Monarda didyma
| Monarda didyma | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Flower being visited by a hummingbird | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Monarda |
| Species: | M. didyma |
| Binomial name | |
| Monarda didyma L. | |
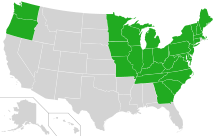 | |
| U.S. distribution of Monarda didyma | |
Monarda didyma (crimson beebalm, scarlet beebalm, scarlet monarda, Oswego tea, or bergamot) is an aromatic herb in the family Lamiaceae, native to eastern North America from Maine west to Ontario and Minnesota, and south to northern Georgia.[1][2][3] Its odor is considered similar to that of the bergamot orange (the source of bergamot oil used to flavor Earl Grey tea). The scientific name comes from Nicolas Monardes, who described the first American flora in 1569.[4]
Description
This hardy perennial plant grows to 0.7-1.5 m in height, with the stems square in cross-section. The leaves are opposite on the square stems, 6–15 cm long and 3–8 cm broad, and dark green with reddish leaf veins and a coarsely-toothed margin; they are glabrous or sparsely pubescent above, with spreading hairs below. It has ragged, bright red tubular flowers 3–4 cm long, borne on showy heads of about 30 together, with reddish bracts. It grows in dense clusters along stream banks, thickets and ditches, flowering from mid- to late summer.[5]
Cultivation and uses
Crimson beebalm is extensively grown as an ornamental plant, both within and outside its native range; it is naturalized further west in the United States and also in parts of Europe and Asia. It grows best in full sun, but tolerates light shade and will thrive in any moist, but well-drained soil. Several cultivars have been selected for different flower color, ranging from white through pink to dark red and purple.[6]
Beebalm has a long history of use as a medicinal plant by many Native Americans, including the Blackfeet. The Blackfeet Indians recognized this plant's strong antiseptic action, and used poultices of the plant for skin infections and minor wounds. An herbal tea made from the plant was also used to treat mouth and throat infections caused by dental caries and gingivitis. Beebalm is the natural source of the antiseptic thymol, the primary active ingredient in modern commercial mouthwash formulas. The Winnebago used an herbal tea made from beebalm as a general stimulant. It was also used as a carminative herb by Native Americans to treat excessive flatulence.[7][8]
References
- ↑ Kew World Checklist of Selected Plant Families
- ↑ Biota of North America Program 2013 county distribution map
- ↑ USDA Plants Profile: Monarda didyma
- ↑ Germplasm Resources Information Network: Monarda didyma
- ↑ Missouri Plants: Monarda didyma
- ↑ Blanchan, Neltje (2005). Wild Flowers Worth Knowing. Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation.
- ↑ Edible and Medicinal Plants of the West, Gregory L. Tilford, ISBN 0-87842-359-1
- ↑ Pink, A. (2004). Gardening for the Million. Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Monarda didyma. |
| Wikiversity has bloom time data for Monarda didyma on the Bloom Clock |