |
100 (38) |
97 (36) |
88 (31) |
74 (23) |
64 (18) |
104 (40) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 24.3 (−4.3) |
28.2 (−2.1) |
39.2 (4) |
53.9 (12.2) |
66.0 (18.9) |
75.3 (24.1) |
79.8 (26.6) |
77.7 (25.4) |
69.9 (21.1) |
56.6 (13.7) |
42.2 (5.7) |
28.5 (−1.9) |
53.5 (11.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 9.0 (−12.8) |
12.4 (−10.9) |
22.4 (−5.3) |
33.8 (1) |
44.0 (6.7) |
54.1 (12.3) |
58.4 (14.7) |
56.9 (13.8) |
48.5 (9.2) |
37.7 (3.2) |
26.9 (−2.8) |
14.4 (−9.8) |
34.9 (1.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −36 (−38) |
−33 (−36) |
−29 (−34) |
7 (−14) |
21 (−6) |
32 (0) |
40 (4) |
38 (3) |
24 (−4) |
8 (−13) |
−12 (−24) |
−27 (−33) |
−36 (−38) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.13 (28.7) |
1.11 (28.2) |
1.85 (47) |
2.63 (66.8) |
2.93 (74.4) |
3.88 (98.6) |
3.50 (88.9) |
3.37 (85.6) |
3.04 (77.2) |
2.44 (62) |
2.13 (54.1) |
1.51 (38.4) |
29.52 (749.8) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 13.0 (33) |
9.9 (25.1) |
8.1 (20.6) |
2.9 (7.4) |
0.2 (0.5) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.2 (0.5) |
4.0 (10.2) |
13.1 (33.3) |
51.4 (130.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 9.9 | 8.4 | 10.6 | 11.1 | 11.4 | 10.3 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 123.0 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 9.6 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 9.2 | 40.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74.0 | 73.5 | 72.8 | 67.0 | 65.9 | 68.9 | 71.3 | 75.1 | 76.5 | 74.4 | 76.9 | 77.3 | 72.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 146.7 | 159.8 | 198.6 | 222.1 | 285.1 | 302.8 | 314.5 | 278.7 | 205.2 | 158.0 | 107.4 | 112.3 | 2,491.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 51 | 55 | 54 | 55 | 62 | 65 | 67 | 64 | 55 | 46 | 37 | 41 | 56 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[22][23][24] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 2,276 | — | |
| 1870 | 4,698 | 106.4% | |
| 1880 | 7,476 | 59.1% | |
| 1890 | 9,069 | 21.3% | |
| 1900 | 23,748 | 161.9% | |
| 1910 | 25,216 | 6.2% | |
| 1920 | 31,643 | 25.5% | |
| 1930 | 37,407 | 18.2% | |
| 1940 | 46,205 | 23.5% | |
| 1950 | 52,735 | 14.1% | |
| 1960 | 62,952 | 19.4% | |
| 1970 | 87,829 | 39.5% | |
| 1980 | 87,947 | 0.1% | |
| 1990 | 96,466 | 9.7% | |
| 2000 | 102,313 | 6.1% | |
| 2010 | 104,057 | 1.7% | |
| Est. 2015 | 105,207 | [25] | 1.1% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[26] 2013 Estimate[27] | |||
2010 census
As of the census[3] of 2010, there were 104,057 people, 42,244 households, and 24,699 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,288.5 inhabitants per square mile (883.6/km2). There were 45,241 housing units at an average density of 995.0 per square mile (384.2/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 77.9% White, 3.5% African American, 4.1% Native American, 4.0% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 7.2% from other races, and 3.1% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 13.4% of the population.
There were 42,244 households of which 31.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.4% were married couples living together, 12.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.6% had a male householder with no wife present, and 41.5% were non-families. 32.4% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 3.06.
The median age in the city was 33.7 years. 24.7% of residents were under the age of 18; 11.7% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 27.7% were from 25 to 44; 24.5% were from 45 to 64; and 11.3% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 49.4% male and 50.6% female.
2000 census
As of the census of 2000,[5] there were 102,313 people, 41,591 households, and 24,663 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,332.1 people per square mile (900.5/km2). There were 43,123 housing units at an average density of 982.9 per square mile (379.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 85.86% White, 1.38% African American, 3.28% Native American, 3.76% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 3.72% from other races, and 1.97% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 7.13% of the population.
There were 41,591 households of which 30.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 44.1% were married couples living together, 10.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.7% were non-families. About 31.6% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.40 and the average family size was 3.06.
In the city the age distribution of the population shows 25.4% under the age of 18, 11.6% from 18 to 24, 31.7% from 25 to 44, 19.5% from 45 to 64, and 11.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33 years. For every 100 females there were 97.2 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $38,820, and the median income for a family was $48,678. Males had a median income of $33,246 versus $23,825 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,269. About 7.4% of families and 10.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 12.7% of those under the age of 18 and 9.2% of those 65 and older.
Government
Green Bay is governed by a mayor and a city council. The mayor is elected in a citywide vote. The city council consists of 12 members each elected from districts.



Green Bay is represented by Reid Ribble (R) in the United States House of Representatives, and by Ron Johnson (R) and Tammy Baldwin (D) in the United States Senate. Frank Lasee (R), Robert Cowles (R), and Dave Hansen (D) represent Green Bay in the Wisconsin State Senate, and Garey Bies (R), Chad Weininger (R), John Klenke (R), and Eric Genrich (D) represent Green Bay in the Wisconsin State Assembly.
Law enforcement
The Green Bay Police Department was established in on August 27, 1857, when the Green Bay Police Corps was established, and Henry Baird was named Chief of Police. The Green Bay Police Department provides many specialized services such as a Dive Team, Harbor Patrol, Motorcycle Patrol, and a S.W.A.T. Team.
Since the establishment of the Green Bay Police Department, one officer has died in the line of duty.[28]
Transportation
Railroads
From 1896 to 1993 the city was the headquarters of the Green Bay and Western Railroad. In 1993, the line was purchased by the Wisconsin Central. In 2001, the WC was merged into the Canadian National Railway. The Chicago and North Western Railway also served Green Bay and its depot still stands. Green Bay was last served with a regular passenger train, the CNW's Peninsula 400, in 1971. The CNW sold its trackage from Green Bay south to Sheboygan in 1987 to the Fox River Valley Railroad, which became part of the WC in 1993. Green Bay also saw passenger service from the Milwaukee Road's Chippewa-Hiawatha, which ran from Chicago into the upper peninsula of Michigan. Green Bay is also served by the Escanaba and Lake Superior Railroad.
Airport
Green Bay is served by Green Bay-Austin Straubel International Airport. Delta Airlines, American Airlines, and United Airlines all offer flights out of Green Bay.[29]
Highways
 I-43 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Manitowoc and Milwaukee.
I-43 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Manitowoc and Milwaukee. I-41 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Appleton and Milwaukee.
I-41 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Appleton and Milwaukee. US 41 travels towards Marinette, and south concurrently with I-41, continuing to Milwaukee.
US 41 travels towards Marinette, and south concurrently with I-41, continuing to Milwaukee. US 141 begins east of Green Bay in Bellevue, and continues north towards Crivitz.
US 141 begins east of Green Bay in Bellevue, and continues north towards Crivitz. WIS 29 travels east towards Kewaunee, and west towards Shawano and Wausau.
WIS 29 travels east towards Kewaunee, and west towards Shawano and Wausau. WIS 32 travels north towards Pulaski, and south towards Chilton and Milwaukee.
WIS 32 travels north towards Pulaski, and south towards Chilton and Milwaukee. WIS 54 travels east to Algoma, and west towards Seymour.
WIS 54 travels east to Algoma, and west towards Seymour. WIS 57 travels north towards Sturgeon Bay, and south towards Milwaukee.
WIS 57 travels north towards Sturgeon Bay, and south towards Milwaukee. WIS 172 begins at I-43 and travels west to Hobart.
WIS 172 begins at I-43 and travels west to Hobart.
Local transit
Green Bay Metro provides mass transit bus service throughout Green Bay and the surrounding suburbs.
Greyhound Lines, Jefferson Lines, Indian Trails, and Lamers Bus Lines provide intercity transportation from the central Green Bay Metro station which is located downtown.
Water
Green Bay is served by the Port of Green Bay. The port handled 1.99 million tons of cargo in 2015.[30] The primary shipments into and out of the port include coal, limestone, salt, and cement.[30]
Education
Green Bay is served by the Green Bay Area Public School District. It operates 25 elementary schools, two K-8 schools, four middle schools, and four high schools in the city and surrounding area. Private schools in Green Bay include Notre Dame de la Baie Academy, Northeastern Wisconsin Lutheran High School, and Bay City Baptist School.
Higher education
Green Bay area colleges and universities:
- Bellin College of Nursing
- Concordia University Wisconsin, Green Bay Center[31]
- College of Menominee Nation
- Lakeland College, Green Bay Center[32]
- Medical College of Wisconsin – Green Bay campus[33][34]
- Northeast Wisconsin Technical College
- Rasmussen College
- University of Wisconsin-Green Bay
Public libraries
The Brown County Library (BCL) Central Branch is located downtown in downtown Green Bay and has served as the county public library since 1968. The Central Branch is the headquarters for the BCL system, which encompasses all public libraries in Brown County, including eight branch libraries and a bookmobile that regularly visits locations throughout the county. In 1994, the Brown County Library was named Wisconsin Library of the Year.[35]
Religion
In 2000, the American Religion Data Archive reported Green Bay to be predominantly Catholic (71.5%), with Lutherans composing an additional 16.4%. The remaining 12% is almost entirely made-up of other Protestant denominations.[36]
The Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod has four churches in Green Bay: St. Paul Lutheran Church,[37] First Evangelical Lutheran Church,[38] Beautiful Savior Lutheran Church,[39] and Messiah Lutheran Church.[40][41]
The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Green Bay. The Cathedral of Saint Francis Xavier in Green Bay is the mother church of the Diocese. The diocese is in the province of the Archdiocese of Milwaukee. The Saint Joseph Oratory is located in Green Bay.
The Islamic Society of Wisconsin, Green Bay serves the Islamic community. The Green Bay Area Unitarian Universalist Fellowship is in the city. Congregation Cnesses Israel Temple, serving the area's Jewish population, is on the city's east side.
Sports
- Professional
- Green Bay Packers (football)
- Green Bay Blizzard (indoor football)
- Collegiate
- Green Bay Phoenix (representing University of Wisconsin–Green Bay)
- St. Norbert Green Knights (representing St. Norbert College, in nearby DePere)
- Green Bay Bullfrogs (summer collegiate baseball)
- Junior
- Green Bay Gamblers (ice hockey)
- Power Green Bay (volleyball)[42]
- Major running races
- Bellin Run
- Cellcom Green Bay Marathon
Arts and culture


The Meyer Theatre and the Hotel Northland are on the National Register of Historic Places. The Northland was once the largest hotel in Wisconsin.[43]
Daddy D Productions perform at Riverside Ballroom and Let Me Be Frank Productions perform at the Meyer Theatre.[44] The Green Bay Civic Symphony performs at the Meyer Theatre, its home venue. The former Green Bay Symphony Orchestra disbanded after their 2014–2015 season, after performing for over 100 years, citing financial difficulties.[45]
Performance venues located in Green Bay include: Lambeau Field, Resch Center, Brown County Veterans Memorial Arena, Shopko Hall, Weidner Center, and the Meyer Theatre.
The Artgarage and the Automotive Gallery are art galleries in the downtown area.[44]
Museums in the city include the Neville Public Museum and the Hazelwood Historic House Museum.[44]
Every summer, the downtown area plays host to ArtStreet, an art festival featuring studio displays, demonstrations, and live entertainment.[46] Dine on the Deck is an event that allows patrons to dine on the CityDeck and features dishes from local restaurants.[47] Taste on Broadway has live entertainment and dishes served by local restaurants who compete for awards.[48]
Media and internet
Television stations in Green Bay are WBAY (2), (ABC); WFRV (5), (CBS); WLUK (11), (FOX); WCWF (14), (CW); WGBA (26), (NBC); WACY (32), (MNT); and WPNE (38), a PBS affiliate. Green Bay is served by the Green Bay Press-Gazette. Another local newspaper, the Green Bay News-Chronicle, ceased publication in 2005.
There is a free public Wi-Fi system in the downtown Green Bay Broadway District that went into operation in 2007.[49]
Economy
Industry
Green Bay is known as the "Toilet Paper Capital of the World" because of the prevalence of the paper industry in the city.[50] Northern Paper Company, Fort Howard Paper Company, and Hoberg Paper Company were among Green Bay's first paper companies. Northern Paper Company offered the first splinter-free toilet paper in the early 1930s.[51] The presence of the paper industry helped Green Bay avoid the worst effects of the Great Depression.[52] Today, major paper producers include Georgia-Pacific,[53] Procter & Gamble,[54] and Steen-Macek Paper Company.[55]
Among the earliest packing companies in Green Bay were Acme Packing Company and Indian Packing Company, the namesake of the Green Bay Packers.[56] Today, major meatpackers in the city include JBS S.A. (formerly Packerland Packing)[57] and American Foods Group.
Largest employers
As of 2014, the largest employers in the city were:[58]
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Humana | 3,167 |
| 2 | Oneida Nation of Wisconsin | 2,690 |
| 3 | Schneider National | 2,580 |
| 4 | Bellin Health | 2,329 |
| 5 | Georgia-Pacific | 2,200 |
| 6 | UnitedHealth Group | 1,894 |
| 7 | Aurora BayCare Medical Center | 1,739 |
| 8 | Wisconsin Public Service Corporation | 1,497 |
| 9 | American Foods Group | 1,480 |
| 10 | St. Vincent Hospital | 1,467 |
Other major employers include Associated Banc-Corp, Green Bay Area Public School District, Shopko, JBS USA, Expert Global Solutions, Walmart, Green Bay Packaging, Procter & Gamble, Schreiber Foods, the Green Bay Packers, Nature's Way, HJ Martin and Son, and Nicolet National Bank.[59]
Points of interest

- Bay Beach Amusement Park
- Bay Beach Wildlife Sanctuary
- Brown County Veterans Memorial Arena
- City Stadium, former home of the Packers
- Cofrin Memorial Arboretum
- Fox River State Recreational Trail
- Green Bay Botanical Garden
- Joannes Stadium
- The Broadway District
- Lambeau Field, home of the Green Bay Packers
- Meyer Theatre
- Neville Public Museum of Brown County
- Northeast Wisconsin Technical College
- NEW Zoo
- Packers Heritage Trail
- Resch Center, home of the Green Bay Blizzard and Green Bay Gamblers
- Weidner Center
Shopping
Green Bay has one enclosed shopping mall. The city is home to the first Shopko discount department store.[60]
East Town Mall
Built in 1982 and remodeled three times, East Town Mall is an enclosed shopping center on Green Bay's east side. East Town's anchors are Hobby Lobby, Office Max, Budget Cinema, Petco & Kohl's. East Town has about 17 specialty shops. A budget cinema is located inside the mall. East Town Mall has seven Windspire vertical wind turbines outside of its main entrance that help reduce costs to the common area.[61]
Green Bay Plaza
Built in 1960, Green Bay Plaza is a large strip mall located on Green Bay's west side. It is anchored by Party City, T.J. Maxx, HomeGoods, Big Lots, Office Depot, and a Sears store. It contains specialty shops and restaurants.
Notable people
|
|
- Sports
- Nate Abrams – NFL player
- John Anderson – ESPN Sportscenter anchor, attended Southwest High School
- Ken Anderson – professional wrestler known as Mr. Kennedy in WWE and Mr. Anderson in TNA
- Wayland Becker – NFL player
- Tony Bennett – University of Virginia men's basketball coach and former NBA player for Charlotte Hornets, attended Preble High School
- Jason Berken – MLB player
- Dan Buenning – guard for NFL Chicago Bears, attended Bay Port High School
- Art Bultman – NFL player for Brooklyn Dodgers and the Green Bay Packers
- George Whitney Calhoun – co-founder of Green Bay Packers
- Dick Campbell – NFL player
- Raymond Joseph Cannon – U.S. Representative, MLB player, attorney for Jack Dempsey and accused players of Black Sox Scandal
- James Cook – NFL player
- Jim Crowley – one-fourth of University of Notre Dame's legendary "Four Horsemen" backfield
- Jerry Daanen – NFL player
- Darroll DeLaPorte – NFL player
- Jay DeMerit – soccer player, English Premier League and Major League Soccer, 2010 World Cup team, attended Bay Port High School
- Dutch Dwyer – NFL player
- Riggie Dwyer – NFL player
- Jim Flanigan – NFL player for Chicago Bears, Green Bay Packers, San Francisco 49ers, and Philadelphia Eagles
- Ted Fritsch – NFL player
- Ted Fritsch, Jr. – NFL player
- Rebecca Giddens – world champion canoer, Olympic medalist
- Scott Hansen – NASCAR driver
- Roger Harring – football coach, University of Wisconsin–La Crosse
- Arnie Herber – NFL player for Green Bay Packers and New York Giants, member of Pro Football Hall of Fame
- Jim Hobbins – NFL player
- Fee Klaus – professional football player
- Greg Knafelc – NFL player
- Tod Kowalczyk – head coach of University of Toledo men's basketball team
- Bob Kroll – NFL player
- Gary Kroner – professional football player
- Curly Lambeau – founder, player, and first coach of Green Bay Packers
- Wes Leaper – NFL player
- Jim Magnuson – MLB player
- Charlie Mathys – NFL player for Hammond Pros and Green Bay Packers
- Terrie Miller – Olympic athlete
- Dennis Murphy – Medal of Honor recipient
- Brian Noble – NFL player
- Drew Nowak – NFL player
- Dominic Olejniczak – Mayor of Green Bay, President and Chairman of Green Bay Packers
- Joe Perrault – Olympic athlete
- Ken Radick – NFL player for Green Bay Packers and Brooklyn Dodgers
- Dick Rehbein – NFL assistant coach
- Chester J. Roberts – head coach of the Miami Redskins football and men's basketball teams
- Chuck Sample – NFL player
- Mary Sauer – pole vaulter
- Joe Secord – NFL player
- Lauren Sesselmann – professional soccer player
- Walter Wellesley Smith (1905–1982) – Pulitzer Prize-winning sportswriter
- Aaron Stecker – NFL player, attended Ashwaubenon High School
- Horst Stemke – Olympic athlete
- Kevin Stemke – NFL player
- Jerry Tagge – NFL player
- Ron Vander Kelen – MVP of 1963 Rose Bowl and NFL player
- Brad Voyles – MLB player
- Cowboy Wheeler – NFL player
- Charlie Whitehurst – NFL player
- Bob Wickman – Major League Baseball pitcher
- Paul Wilmet – MLB player
- Eliot Wolf – NFL executive
- Vince Workman – NFL player
- Dick Zoll – NFL player for Cleveland Rams and Green Bay Packers
- Literature, music, arts
- Karen Borca – musician
- Eric Bray – record producer
- Paul Gigot – Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist
- Richard Gilliam – fantasy author and editor
- Sally Anne Golden – actress
- Thom Hazaert – record producer, journalist, radio personality, film producer/director. Publicly credited with saving Slipknot/Stone Sour vocalist Corey Taylor's life.
- Joel Hodgson – creator and star of TV show Mystery Science Theater 3000, graduated from Ashwaubenon High School in 1978
- Jim Knipfel – author
- Jeff Kurtenacker – composer
- Doug Larson – newspaper columnist
- Pat MacDonald – singer in Timbuk3
- Leo Ornstein – composer, pianist, finished his life in Green Bay
- Dave Pirner – lead singer of Soul Asylum
- Tony Shalhoub – actor, star of films, stage and TV series Monk and Wings, attended Green Bay East High School
- Mona Simpson – novelist and essayist; younger sister of Steve Jobs, co-founder and CEO of Apple Inc.; wife of Richard Appel, a writer for The Simpsons; Homer Simpson's mother is named after her
- Red Smith – Pulitzer Prize-winning sportswriter
- Zack Snyder – director of films Man of Steel, Dawn of the Dead (2004 version), 300.
- Margaret Teele (Margaret Poby) – actress, attended St. Joseph's Academy (now Notre Dame de la Baie Academy)
- Louise Adeline Weitzel (1862–1934) – Pennsylvania Dutch poet
- Inventors, business leaders
- Leo Frigo – civic and philanthropic leader
- Augustin Grignon – fur trader and businessman
- Alfred Lawson – credited as inventor of the airliner
- James Mulva – Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of ConocoPhilips
- Daniel Whitney – businessman and pioneer
Gallery
-

South Village Historical District
-
Adams Street
-
Nicolet Bank
-
Downtown Green Bay YMCA
-
The Broadway District
-

Large South Side home
-
South Washington Street on the near east side of Green Bay
-
The Northern Building
-

Schreiber Foods Headquarters, downtown
-
View of Downtown from the Fox River
-
The east side of Green Bay
-

Thome Fountain, in Green Bay Botanical Garden
Buildings
| Building | Year Built | Height | Floors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lambeau Field | 1957 | 232 feet | N/A |
| St. Vincent Hospital | 1957 | 10 | |
| 400 Monroe Plaza | 10 | ||
| Bellin Building[65] | 1915 | 114 feet | 9 |
| Hotel Northland | 1924 | 98 feet | 9 |
| Bellin Hospital | 8 | ||
| Flats on the Fox | 2008 | 8 | |
| Hyatt Regency Hotel | 1984 | 8 | |
| Mason Manor | 8 | ||
| Metreau Apartments | 2015 | 80 feet | 8 |
| U.S. Bank Building | 7 | ||
| Wisconsin Public Service | 7 | ||
| Hampton Inn Downtown Green Bay | 1973 | 7 | |
| YMCA | 1924 | 7 | |
| Green Bay State Office Building | 1983 | 6 | |
| Watermark | 6 | ||
Sister cities
 Irapuato, Guanajuato, Mexico (since 2006)[66]
Irapuato, Guanajuato, Mexico (since 2006)[66]
Trivia
- Green Bay featured in the 1992 TV Show "Picket Fences", as being the point of origin of 400 school children to be bussed to Rome, Wisconsin.
Notes
References
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- 1 2 "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2012-01-24. Retrieved 2012-11-18.
- 1 2 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-11-18.
- ↑ "Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2016-05-22.
- 1 2 3 4 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2013-09-11. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ↑ METROPOLITAN STATISTICAL AREAS AND COMPONENTS Archived May 26, 2007, at the Wayback Machine., Office of Management and Budget, 2007-05-11. Accessed 2008-07-30.
- ↑ "Jean Nicolet", Wisconsin History
- 1 2 City of Green Bay. "City of Green Bay." www.ci.green-bay.wi.us. 5 Oct. 2008 <http://www.ci.green-bay.wi.us/geninfo/history_o.html>
- ↑ "Jean Nicolet", Enchanted Learning
- 1 2 Rodesch, Jerrold C. (1984). "Jean Nicolet". University of Wisconsin–Green Bay. Retrieved 2007-10-13.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 City of Green Bay
- ↑ "Langlade, Charles Michel 1729–1801", Dictionary of Wisconsin Biographyhttp://www.wisconsinhistory.org/dictionary/index.asp?action=view&term_id=2266&search_term=langlade Archived November 12, 2014, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Wisconsin, a Guide to the Badger State page 188
- ↑ Wisconsin Encyclopedia By Federal Writers' Project of the Works Progress Administration, Jennifer L. Herman page 336
- ↑ Warren Gerds, A is for architecture: Hazelwood stands out in Greek Revival style, Press-Gazette, July 16, 2009, Accessed July 16, 2009.
- ↑ Martin, Deborah Beaumont; Beaumont, Sophie (1899). Old Green Bay. New York: Cheltenham Press. Retrieved September 13, 2013.
- ↑ Mayor Denissen
- ↑ M. Kottek, J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf, & F.Rubel, "World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated", Meteorologische Zeitschrift, Vol. 15, No. 3, 259-263 (June 2006).
- ↑ http://www.tornadohistoryproject.com
- 1 2 3 "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-12-27.
- ↑ "Station Name: WI GREEN BAY". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2014-03-26.
- ↑ "WMO Climate Normals for GREEN BAY/A.-STRAUBEL, WI 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2014-03-10.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- ↑ United States Census Bureau. "Census of Population and Housing". Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
- ↑ "Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2014-08-22.
- ↑
- ↑ http://flygrb.com/airline-travel-info/airline-information
- 1 2 http://portofgreenbay.com/about/history
- ↑ https://www.cuw.edu/admissions/adult-accelerated/locations/greenbay.html
- ↑ http://lakeland.edu/Evening-Weekend-and-Online/green-bay-center
- ↑ Kathleen Gallagher (June 25, 2012). "Medical College plans campuses in Green Bay, central Wisconsin". Milwaukee Journal-Sentinel. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ↑ Amy Bailey (August 22, 2014). "Medical College of Wisconsin-Green Bay loses a partner". Green Bay-Press Gazette. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ↑ Brown County Library: General Information Accessed 23 October 2011
- ↑ American Religion Data Archive
- ↑ "Our Mission".
- ↑ "Church".
- ↑ "About Us".
- ↑ "Messiah Lutheran Church".
- ↑ "WELS Locator Search – Results".
- ↑ http://www.wisconsinpower.net/gb/
- ↑ City of Green Bay "Hotel Northland"
- 1 2 3 https://www.greenbay.com/things-to-do/arts-culture/
- ↑ http://www.greenbaypressgazette.com/story/news/local/2015/04/09/green-bay-symphony-orchestra-taking-final-bow/25556971/
- ↑ http://www.mosaicartsinc.org/artstreet/
- ↑ http://www.ci.green-bay.wi.us/CityDeck/DineOnDeck.html
- ↑ http://www.onbroadway.org/taste
- ↑ Ryman, Richard (October 12, 2007). "Broadway District businesses go Wi-Fi". Green Bay Press-Gazette. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- ↑ https://www.greenbay.com/media/trivia/
- ↑ http://www.quiltednorthern.com/about
- ↑ Brian Tuohy (December 3, 2014). "Debt, Toilet Paper, and Scandals: How the Green Bay Packers Became a Non-Profit". Retrieved March 21, 2016.
- ↑ http://www.gp.com/Company/Company-Overview/Locations/Green-Bay#tab-1
- ↑ http://www.greenbaypressgazette.com/story/money/2014/08/04/procter-gamble-slim-product-lineup/13602181/
- ↑ http://www.bloomberg.com/profiles/companies/0394255D:US-steen-macek-paper-co-inc
- ↑ "Birth of a Team and a Legend". Green Bay Packers. Retrieved March 21, 2016.
- ↑ http://jbssa.com/about/locations/
- ↑ "City of Green Bay 2014 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report" (PDF). Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Private Industry Employers
- ↑ http://www.shopko.com/category/Company/Our-History/pc/2176/2179.uts?&pageSize=
- ↑ http://easttownmallgb.com/wp-content/uploads/gaiabrochure.pdf
- ↑ "W. J. Abrams (1829-1900)". City of Green Bay. Retrieved 2011-11-30.
- ↑ Martin, Deborah Beaumont (1913). History of Brown County, Wisconsin: Past and Present, Volume 1. S.J. Clarke publishing Company. p. 270.
- ↑ 'Wisconsin Blue Book 1960, Biographical Sketch of A.A. Deering, pg. 32
- ↑ http://bellinbuilding.com/history_2.html
- ↑ http://www.ci.green-bay.wi.us/GBSisterCities/history.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Green Bay, Wisconsin. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Green Bay. |
| Wikisource has the text of The New Student's Reference Work article Green Bay, Wis.. |
- City of Green Bay
- Green Bay Area Chamber of Commerce
- Greater Green Bay Convention & Visitor Bureau
- Sanborn fire insurance maps: 1883 1887 1894 1900 1907


.jpg)