Kearny, New Jersey
| Kearny, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
| Town | |
| Town of Kearny | |
|
| |
| Nickname(s): Soccer Town, U.S.A.[1] | |
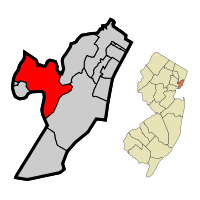 Location of Kearny within Hudson County and the state of New Jersey | |
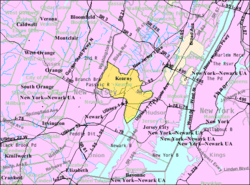 Census Bureau map of Kearny, New Jersey | |
| Coordinates: 40°45′13″N 74°07′15″W / 40.75372°N 74.120875°WCoordinates: 40°45′13″N 74°07′15″W / 40.75372°N 74.120875°W[2][3] | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| County | Hudson |
| Incorporated | April 8, 1867 |
| Named for | Philip Kearny |
| Government[4] | |
| • Type | Town |
| • Body | Town Council |
| • Mayor | Albert G. Santos (D, term ends December 31, 2017)[5][6] |
| • Administrator | Michael J. Martello[7] |
| • Clerk | Pat Carpenter[8] |
| Area[2] | |
| • Total | 10.193 sq mi (26.399 km2) |
| • Land | 8.775 sq mi (22.726 km2) |
| • Water | 1.418 sq mi (3.673 km2) 13.91% |
| Area rank |
209th of 566 in state 3rd of 12 in county[2] |
| Elevation[9] | 7 ft (2 m) |
| Population (2010 Census)[10][11][12][13] | |
| • Total | 40,684 |
| • Estimate (2015)[14] | 42,137 |
| • Rank |
51st of 566 in state 7th of 12 in county[15] |
| • Density | 4,636.5/sq mi (1,790.2/km2) |
| • Density rank |
122nd of 566 in state 11th of 12 in county[15] |
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC−5) |
| • Summer (DST) | Eastern (EDT) (UTC−4) |
| ZIP codes | 07032, 07099[16][17] |
| Area code(s) | 201 and 973[18] |
| FIPS code | 3401736510[2][19][20] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0885266[2][21] |
| Website |
www |
Kearny (/ˈkɑːrni/ KAR-nee[1][22]) is a town in Hudson County, New Jersey, United States and a suburb of Newark. As of the 2010 United States Census, the town's population was 40,684,[11][12][13] reflecting an increase of 171 (+0.4%) from the 40,513 counted in the 2000 Census, which had in turn increased by 5,639 (+16.2%) from the 34,874 counted in the 1990 Census.[23]
Kearny is named after Civil War general Philip Kearny.[24][25] It began as a township formed by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on April 8, 1867, from portions of Harrison Township. Portions of the township were taken on July 3, 1895, to form East Newark. Kearny was incorporated as a town on January 19, 1899, based on the results of a referendum held two days earlier.[26] The Arlington section of town was named for Arlington Station on the Erie Railroad at the Arlington Mill plant, owned by Arlington Mills of Lawrence, Massachusetts.
History
Colonial roots
The area of Kearny Township, created in 1867, had been part of the original Crown Grant of 30,000 acres (120 km2) obtained by Major William Sandford of Barbados on July 4, 1668. Major Sandford named it New Barbadoes Neck after his old home.[27] As was the custom of the time, the Major paid 20 pounds sterling to Chief Tantaqua of the Hackensack tribe for all their reserve rights and titles.
Sanford's friend Major Nathaniel Kingsland acquired the property in 1708 and sold the upper western tract of the Grant for 300 pounds sterling to Captain Arent Schuyler two years later. The new purchase included present-day Kearny, North Arlington, Lyndhurst and Kingsland.[28]
Shortly after Schuyler's purchase of his new homestead, a peculiar green stone was uncovered. It was sent to England for analysis and he learned that it contained 80% copper. His opening of a copper mine brought the first steam engine to America from England; it was used to pump out the deep mine shaft. The engine was secretly delivered by its engineer, Josiah Hornblower. The engine and mines were destroyed by fire in 1772 and remained idle for some years.[29][30]
Schuyler Mansion played a role during the American Revolutionary War Era. When Lord Howe of England took possession of New York Harbor, the proximity of Schuyler Mansion drew many of his officers. They generally traveled over a road that today is referred to as the Belleville Turnpike, which was originally constructed in 1759 using cedar logs from the nearby swamps.[28]
During September 1777, General Henry Clinton, head of the British Expeditionary Forces in America, selected Schuyler Mansion for his headquarters during one of his more important raiding operations which included the famed Battle of Second River. The Mansion stood until 1924, a period of 214 years, when it was torn down by a land development company, despite the company's offers to transfer the land an organization that would be able to pay to maintain the property.[31]
19th century

In the middle 19th century, Kearny was the upper, or northern, section of the Township of Harrison. A prominent citizen and resident of the upper section, General N. M. Halsted, felt it was impossible under these political conditions for his section to obtain proper recognition. He engaged an energetic campaign for an independent township. He succeeded when the NJ Legislature of 1867 on March 14, adopted "an act creating the Township of Kearny". The town was named to honor Major General Phil Kearny, Commander of the New Jersey Forces in the Civil War and the owner of the mansion known as Belle Grove (or Belgrove), locally called "Kearny Castle".[32]
On April 8, 1867, the first election of town officers was held. General N. M. Halsted was elected Chairman. The first official seat of Government was three rooms in the old Lodi Hotel, on the northeast corner of Schuyler and Harrison Avenues.[33]
In the early 1870s, Kearny erected its first Town Hall, on the corner of Kearny and Woodland Avenues, the present site of the Knox Presbyterian Church Parish Hall. This served as a Town Hall, Court House, and Schoolhouse. The Minute Book of the Township states on August 16, 1870, the first step toward establishing Kearny's present public school system was taken. The first schoolhouse was housed in the Town Hall built at Kearny and Woodland Avenues in 1873.[33]

The Highland Hose No. 4 firehouse which is now on the National Register of Historic Places list was built in 1895.
The town's nickname, "Soccer Town, U.S.A." is derived from a soccer tradition that originated in the mid-1870s, when thousands of Scottish and Irish immigrants settled in the town, after two Scottish companies, Clark Thread Company and Nairn Linoleum, opened two local mills and a factory.[1]
When the town's growth demanded larger quarters, the present Kearny Town Hall, built of Indiana limestone, was erected in 1909.[33]
Factory town
The early influx and development of industry in Kearny dates back to 1875 when the Clark Thread Company of Paisley in Scotland extended its activities to the United States by erecting two large mills in Kearny, and adding two others in 1890. These mills brought to Kearny thousands of Scots immigrants. Many of them would play on Kearny's soccer teams in National Association Football League. Many are buried at Arlington Memorial Park in the Kearny Uplands.[34]
In 1876, the Mile End Thread Mills started operating, giving employment to several hundred operators.
In 1883, the Marshall Flax Spinning Company of England erected a large plant in Kearny, known as the Linen Thread Company. Their need for experienced flax spinners brought an influx of workers from other sections of the British Isles. Families of those early textile workers were the nucleus of Kearny's present population.
The Puraline Manufacturing Company, later called the Arlington Company, which became a subsidiary of E. I. DuPont de Nemours Company, had purchased a large tract of land east of the Arlington Station on the Erie Railroad extending well out, north of the railroad embankment, into the meadowland.
In 1887, Sir Michael Nairn established the Nairn Linoleum Company of Kirkcaldy in Scotland, now the Congoleum Nairn Company of Kearny, giving further impetus to local industrial growth. This also lead to the growth in the Scottish American population which In the 1960s was about 21,000.[35]
In 1902, the Lovell–Dressel Company, manufacturers of marine and railway lamps and fixtures, located in Kearny adjacent to the Erie Railroad.
Other industries which located in Kearny include: Swift & Company, Koppers Company, Theobald Industries, Standard Tool & Manufacturing, Wilkata Box Company, Harris Steel Company and L & R Manufacturing. Between 1926 and 1986, the Kearny Works of Western Electric employed as many as 24,000 in producing a variety of hardware and supplies for the Bell System and was the home of the "Kearny Standard" for tools and equipment, and was sold by AT&T in 1984 by which time the plant had 4,000 employees who earned a total of $128 million a year, making it one of the county's largest employers.[36][37]
Cargo ships were built at Kearny Yards during World War I, and warships during World War II.[38]
21st century
The HBO drama series The Sopranos was filmed partially in Kearny. One of its buildings, used for Satriale's Pork Store, was later razed to prepare for a condominium development.[39]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town had a total area of 10.193 square miles (26.399 km2), including 8.775 square miles (22.726 km2) of land and 1.418 square miles (3.673 km2) of water (13.91%).[2][3]
Unincorporated communities, localities and place names located partially or completely within the town include Arlington, Schuylers Corner and West Arlington.[40]
The town is bordered by East Newark, Harrison and North Arlington (which is located in Bergen County). The Passaic River separates the town from Newark and Belleville, both located in Essex County. The Hackensack River separates it from Jersey City.[41][42]
The town is varied in topography and roughly divided into three parts: the Kearny Uplands, the Kearny Meadows and Kearny Point.[43] Main thoroughfares include the eponymous Kearny Avenue (the local segment of Ridge Road / Frank E. Rodgers Boulevard), Bergen Avenue, Midland Avenue, Schuyler Avenue and Passaic Avenue. The unincorporated community of Arlington is located within the town.
A number of small parks running along Passaic River are collectively called Riverbank Park. The largest, located on the colloquial "Bunnyland Hill", is a gift from Kearny's veterans. It is named after a small zoo named Bunnyland, which was maintained by the local Kiwanis Club, that occupied part of the present Bunnyland Hill in the 20th century. During Kearny's Fourth of July celebrations (which include a fireworks display), Bunnyland Hill is the primary gathering spot for celebrants and observers. The largest park is West Hudson Park, shared with Harrison, which contains a variety of sports fields, recreational areas, and an artificial pond.[44] The second largest recreational zone is the Kearny Playground at Gunnel Oval.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 777 | — | |
| 1890 | 7,064 | 809.1% | |
| 1900 | 10,896 | 54.2% | |
| 1910 | 18,659 | 71.2% | |
| 1920 | 26,724 | 43.2% | |
| 1930 | 40,716 | 52.4% | |
| 1940 | 39,467 | −3.1% | |
| 1950 | 39,952 | 1.2% | |
| 1960 | 37,472 | −6.2% | |
| 1970 | 37,585 | 0.3% | |
| 1980 | 35,735 | −4.9% | |
| 1990 | 34,874 | −2.4% | |
| 2000 | 40,513 | 16.2% | |
| 2010 | 40,684 | 0.4% | |
| Est. 2015 | 42,137 | [14][45] | 3.6% |
| Population sources: 1880–1920[46] 1880–1890[47] 1890–1910[48] 1900–1930[49] 1930–1990[50] 2000[51][52] 2010[11][12][13] | |||
Census 2010
At the 2010 United States Census, there were 40,684 people, 13,462 households, and 9,921 families residing in the town. The population density was 4,636.5 per square mile (1,790.2/km2). There were 14,180 housing units at an average density of 1,616.0 per square mile (623.9/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 73.57% (29,933) White, 5.37% (2,186) Black or African American, 0.40% (163) Native American, 4.41% (1,793) Asian, 0.08% (32) Pacific Islander, 12.53% (5,099) from other races, and 3.63% (1,478) from two or more races. Hispanics or Latinos of any race were 39.95% (16,253) of the population.[11]
There were 13,462 households, of which 33.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.6% were married couples living together, 15.6% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.3% were non-families. 21.0% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.83 and the average family size was 3.28.[11]
In the town, 20.7% of the population were under the age of 18, 11.0% from 18 to 24, 31.2% from 25 to 44, 26.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.7% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36.4 years. For every 100 females there were 106.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 105.7 males.[11]
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $58,698 (with a margin of error of ±$3,838) and the median family income was $66,272 (±$3,803). Males had a median income of $45,360 (±$2,598) versus $38,668 (±$3,893) for females. The per capita income for the borough was $24,977 (±$1,022). About 7.6% of families and 10.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 14.2% of those under age 18 and 8.1% of those age 65 or over.[53]
Census 2000
As of the 2000 United States Census[19] there were 40,513 people, 13,539 households, and 9,802 families residing in the town. The population density was 4,433.2 people per square mile (1,711.4/km²). There were 13,872 housing units at an average density of 1,518.0 per square mile (586.0/km²). The racial makeup of the town was 75.75% White, 3.97% African American, 0.37% Native American, 5.50% Asian, 0.07% Pacific Islander, 10.04% from other races, and 4.31% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 27.34% of the population.[51][52]
There were 13,539 households out of which 34.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 53.8% were married couples living together, 13.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 27.6% were non-families. 21.8% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.81 and the average family size was 3.28.[51][52]
In the town the population was spread out with 21.5% under the age of 18, 10.7% from 18 to 24, 35.7% from 25 to 44, 21.3% from 45 to 64, and 10.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 106.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 107.0 males.[51][52]
The median income for a household in the town was $47,757, and the median income for a family was $54,596. Males had a median income of $38,672 versus $30,620 for females. The per capita income for the town was $20,886. About 6.1% of families and 8.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 9.1% of those under age 18 and 10.0% of those age 65 or over.[51][52]
Economy
Portions of Kearny are part of an Urban Enterprise Zone.[54] In addition to other benefits to encourage employment within the Zone, shoppers can take advantage of a reduced 3½% sales tax rate at eligible merchants (versus the 7% rate charged statewide) at eligible merchants.[55]
Government
Local government

Kearny is governed under the Town form of New Jersey municipal government. The government consists of a Mayor and Town Council comprising eight council members. A Mayor is elected directly by the voters at-large to a four-year term of office. The Town Council is elected by the voters to four-year terms of office in partisan elections, on a staggered basis, with one of the two seats from each ward coming up for election in two consecutive years followed by two years with no elections.[4] The Mayor and Council operate on a legislative basis, with the Mayor having veto power. The day-to-day operations are the responsibility of the Town Administrator whose duties are specified by local ordinance, and who generally carries out the policies adopted by the Mayor and Council.[56]
As of 2016, the Mayor of Kearny is Al Santos, who has been Mayor of Kearny since January 1, 2000, and whose current term of office ends December 31, 2017. Before his election as mayor, Santos served as councilman of Kearny's Second Ward for one year.[5] Members of the Town Council are:[57][58][59][60][61]
- Council members 1st Ward: Albino Cardoso (D, 2018) and Marytrine De Castro (D, 2017; elected to serve an unexpired term)[62]
- Council members 2nd Ward: Jonathan D. Giordano (D, 2018) and Richard P. Konopka (D, 2017)[63]
- Council members 3rd Ward: Carol Jean Doyle (D, 2017) and Eileen Eckel (D, 2018)[64]
- Council members 4th Ward: Michael D. Landy (D, 2017) and Susan A. McCurrie (D, 2018)[65]
In February 2015, the Town Council selected Marytrine De Castro, as chosen by the Democratic municipal committee, to fill the vacant First Ward seat expiring in December 2017 that had been held by Alexa Arce until she resigned from office the previous month.[66] In the November general election, De Castro was elected to serve the balance of the term.[59]
Fire department
The town is protected by the Kearny Fire Department,[67] which operates out of four fire stations.[68] The current Chief of Department is Steve Dyl.[69] Below is a list of fire station locations and apparatus of the Kearny Fire Department.
| Engine company | Ladder company | special unit | Command unit | Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine 1 | 2 Rescue Boats | 47 Davis Avenue[68] | ||
| Squad 2(Rescue Pumper) | Tower Ladder 2 | Rescue 2 | Car 2 (Deputy Chief) | 109 Kearny Avenue[68] |
| Engine 3 ,Engine 5 (Reserve) | Ladder 1 (Reserve) | Quick Attack Response Vehicle 1(QRV) Marine 3 | Car 3 (Safety Officer) | 109 Midland Avenue[68] |
| Engine 4 | Foam Unit 1,MPV 4 (Multi Purpose Vehicle) | 83 John Miller Way[68] |
Federal, state and county representation
Kearny is split between the 8th and 9th Congressional Districts[70] and is part of New Jersey's 32nd state legislative district.[12][71][72] Prior to the 2010 Census, Kearny had been part of the 9th Congressional District and the 13th Congressional District, a change made by the New Jersey Redistricting Commission that took effect in January 2013, based on the results of the November 2012 general elections.[73] In the redistricting that took effect in 2013, 22,572 (about 55%) Kearny residents were placed in the 8th District, with the remaining 18,112 (about 45%) located in the extreme northwest corner of the town placed in the 9th District.[70][74]
New Jersey's Eighth Congressional District is represented by Albio Sires (D, West New York).[75] New Jersey's Ninth Congressional District is represented by Bill Pascrell (D, Paterson).[76] New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Cory Booker (D, Newark, term ends 2021)[77] and Bob Menendez (D, Paramus, 2019).[78][79]
For the 2016–2017 session (Senate, General Assembly), the 32nd Legislative District of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Nicholas Sacco (D, North Bergen) and in the General Assembly by Angelica M. Jimenez (D, West New York) and Vincent Prieto (D, Secaucus).[80] The Governor of New Jersey is Chris Christie (R, Mendham Township).[81] The Lieutenant Governor of New Jersey is Kim Guadagno (R, Monmouth Beach).[82]
Hudson County is governed by a directly elected County Executive and by a Board of Chosen Freeholders, which serves as the county's legislative body. As of 2015, the County Executive is Democrat Thomas A. DeGise, whose term of office ends December 31, 2015.[83] Hudson County's nine Freeholders (with district, municipalities in district and place of residence) are Kenneth Kopacz (District 1, Bayonne and parts of Jersey City; Bayonne),[84] William O'Dea (District 2, parts of Jersey City),[85] Gerard M. Balmir (District 3, parts of Jersey City),[86] Chairman E. Junior Maldonado (District 4, parts of Jersey City),[87] Anthony Romano (District 5, Hoboken and parts of Jersey City; Hoboken),[88] Vice-Chairman Tilo Rivas (District 6, Union City),[89] Caridad Rodriguez (District 7, Guttenberg, Weehawken and West New York; West New York),[90] Chairman Pro-Tempore Anthony P. Vainieri, Jr. (District 8, North Bergen, parts of Jersey City and Secaucus; North Bergen)[91] and Albert Cifelli (District 9, East Newark, Harrison, Kearny and parts of Secaucus; Kearny),[92][93] all Democrats serving terms of office ending December 31, 2017.[94] Constitutional officers elected on a countywide basis are County Clerk Barbara A. Netchert, Sheriff Frank X. Schillari and Surrogate Joseph J. Ryglicki.[95]
Politics
As of March 23, 2011, there were a total of 16,348 registered voters in Kearny, of which 7,030 (43.0%) were registered as Democrats, 1,922 (11.8%) were registered as Republicans and 7,390 (45.2%) were registered as Unaffiliated. There were 6 voters registered to other parties.[96]
In the 2012 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 68.9% of the vote (7,579 cast), ahead of Republican Mitt Romney with 29.9% (3,293 votes), and other candidates with 1.2% (129 votes), among the 11,076 ballots cast by the town's 17,601 registered voters (75 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 62.9%.[97][98] In the 2008 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 60.4% of the vote (6,953 cast), ahead of Republican John McCain with 37.9% (4,365 votes) and other candidates with 1.1% (121 votes), among the 11,508 ballots cast by the town's 18,057 registered voters, for a turnout of 63.7%.[99] In the 2004 presidential election, Democrat John Kerry received 57.0% of the vote (6,363 ballots cast), outpolling Republican George W. Bush with 41.7% (4,650 votes) and other candidates with 0.5% (87 votes), among the 11,154 ballots cast by the town's 16,633 registered voters, for a turnout percentage of 67.1.[100]
In the 2013 gubernatorial election, Democrat Barbara Buono received 49.5% of the vote (2,667 cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 48.8% (2,634 votes), and other candidates with 1.7% (92 votes), among the 5,597 ballots cast by the town's 18,001 registered voters (204 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 31.1%.[101][102] In the 2009 gubernatorial election, Democrat Jon Corzine received 52.9% of the vote (3,838 ballots cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 38.5% (2,790 votes), Independent Chris Daggett with 5.4% (390 votes) and other candidates with 1.1% (80 votes), among the 7,249 ballots cast by the town's 16,417 registered voters, yielding a 44.2% turnout.[103]
Education


Public Schools
The Kearny School District serves public school students in preschool through twelfth grade. As of the 2011-12 school year, the district's seven schools had an enrollment of 5,921 students and 442.6 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 13.38:1.[104] Schools in the district (with 2011-12 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics[105]) are six elementary schools — Franklin School[106] (PreK–8; 1,066 students), Garfield School[107] (PreK–6; 663), Lincoln School[108] (PreK–8; 795), Roosevelt School[109] (PreK–6; 465), Schuyler School[110] (PreK–6; 520) and Washington School[111] (PreK–8; 681) — and Kearny High School[112] (9–12; 1,735).[113][114]
Private Schools
Schools in Kearny include:[115]
- Kearny Christian Academy, a Christian school founded in 1981 by the City of Hope International Church that serves students in Kindergarten through twelfth grade.[116]
- Mt. Carmel Guild School
- The Little Neighborhood Learning Center
- Happy Time Preschool & Day Care
In the face of declining enrollment, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark closed Mater Dei Academy at the conclusion of the 2011–12 school year. Mater Dei had been opened three years earlier as the merger of two existing schools, St. Stephen's and Holy Cross, but attendance declined from 250 in its first year to 170 in its final year[117]
Library and museum
The Kearny Public Library is one of New Jersey's remaining Carnegie libraries,[118] and houses a museum on its third floor which mounts exhibitions related to the history and culture of the town and has a collection of artifacts related to the town's namesake.[119][120]
Transportation
Roads and highways
As of May 2010, the town had a total of 70.89 miles (114.09 km) of roadways, of which 50.75 miles (81.67 km) were maintained by the municipality, 7.30 miles (11.75 km) by Hudson Countyand 7.73 miles (12.44 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation and 5.11 miles (8.22 km) by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority.[121]
The Belleville Turnpike (Route 7) forms the northern border of the town with North Arlington and crosses the Rutgers Street Bridge over the Passaic River into Belleville. Kearny Avenue passes through the town and continues north as Ridge Road, the beginning of NJ 17. US 1/9 (Pulaski Skyway) and US 1/9 Truck pass through. The Essex Freeway (Interstate 280) passes through the town and ends at Interstate 95(W) (the New Jersey Turnpike eastern and western spurs) at the tollgate for Exit 15W.
Public transportation
New Jersey Transit offers bus service to the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan and to other New Jersey communities. Bus service to Newark is available on the 1, 30, 40, 43, 76 and 80 routes.[122]
Kearny was formerly served by trains of both the Erie Railroad's Newark Branch (later Erie-Lackawanna Newark Branch) and its Greenwood Lake Division (later the Erie-Lackawanna's Greenwood Lake-Boonton Line; and Conrail and New Jersey Transit's Boonton Line) which stopped at the now abandoned Arlington Station. Newark Branch service was terminated in October, 1966. New Jersey Transit discontinued Boonton Line service in 2002 when the Montclair Connection was opened.[123][124] Through the early 1970s trains also stopped at a second station along this route known as West Arlington. This station was just to the east of the now abandoned WR Draw movable bridge. Prior to April 30, 1967, a station in South Kearny, was served by the Central Railroad of New Jersey's Newark and New York Railroad via the PD Draw over the Passaic River. This station was popular with employees of the giant Western Electric plant, and other industries in the area. In the final years of this service a pair of rush hour trains ran in each direction between South Kearny, and the CNJ's Broad Street Station in downtown Newark, as well as a single rush hour round trip between South Kearny, and Plainfield. This train operated via Elizabethport, and the CNJ main line.
The closest airport with scheduled passenger service is Newark Liberty International Airport, located 6.5 miles (10.5 km) away in Newark and Elizabeth.
Notable people
People who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Kearny include:
- Tomasz Adamek (born 1976), Polish professional heavyweight boxer who is the former WBC Light Heavyweight Champion and the former IBF & IBO & The Ring Cruiserweight Champion.[125]
- Davey Brown (1898–1970), U.S. soccer forward who was inducted into the US Soccer Hall of Fame.[126]
- Guy W. Calissi (c. 1909–1980), New Jersey Superior Court judge who lived in an orphanage here.[127]
- Gary Michael Cappetta (born 1952), professional wrestling ring announcer, author, voice over artist, screenwriter and stage performer.[128]
- Ownie Carroll (1902–1975), Major League Baseball pitcher who played nine seasons in the major, from 1925 to 1934 .[129][130]
- Ted Gillen (born 1968), former professional soccer player.[131]
- Albert Gonzalez (born 1981), government informant and computer criminal.[132][133]
- Ed Halicki (born 1950), former professional baseball pitcher with a no-hitter to his credit, pitched on August 24, 1975, against the New York Mets.[134][135]
- John Harkes (born 1967), professional soccer player.[1][136]
- Al Hartley (1921–2003), comic book writer-artist known for his work on Archie Comics.[137]
- Fred A. Hartley Jr. (1909–1969), New Jersey Congressman best known for being the House of Representatives sponsor of the Taft-Hartley Act.[138][139]
- Herbie Haymer (1916–1949), jazz saxophonist.[140]
- Frank Iero (born 1981), rhythm guitarist and backup vocalist for My Chemical Romance.[141]
- Jeffrey Klepacki (born 1968), three-time US Olympian in rowing and three-time world champion.[142]
- Buzz Kulik (1922–1999), film director and producer.[143]
- Joe Kyrillos (born 1960), politician who has served in the New Jersey Senate since 1992, where he represents the 13th Legislative District.[144]
- Joan Lippincott (born 1935), concert organist.[145]
- Hugh MacDonald (born 1985), soccer defender who was last rostered with New York Red Bulls.[146]
- Kevin Maguire (born 1960), comic book artist.[147]
- Tony Meola (born 1969), professional soccer player.[148]
- Dots Miller (1886–1923), Major League Baseball player from 1909 to 1921.[149]
- Tony Mottola (1918–2004), jazz guitarist.[150][151]
- Shamus O'Brien (1907–1981), soccer player inducted in 1990 into the National Soccer Hall of Fame.[152]
- Greg Pason (born 1966), National Secretary of the Socialist Party USA.[153]
- George Paxton (c. 1914–1989), big band jazz leader, saxophonist, composer, producer.[140][154]
- Bill Raftery (born 1943), college basketball analyst and former college basketball player for La Salle University.[155]
- Tab Ramos (born 1966), retired soccer midfielder.[156]
- Harold Hill Smith (1910–1994), geneticist who first fused a human cell and a plant cell.[157]
- Archie Stark (1897–1985), soccer pioneer in the United States and member of National Soccer Hall of Fame.[158]
- Ray Toro (born 1977), My Chemical Romance lead guitarist.[159]
- Alex Webster (1931-2012), professional football player for the Montreal Alouettes[160] and New York Giants.[161]
- Dick Weisgerber (born 1913), professional football player for the Green Bay Packers.[162]
- Kenneth G. Wiman (born 1930), U.S. Coast Guard Rear Admiral.[163]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Hernandez, Raymond. "World Cup Hits Home In Soccer Town, U.S.A." The New York Times June 26, 1994. Accessed September 12, 2013. "In a nation that has not yet shared the world's enthusiasm for soccer, Kearny (pronounced CAR-nee) is certainly an anomaly. The town has two local soccer historians. On Kearny Avenue, the main strip, a sign proclaims: 'Welcome to Kearny. Soccer Town, U.S.A.'"
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 2010 Census Gazetteer Files: New Jersey County Subdivisions, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 21, 2015.
- 1 2 US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- 1 2 2012 New Jersey Legislative District Data Book, Rutgers University Edward J. Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy, March 2013, p. 142.
- 1 2 Mayor Alberto G. Santos, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ 2016 New Jersey Mayors Directory, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed June 14, 2016.
- ↑ Town Administrator, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Town Clerk, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Town of Kearny, Geographic Names Information System. Accessed March 6, 2013.
- ↑ 2010 Census: Hudson County, Asbury Park Press. Accessed April 20, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Kearny town, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 15, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 Municipalities Grouped by 2011-2020 Legislative Districts, New Jersey Department of State, p. 13. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- 1 2 3 Table DP-1. Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2010 for Kearny town, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 15, 2011.
- 1 2 PEPANNRES - Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015 - 2015 Population Estimates for New Jersey municipalities, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 22, 2016.
- 1 2 GCT-PH1 Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 – State – County Subdivision from the 2010 Census Summary File 1 for New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ Look Up a ZIP Code for Kearny, NJ, United States Postal Service. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ Zip Codes, State of New Jersey. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ↑ Area Code Lookup – NPA NXX for Kearny, NJ, Area-Codes.com. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- 1 2 American FactFinder, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ↑ A Cure for the Common Codes: New Jersey, Missouri Census Data Center. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ US Board on Geographic Names, United States Geological Survey. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ↑ Wright, E. Assata. "Secaucus: How do you pronounce it? Development put town on map, but newcomers don't know where they are", The Hudson Reporter, July 6, 2011. "Therefore, the new neighbors may proudly totter about telling folks they live in Sih-KAW-cus or See-KAW-cus. However, natives prefer that the accent be on the first syllable, as in: SEE-kaw-cus.... Bayonne is bay-OWN, not ba-YON, locals say. Kearny is Kar-nee, not Keer-nee."
- ↑ Table 7. Population for the Counties and Municipalities in New Jersey: 1990, 2000 and 2010, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, February 2011. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed September 2, 2015.
- ↑ Gannett, Henry. The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States, p. 172. United States Government Printing Office, 1905. Accessed September 2, 2015.
- ↑ Snyder, John P. The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606–1968, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 147. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ Harvey, Cornelius Burnham. "Genealogical History Of Hudson And Bergen Counties New JerseyEARLY SETTLERS OF HUDSON COUNTY – Part A", Getnj.com, 1900. Accessed October 29, 2014.
- 1 2 History, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2011.
- ↑ Documents, Manuscripts, Maps, & Photographs; Manuscript Group 651, Schuyler Family (New Barbados Neck, NJ), New Jersey Historical Society. Accessed October 29, 2014.
- ↑ Lienhard, John H. "No. 1085: THE FIRST AMERICAN STEAM ENGINE", University of Houston Engines of Our Ingenuity. Accessed October 29, 2015.
- ↑ Krasner, Barbara. Kearny, p. 10. Arcadia Publishing, 2000. ISBN 0-7385-0403-3. Accessed July 7, 2011. "Constructed of stone and bricks imported from Holland, the mansion stood as a source of pride until 1924. When the mansion was about to be torn down, a development company offered to deed a section of the 60 acres to any historical society that would pay for the upkeep.... no one was able to do so and this monument was destroyed."
- ↑ Cooper, Lee E. "Historic Kearny Family Plot in Jersey To Be Used as Site for New Apartments", The New York Times, January 4, 1939. Accessed October 27, 2011. "This was a part of 'Belgrove,' purchased about 1850 by Philip Kearny, father of General John Watts Kearny, and utilized by him as a site for a mansion which became popularly known as 'Kearny Castle.'"
- 1 2 3 Hipp, Jessie M. Seventy-fifth Anniversary of Kearny Town Hall, Town of Kearny, November 1984. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ Sarapin, Janice Kohl (1994), Old Burial Grounds of New Jersey, Rutgers University Press, ISBN 0-8135-2111-4
- ↑ Prentice, Claire (March 22, 2010). "The Scots of Kearny, New Jersey – home of The Sopranos". The Herald (Glasgow). Retrieved June 27, 2012.
- ↑ via Associated Press. "Kearny, N.J., Plant Is Sold", The New York Times, May 22, 1984. Accessed September 12, 2013. "A.T.& T. Technologies Inc. today announced the sale of the Western Electric Company plant here to the Union Minerals and Alloys Corporation for use as an industrial park designed to employ more than 4,000 people.... In January 1983, Western Electric said it would phase out the 59-year-old Kearny works by mid-1985."
- ↑ Hanley, Robert. "KEARNY PLANT IS DYING, ALONG WITH AN OLD ERA", The New York Times, January 29, 1983. Accessed September 12, 2013. "At its robust best just after World War II, Western Electric's Kearny Works employed 24,000 people and boasted that it was the busiest manufacturing plant in the American Telephone and Telegraph Company's empire.... Only about 4,000 workers remain.... The plant's annual payroll is $128 million, money that is spent in thousands of small businesses in the dozens of communities where the workers live."
- ↑ Kearny Yards, GlobalSecurity.org
- ↑ Caldwell, Dave. "Ice Cream, Onion Rings and Tony Soprano", The New York Times, August 26, 2007. Accessed September 1, 2014. "The owner of the Kearny building used for Satriale's pork store intends to sell pieces of the facade when he has it razed for a condo development."
- ↑ Locality Search, State of New Jersey. Accessed May 21, 2015.
- ↑ Information, Town of Kearny. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ Areas touching Kearny, MapIt. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ↑ Why Kearny, Town of Kearny. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ West Hudson Park, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed November 12, 2012.
- ↑ Census Estimates for New Jersey April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 22, 2016.
- ↑ Compendium of censuses 1726–1905: together with the tabulated returns of 1905, New Jersey Department of State, 1906. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Porter, Robert Percival. Preliminary Results as Contained in the Eleventh Census Bulletins: Volume III – 51 to 75, p. 97. United States Census Bureau, 1890. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Thirteenth Census of the United States, 1910: Population by Counties and Minor Civil Divisions, 1910, 1900, 1890, United States Census Bureau, p. 337. Accessed November 12, 2012. Population of Kearny Township of 7,064 in 1890 is listed in Footnote 1.
- ↑ Fifteenth Census of the United States : 1930 – Population Volume I, United States Census Bureau, p. 711. Accessed December 15, 2011.
- ↑ Table 6. New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1930 - 1990, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed August 9, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Census 2000 Profiles of Demographic / Social / Economic / Housing Characteristics for Kearny town, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 DP-1: Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 – Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for Kearny town, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ DP03: Selected Economic Characteristics from the 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Kearny town, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ Urban Enterprise Zone, Town of Kearny. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ Geographic & Urban Redevelopment Tax Credit Programs: Urban Enterprise Zone Employee Tax Credit, State of New Jersey, backed up by the Internet Archive as of May 25, 2009. Accessed July 7, 2011.
- ↑ Mayor & Council, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ 2016 Municipal Data Sheet, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Directory of Elected Officials: Federal, State, County, & Municipal Officials, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk, updated July 6, 2016. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- 1 2 Hudson County General Election November 3, 2015 Official Results, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 10, 2015. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Hudson County General Election November 4, 2014 Official Results, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 13, 2014. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Hudson County General Election November 5, 2013 Official Results, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 13, 2013. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Council Members 1st Ward, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Council Members 2nd Ward, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016. As of date accessed, Madeline Peyko is still listed as in office.
- ↑ Council Members 3rd Ward, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Council Members 4th Ward, Town of Kearny. Accessed July 7, 2016.
- ↑ Duger, Rose. "De Castro selected to fill vacant council seat in Kearny", The Jersey Journal, February 20, 2015. Accessed July 7, 2016. "Kearny's Democratic County Committee has named Marytrine De Castro to fill the vacant First Ward seat on the Town Council.... De Castro will occupy Arce's First Ward seat until after November's general election, when a permanent replacement will be selected to complete the final two years of Arce's unexpired term."
- ↑ Home. Kearny Fire Department. Accessed March 8, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stations. Kearny Fire Department. Accessed March 8, 2012.
- ↑ Members. Kearny Fire Department. Accessed March 8, 2012.
- 1 2 Plan Components Report, New Jersey Redistricting Commission, December 23, 2011. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- ↑ 2016 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, p. 59, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed July 20, 2016.
- ↑ Districts by Number for 2011–2020, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- ↑ 2011 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, p. 59, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed May 22, 2015.
- ↑ New Jersey Congressional Districts 2012–2012: Kearny Map, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- ↑ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 5, 2012.
- ↑ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 5, 2012.
- ↑ About Cory Booker, United States Senate. Accessed January 26, 2015. "He now owns a home and lives in Newark's Central Ward community."
- ↑ Biography of Bob Menendez, United States Senate, January 26, 2015. "He currently lives in Paramus and has two children, Alicia and Robert."
- ↑ Senators of the 114th Congress from New Jersey. United States Senate. Accessed January 26, 2015. "Booker, Cory A. - (D - NJ) Class II; Menendez, Robert - (D - NJ) Class I"
- ↑ Legislative Roster 2016-2017 Session, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 17, 2016.
- ↑ "About the Governor". State of New Jersey. Retrieved 2010-01-21.
- ↑ "About the Lieutenant Governor". State of New Jersey. Retrieved 2010-01-21.
- ↑ Thomas A. Degise, Hudson County Executive, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 1, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 2, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 3, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 4, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 5, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 6, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 7, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 8, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder District 9, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Freeholder Biographies, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Staff. "Hudson County election results 2014", The Jersey Journal, November 4, 2014. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Directory of Elected Officials, Hudson County Clerk. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- ↑ Voter Registration Summary – Hudson, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 23, 2011. Accessed November 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Presidential General Election Results - November 6, 2012 - Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast - November 6, 2012 - General Election Results - Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ↑ 2008 Presidential General Election Results: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 23, 2008. Accessed November 13, 2012.
- ↑ 2004 Presidential Election: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 13, 2004. Accessed November 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Governor - Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast - November 5, 2013 - General Election Results - Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ↑ 2009 Governor: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 31, 2009. Accessed November 13, 2012.
- ↑ District information for Kearny School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed July 26, 2014.
- ↑ School Data for the Kearny School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed July 26, 2014.
- ↑ Franklin School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Garfield School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Lincoln School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Roosevelt School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Schuyler School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Washington School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Kearny High School, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Schools, Kearny School District. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ New Jersey School Directory for the Kearny School District, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Schools, Town of Kearny. Accessed October 27, 2011.
- ↑ Our History, Kearny Christian Academy. Accessed September 12, 2013.
- ↑ Conte, Michaelangelo, Conte. "Newark Archdiocese to close St. Anne's School in Jersey City, Mater Dei Academy in Kearny", The Jersey Journal, February 17, 2012. Accessed October 15, 2012. "St. Anne's School in Jersey City and Mater Dei Academy in Kearny are slated to close their doors after this school year because of diminishing attendance and rising debt, school and church officials said today."
- ↑ Homepage, Kearny Public Library. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ↑ Krasner, Barbara. Kearny's Immigrant Heritage, Arcadia Publishing, 2003. ISBN 0-7385-3473-0. Accessed September 1, 2014.
- ↑ Kearny Museum
- ↑ Hudson County Mileage by Municipality and Jurisdiction, New Jersey Department of Transportation, May 2010. Accessed December 1, 2013.
- ↑ Hudson County Bus/Rail Connections at the Wayback Machine (archived May 22, 2009), New Jersey Transit. Accessed July 7, 2011.
- ↑ Galant, Debra. "JERSEY; Montclair's Connection Has Its Price", The New York Times, September 29, 2002. Accessed July 7, 2011. "On Sept. 20, New Jersey Transit officially terminated service at Mr. Wilson's beloved Benson Street stop, as well as at the Rowe Street stop in Bloomfield and the Arlington stop in Kearny. Those closings were part of the price of progress."
- ↑ "RAIL SHUTTLE BUSES TO TRANSPORT COMMUTERS AFFECTED BY STATION CLOSURES: NJ TRANSIT Buses and Trains Will Cross-Honor September Monthly Passes For Arlington Station Customers", New Jersey Transit press release dated August 27, 2002. Accessed July 7, 2011. "On Monday, September 30, NJ TRANSIT will launch its MidTOWN DIRECT – Montclair rail service, resulting in the closure of Benson Street, Rowe Street and Arlington stations on the Boonton Line following the last scheduled trip on Friday, September 20."
- ↑ Idec, Keith. "Tomasz Adamek impressive in victory", The Record (Bergen County), March 25, 2012. Accessed October 12, 2012. "Tomasz Adamek methodically made a successful comeback Saturday night from his lopsided loss to Vitali Klitschko.... Adamek, a native of Poland who resides in Kearny, improved to 45–2."
- ↑ Player Bios, US Soccer Hall of Fame. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Brown, who lived his entire life in Kearny, N.J., scored 189 goals during his 11 ASL seasons."
- ↑ Kihss, Peter. "Guy W. Calissi, 71, Retired Judge And a Jersey Prosecutor, Is Dead; College Scholarship Yielded Byrne Made 1970 Appointment", The New York Times, December 9, 1980. Accessed October 19, 2009.
- ↑ Cappetta, Gary Michael. Bodyslams!: Memoirs of a Wrestling Pitchman, p. xvii. ECW Press, 2006. ISBN 9781550227093. Accessed October 2, 2015. "As a child, my family lived every summer in the shore community of Seaside Park. The month I graduated from Kearny High School in Northern New Jersey, my family moved to Ocean County, where my father established a lucrative amusement business on the local boardwalk."
- ↑ Staff. "Ownie Carroll, Baseball Coach, Holy Cross Pitching Star, Dies", The New York Times, June 10, 1975. Accessed October 12, 2012. "Mr. Cartoll,' a native of Kearny, NJ; had a 49–2 record at St. Benedict's Prep in Newark before going to Holy Cross."
- ↑ Ownie Carroll, The Baseball Cube. Accessed August 19, 2007.
- ↑ Kurland, Bob. "METROSTARS MINUS TWO – DONADONI, RAMOS TO MISS OPENER", The Record (Bergen County), April 12, 1996. Accessed September 12, 2013. "Kearny native Ted Gillen, who grew up in Toms River, was placed on injured reserve due to a slow-healing hamstring."
- ↑ Meek, James Gordon; and Siemaszko, Corky. "'Soupnazi' hacker Albert Gonzalez went from nerdy past to life of sex, guns and drugs", Daily News (New York), August 19, 2009. Accessed October 12, 2012. "After graduation, Gonzalez moved north to Manhattan and lived on the East Side for three months in 2000 before setting up shop in Kearny, N.J., records show. It was while living there in an anonymous garden apartment with mostly senior citizens as neighbors that Gonzalez was busted for hacking in 2003."
- ↑ Gaudin, Sharon. Government informant is called kingpin of largest "Government informant is called kingpin of largest U.S. data breaches", Computerworld, August 18, 2009. Accessed October 12, 2012.
- ↑ Koppett, Leonard. "Jersey Pitcher Recalled From Minors in May; Halicki's No-Hitter Beats Mets", The New York Times, August 25, 1975. Accessed October 12, 2012. "A native of New Jersey, where he was a star at Kearny High School, Halicki is a self-confessed Met fan who turned pro in 1972 while attending Monmouth College."
- ↑ Ed Halicki, CNN/SI. Accessed April 17, 2008.
- ↑ Bondy, Filip. "SOCCER; Harkes, Accent and All, Back for Tourney", The New York Times, June 6, 1993. Accessed August 29, 2013. "John Harkes, the pride of Kearny, N.J., rejoined the United States national soccer team this week to resuscitate his old mates in the U.S. Cup '93 opener today against Brazil in New Haven."
- ↑ Staff. "Al Hartley, 81; Illustrated 'Archie' Comic Strips", Los Angeles Times, May 29, 2003. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Al Hartley, 81, who spent nearly three decades illustrating the 'Archie' comic strips and also drew for Marvel Comics, died Tuesday in Fort Myers, Fla.... Hartley was a native of Kearny, N.J."
- ↑ HARTLEY, Fred Allan Jr., (1902 - 1969), Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 1, 2014. "library commissioner of Kearny, N.J., in 1923 and 1924; police and fire commissioner 1924-1928"
- ↑ Staff. "Fred A. Hartley, Labor Act's Co-Author, Dies; Called 1947 Law Correction of New Deal's Mistakes Jersey Republican Rebelled Against Case Nomination", The New York Times, May 12, 1969. Accessed September 1, 2014. "He was first elected as a municipal commissioner in 1924 in Kearny, N. J."
- 1 2 http://www.allmusic.com/artist/p107918 allmusic guide. "Tony Mottola... attended high school alongside ill-fated jazz saxophonist Herbie Haymer and future bandleader George Paxton..."
- ↑ La Gorce, Tammy. "Bellowing Like Iron Maiden, but Very, Very Sensitive", The New York Times, November 7, 2004. Accessed November 2, 2007. "Which is more what Mr. Way – along with his bassist and brother, Mikey; Ray Toro, a guitarist from Belleville; Frank Iero, a guitarist from Kearny; and the Chicago-area drummer Bob Bryer – is going for..."
- ↑ Wallace, William N. "ROWING; U.S. Heavyweights Win Gold at the Wire", The New York Times, September 19, 1994. Accessed October 27, 2011. "The favored United States crew, stroked by Jeff Klepacki, a Rutgers alumnus from Kearny, N.J., faltered in the final 500 meters after leading by almost a full boat length and won by six-tenths of a second over a surprising crew from the Netherlands."
- ↑ Vallance, Tom. "Obituary: Buzz Kulik", The Independent, January 29, 1999. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Born Seymour Kulik in Kearney [sic], New Jersey, in 1922, he served in the army during the Second World War, then worked in the mailroom of the large advertising agency J. Walter Thompson."
- ↑ "Joe Kyrillos (R)", The Wall Street Journal. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Joe Kyrillos was born in Kearney, N.J., and raised in Middletown, where he still resides."
- ↑ Wright, Chase. "Acclaimed organist to appear at St. Paul's on the Green", The Hour (newspaper), April 24, 2010. Accessed September 1, 2014. "A native of Kearny, N.J., Lippincott is a graduate of The Curtis Institute of Music and Westminster Choir College, where she studied under notable organist and educator Alexander McCurdy."
- ↑ Staff. "Red Bulls sign Kearny native MacDonald", MLSSoccer.com, January 23, 2010. Accessed September 1, 2014.
- ↑ Khoury, George; Nolen-Weathington, Eric (2007). Modern Masters Volume 10: Kevin Maguire. TwoMorrows Publishing. p. 6. ISBN 978-1893905665.
- ↑ Curry, Jack. 'The Goalie With No Nerves; Meola's Calm Helps Keep U.S. in World Cup Play", The New York Times, January 3, 1990. Accessed September 12, 2013. "KEARNY, N.J.— Whether reclining in a chair in his living room here or positioning himself on a soccer field in some other part of the world, Tony Meola, the goalkeeper for the United States national team, is relaxed."
- ↑ The ESPN Baseball Encyclopedia. Sterling Publishing. 2007. p. 742. ISBN 1-4027-4771-3.
- ↑ Staff. "PASSINGS; Tony Mottola; 86; Composer, Guitarist Played With Sinatra", Los Angeles Times, August 13, 2004. Accessed October 12, 2012. "Mottola, a native of Kearny, NJ, began his career in 1936 when he toured with George Hall's orchestra."
- ↑ allmusic guide. "Tony Mottola was born April 18, 1918 in Kearny, NJ. He began playing guitar at the age of nine, and attended high school alongside ill-fated jazz saxophonist Herbie Haymer and future bandleader George Paxton; after graduating, Mottola toured with George Hall's orchestra, making his recorded debut on the group's rendition of 'Shine.'"
- ↑ Shamus O'Brien, National Soccer Hall of Fame. Accessed December 13, 2007.
- ↑ Staff. "A Socialist Speaks: Interview with Greg Pason", Socialist WebZine, August 4, 2009. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Greg Pason: I was born in Kearny, NJ in 1966."
- ↑ Staff. "GEORGE E. PAXTON", The Miami Herald, April 21, 1989. Accessed May 3, 2011. "He was a native of Kearny, N.J., and learned his trade at the Julliard [sic] School of Music, where he mastered many musical instruments."
- ↑ Bill Raftery Commentator Men's College Basketball Analyst, ESPN MediaZone. Accessed November 7, 2014. "He is a native of Kearny, N.J."
- ↑ Mifflin, Lawrie. "Doing a Star Turn for the Home Team, at Last", The New York Times, August 18, 1996. Accessed February 25, 2012. "Giants Stadium is a short trip up the turnpike from Old Bridge, where Mr. Ramos lives with his wife, Amy – a former North Carolina State University soccer player like her husband – and their 16-month-old son, Alex. And it's just a few miles from where he grew up, in Harrison and Kearny, towns that have been soccer hotbeds for generations."
- ↑ Saxon, Wolfgang. "Harold Hill Smith, 84, Geneticist Whose Work Led to Cell Fusion", The New York Times, October 25, 1994. Accessed September 1, 2014. "Dr. Smith was born in Kearny, N.J. He graduated from Rutgers University and received master's and doctoral degrees in genetics at Harvard University."
- ↑ Francis, Shawn. "Welcome to New Jersey, home of the real football giants", Major League Soccer, July 21, 2011. Accessed February 25, 2011. "Among the notables who called Kearny home are Archie Stark (232 goals in 205 matches for Bethlehem Steel), John Harkes (former U.S. national-team captain), Tony Meola (former U.S. captain and keeper) Ted Gillen (former MLS and U.S. player) and Billy Gonsalves (a U.S. veteran of two World Cups)."
- ↑ Holahan, Catherine. "No Way Back;My Chemical Romance is too big for New Jersey's basements", The Record (Bergen County), October 12, 2005. Accessed August 29, 2013. "Part of the reason Toro might feel so nostalgic for Kearny and Belleville, where he and his band mates grew up, is they have been home for a total of about four weeks since releasing their major label debut, Three Cheers for Sweet Revenge, in June 2004."
- ↑ "Giant Star Compares Grid Loops", Hartford Courant, December 18, 1955. Accessed March 29, 2011. "Alex Webster returned to his Kearny, N.J. home today, but before he left the former star Montreal Alouette halfback made it clear he "wants to jump back to Canada" rather than play again for the New York Giants in 1956."
- ↑ Alex Webster career statistics, The Star-Ledger. Accessed July 7, 2011.
- ↑ Dick Weisgerber at Pro Football Reference, accessed December 28, 2010.
- ↑ Rear Admiral Kenneth G. Wiman, United States Coast Guard. Accessed May 8, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kearny, New Jersey. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Kearny. |