Physiognomy

Physiognomy (from the Gk. physis meaning "nature" and gnomon meaning "judge" or "interpreter") is the assessment of a person's character or personality from his or her outer appearance, especially the face. The term can also refer to the general appearance of a person, object, or terrain, without reference to its implied characteristics, as in the physiognomy of an individual plant (see plant life-form) or of a plant community (see vegetation).
Credence of such study has varied from time to time. The practice was well accepted by the ancient Greek philosophers, but fell into disrepute in the Middle Ages when practised by vagabonds and mountebanks. It was then revived and popularised by Johann Kaspar Lavater before falling from favour again in the late 19th century.[1] Physiognomy as understood in the past meets the contemporary definition of a pseudoscience.[2]
No clear evidence indicates physiognomy works, though recent studies have suggested that facial appearances do "contain a kernel of truth" about a person's personality.[1]
Physiognomy is also sometimes referred to as anthroposcopy, though the expression was more common in the 19th century when the word originated.[3]
Ancient physiognomy
Notions of the relationship between an individual's outward appearance and inner character are historically ancient, and occasionally appear in early Greek poetry. Siddhars from ancient India are also known to have defined samudrika lakshanam that identifies personal characteristics with body features. Chinese physiognomy or face reading (mianxiang) reaches back at least to the Northern Song period.[4] The first indications of a developed physiognomic theory appear in fifth century BC Athens, with the works of Zopyrus (who was featured in a dialogue by Phaedo of Elis), who was said to be an expert in the art. By the fourth century BC, the philosopher Aristotle made frequent reference to theory and literature concerning the relationship of appearance to character. Aristotle was apparently receptive to such an idea, as evidenced by a passage in his Prior Analytics:
It is possible to infer character from features, if it is granted that the body and the soul are changed together by the natural affections: I say "natural", for though perhaps by learning music a man has made some change in his soul, this is not one of those affections natural to us; rather I refer to passions and desires when I speak of natural emotions. If then this were granted and also that for each change there is a corresponding sign, and we could state the affection and sign proper to each kind of animal, we shall be able to infer character from features.— Prior Analytics 2.27 (Trans. A. J. Jenkinson)
The first systematic physiognomic treatise to survive to the present day is a slim volume, Physiognomonica (English: Physiognomonics), ascribed to Aristotle (but probably of his "school" rather than created by the philosopher himself). The volume is divided into two parts, conjectured to have been originally two separate works. The first section discusses arguments drawn from nature or other races, and concentrates on the concept of human behavior. The second section focuses on animal behavior, dividing the animal kingdom into male and female types. From these are deduced correspondences between human form and character.
After Aristotle, the major extant works in physiognomy are:
- Polemo of Laodicea, de Physiognomonia (second century AD), in Greek
- Adamantius the Sophist, Physiognomonica (fourth century), in Greek
- An anonymous Latin author de Phsiognomonia (about fourth century)
Ancient Greek mathematician, astronomer, and scientist Pythagoras—who some believe originated physiognomics—once rejected a prospective follower named Cylon because, to Pythagoras, his appearance indicated bad character.[5]
After inspecting Socrates, a physiognomist announced that he was given to intemperance, sensuality, and violent bursts of passion—which was so contrary to Socrates's image that his students accused the physiognomist of lying. Socrates put the issue to rest by saying that originally he was given to all these vices, but had particularly strong self-discipline.[6]
Middle Ages and Renaissance
The term was common in Middle English, often written as 'fisnamy' or 'visnomy', as in the The Tale of Beryn, a spurious addition to The Canterbury Tales: "I knowe wele by thy fisnamy, thy kynd it were to stele".
Physiognomy's validity was once widely accepted. English universities taught it until Henry VIII of England outlawed "beggars and vagabonds playing 'subtile, crafty and unlawful games such as physnomye or 'palmestrye'" in 1530 or 1531.[7][8] Around this time, scholastic leaders settled on the more erudite Greek form 'physiognomy' and began to discourage the whole concept of 'fisnamy'.
Leonardo da Vinci dismissed physiognomy in the early 16th century as "false", a chimera with "no scientific foundation".[9] Nevertheless, Leonardo believed that lines caused by facial expressions could indicate personality traits. For example, he wrote that "those who have deep and noticeable lines between the eyebrows are irascible".[9]
Modern physiognomy
The principal promoter of physiognomy in modern times was the Swiss pastor Johann Kaspar Lavater (1741–1801) who was briefly a friend of Goethe. Lavater's essays on physiognomy were first published in German in 1772 and gained great popularity. These influential essays were translated into French and English.
Browne and Physiognomy
Lavater found 'confirmation' of his ideas primarily from the English physician-philosopher Sir Thomas Browne (1605–1682), and the Italian Giambattista Della Porta (1535–1615). Browne in his Religio Medici (1643) discusses the possibility of the discernment of inner qualities from the outer appearance of the face, thus:
there is surely a Physiognomy, which those experienced and Master Mendicants observe....For there are mystically in our faces certain Characters that carry in them the motto of our Souls, wherein he that cannot read A.B.C. may read our natures. R.M. part 2:2
Late in his life, Browne re-affirmed his physiognomical beliefs, stating in Christian Morals (circa 1675):
Since the Brow speaks often true, since Eyes and Noses have Tongues, and the countenance proclaims the heart and inclinations; let observation so far instruct thee in Physiognomical lines....we often observe that Men do most act those Creatures, whose constitution, parts, and complexion do most predominate in their mixtures. This is a corner-stone in Physiognomy… there are therefore Provincial Faces, National Lips and Noses, which testify not only the Natures of those Countries, but of those which have them elsewhere.— C.M. Part 2 section 9
Sir Thomas Browne is also credited with introducing the word caricature into the English language, whence much of physiognomical belief attempted to entrench itself by illustrative means, in particular through the medium of political satire.
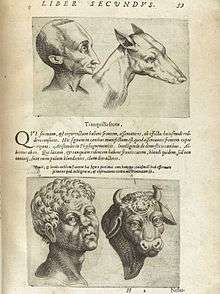
Della Porta's works are well represented in the Library of Sir Thomas Browne including Of Celestial Physiognomy, in which Porta argued that it was not the stars but a person's temperament that influences their facial appearance and character. In De humana physiognomia (1586), Porta used woodcuts of animals to illustrate human characteristics. Both Della Porta and Browne adhered to the 'doctrine of signatures'—that is, the belief that the physical structures of nature such as a plant's roots, stem, and flower, were indicative keys (or 'signatures') to their medicinal potentials.
Lavater's critics
Lavater received mixed reactions from scientists, with some accepting his research and others criticizing it.[2] For example, the harshest critic was scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg, who said pathognomy, discovering the character by observing the behaviour, was more effective. Writer Hannah More complained to Horace Walpole, "In vain do we boast (...) that philosophy had broken down all the strongholds of prejudice, ignorance, and superstition; and yet, at this very time (...) Lavater's physiognomy books sell at fifteen guineas a set."[2][10]
Period of popularity
The popularity of physiognomy grew throughout the 18th century and into the 19th century, and it was discussed seriously by academics, who saw a lot of potential in it.[2] Many European novelists used physiognomy in the descriptions of their characters.[2] notably Balzac, Chaucer[11] and portrait artists, such as Joseph Ducreux. A host of 19th-century English authors were influenced by the idea, notably evident in the detailed physiognomic descriptions of characters in the novels of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, and Charlotte Brontë.
In addition to Thomas Browne, other literary authors associated with Norwich who made physiognomical observations in their writings include the romantic novelist Amelia Opie, and the travelogue author George Borrow.
Physiognomy is a central, implicit assumption underlying the plot of Oscar Wilde's The Picture of Dorian Gray. In 19th-century American literature, physiognomy figures prominently in the short stories of Edgar Allan Poe.[12]
Phrenology, also considered a form of physiognomy, was created around 1800 by German physician Franz Joseph Gall and Johann Spurzheim, and was widely popular in the 19th century in Europe and the United States. In the U.S., physician James W. Redfield published his Comparative Physiognomy in 1852, illustrating with 330 engravings the "Resemblances between Men and Animals". He finds these in appearance and (often metaphorically) character, e.g. Germans to Lions, Negroes to Elephants and Fishes, Chinamen to Hogs, Yankees to Bears, Jews to Goats.[13]
During the late 19th century, English psychometrician Sir Francis Galton attempted to define physiognomic characteristics of health, disease, beauty, and criminality, via a method of composite photography.[14][15] Galton's process involved the photographic superimposition of two or more faces by multiple exposures. After averaging together photographs of violent criminals, he found that the composite appeared "more respectable" than any of the faces comprising it; this was likely due to the irregularities of the skin across the constituent images being averaged out in the final blend. With the advent of computer technology during the early 1990s, Galton's composite technique has been adopted and greatly improved using computer graphics software.[16]
In the late 19th century, it became associated with phrenology and consequently discredited and rejected.[1] Nevertheless, the German physiognomist Carl Huter (1861–1912) became popular in Germany with his concept of physiognomy, called "psycho-physiognomy".[17] Modern scientists now consider physiognomy a form of pseudoscience.[2]
Modern usage
In France, the concept developed in the 20th century under the name morphopsychology, developed by Louis Corman (1901–1995), a French psychiatrist who argued that the workings of vital forces within the human body resulted in different facial shapes and forms.[18] For example, full and round body shapes are considered the expression of the instinct of expansion while the hollow or flat shapes are an expression of self-preservation. The term "morphopsychology" is a translation of the French word morphopsychologie, which Louis Corman coined in 1937 when he wrote his first book on the subject, Quinze leçons de morphopsychologie (Fifteen Lessons of Morphopsychology). Corman was influenced by the French doctor Claude Sigaud (1862–1921), incorporating his idea of "dilation and retraction" into morphopsychology.

Experimental evidence has shown that people regularly judge personality characteristics from facial features, and that these judgements are shared by others; it appears, moreover, that the same judgements occur cross-culturally. Research into the validity of these judgements has not been generally supportive, however. Nevertheless, later research in the 1990s indicated that three elements of personality in particular - power, warmth and honesty - can be reliably inferred.[19] Some evidence indicates people can detect male homosexuality by looking at facial characteristics[20] or at the pattern of whorls in the scalp,[21] though subsequent research has largely refuted the findings on hair whorl patterns.[22]
Physical attractiveness (both facial and in terms of body shape) can have a significant impact on an individual's employment prospects. Obesity is detrimental, often even before a job interview.[19]
A February 2009 article in NewScientist magazine reported that physiognomy is living a small revival, with research papers trying to find links between personality traits and facial traits.[1] A study of 90 ice-hockey players found that a wider face in which the cheekbone-to-cheekbone distance was unusually large relative to the distance between brow and upper lip was linked in a statistically significant way with the number of penalty minutes a player was given for violent acts including slashing, elbowing, checking from behind and fighting.[23]
Alternative theories have also been proposed.[1] For example, the human brain tends to extrapolate emotions from facial expressions (e.g., blushing) and physiognomy, with its assumption of permanent characteristics, would only be an over-generalization of this skill.[1] Also, if one classifies a person as untrustworthy due to facial features, and treats them as such, that person eventually behaves in an untrustworthy way toward the person holding this belief (see self-fulfilling prophecy).[1]
A physiognomist named Yoshito Mizuno was employed from 1936 to 1945 by the Imperial Japanese Naval Aeronautics Department, examining candidates for the Naval Air Corps, after—to their surprise—Admiral Yamamoto's staff discovered that he could predict with over 80% accuracy the qualifications of candidates to become successful pilots.[24]
In 2011, the South Korean news agency Yonhap published a physiognomical analysis of the current leader of North Korea, Kim Jong-Un.[25]
From "physiognomy" is derived the British English slang noun "fizzog" meaning "face".
Related disciplines
- Anthropological criminology
- Anthropometry
- Characterology
- Metoposcopy
- Morphopsychology
- Palmistry
- Pathognomy
- Phrenology
- Somatotype and constitutional psychology
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 How your looks betray your personality – New Scientist (Magazine issue 2695) – 11 February 2009: Roger Highfield, Richard Wiseman, and Rob Jenkins
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Roy Porter (2003). "Marginalized practices". The Cambridge History of Science: Eighteenth-century science. The Cambridge History of Science. 4 (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 495–497. ISBN 978-0-521-57243-9.
Although we may now bracket physiognomy with Mesmerism as discredited or even laughable belief, many eighteenth-century writers referred to it in all seriousness as a useful science with a long history(...) Although many modern historians belittle physiognomy as a pseudoscience, at the end of the eighteenth century it was not merely a popular fad but also the subject of intense academic debate about the promises it held for future progress.
- ↑ "Anthroposcopy - Define Anthroposcopy at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.com.
- ↑ TJ Hinrichs; Linda L. Barnes (2013). Chinese Medicine and Healing: An Illustrated History. Belknap Press, p. 374.
- ↑ Riedweg, Christop, Pythagoras: His Life,Teaching, and Influence.
- ↑ William Godwin (1876). "Lives of the Necromancers". p. 8.
- ↑ Stimson, Frederic Jesup (1910). Popular Law-Making: A Study of the Origin, History, and Present Tendencies of Law-Making by Statute. (Reprinted 2002 by The Lawbook Exchange, Ltd.). New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 81–82, 86. ISBN 1-58477-094-5. LCCN 00-022513.
- ↑ "Popular Law-making by Frederic Jesup Stimson - Full Text Free Book (Part 2/8)". fullbooks.com.
- 1 2 Leonardo da Vinci (2002). André Chastel, ed. Leonardo on Art and the Artist. Translated from French by Ellen Callman. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 144–45. ISBN 0-486-42166-X. Unabridged republication of The Genius of Leonardo da Vinci, originally published by Orion Press, New York, 1961.
- ↑ Letter to Horace Walpole of September 1788, reproduced in W.S. Lewis, The Yale Edition of Horace Walpole's Correspondence, 48 vols. (London: oxford University Press, 1937–83), 31:279–81 (quotation at p. 280). Citation taken from Roy Porter's The Cambridge History of Science: Eighteenth-century science.
- ↑ Auguste Elfriede Christa Canitz, Gernot Rudolf Wieland, ed. (1999). "Another look at an Old 'Science': Chaucer's Pilgrims and Physiognomy". From Arabye to Engelond: medieval studies in honour of Mahmoud Manzalaoui on his 75th birthday. Actexpress Series. University of Ottawa Press. pp. 93–110. ISBN 978-0-7766-0517-3.
- ↑ Grayson, Erik (2005). "Weird Science, Weirder Unity: Phrenology and Physiognomy in Edgar Allan Poe". Mode. 1: 56–77.
- ↑ "Comparative Physiognomy or Resemblances between Men and Animals: Illustrated" by Jam. W. Redfield Full text on Google Books
- ↑ Benson, P., & Perrett, D. (1991). Computer averaging and manipulations of faces. In P. Wombell (ed.), Photovideo: Photography in the age of the computer (pp. 32–38). London: Rivers Oram Press.
- ↑ Galton, Francis (1879). "Composite Portraits, Made by Combining Those of Many Different Persons Into a Single Resultant Figure". The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland. 8: 132–44. doi:10.2307/2841021. JSTOR 2841021.
- ↑ Yamaguchi MK, Hirukawa T, Kanazawa S (1995). "Judgment of gender through facial parts". Perception. 24 (5): 563–75. doi:10.1068/p240563. PMID 7567430.
- ↑ Burguete, Maria (2008). Science Matters: Humanities as Complex Systems. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., p. 66.
- ↑ Merlini, C. (1999). "Chapter 7 - Face Profile Improvement: Psychological Aspects". Advances in Clinical Prosthodontics. Padova, Italy: Piccin Nuova Libraria, S.p.A. p. 134. ISBN 88-299-1300-6.
- 1 2 Chamorro-Premuzic, Tomas and Adrian Furnham. The Psychology of Personnel Selection. 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010. Cambridge Books Online. Web. 07 April 2016. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511819308 pages 13-14
- ↑ There's Something Queer about that Face, Scientific American
- ↑ Abrahams, Marc (14 September 2009), "Sexual swirls: how your hair can say a lot about you", The Guardian, retrieved 10 October 2013
- ↑ Rahman Q, Clarke K, Morera T (April 2009). "Hair whorl direction and sexual orientation in human males". Behavioral Neuroscience. 123 (2): 252–6. doi:10.1037/a0014816. PMID 19331448.
- ↑ Carré, Justin M.; McCormick, Cheryl M. (2008-11-22). "In your face: facial metrics predict aggressive behaviour in the laboratory and in varsity and professional hockey players". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences. 275 (1651): 2651–2656. doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0873. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2570531
 . PMID 18713717.
. PMID 18713717. - ↑ Agawa, The Reluctant Admiral, pp. 110–115.
- ↑ The Face tells all, The Center For Arms Control And Non-Proliferation
Further reading
- Claudia Schmölders, Hitler's Face: The Biography of an Image. Translated by Adrian Daub. University of Pennsylvania Press: 2006. ISBN 0-8122-3902-4.
- Liz Gerstein, About Face. SterlingHouse Publisher, Inc. ISBN 1-58501-088-X
External links
| Look up physiognomy in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Physiognomy |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Physiognomy. |
- Johann Kaspar Lavater On The Nature of Man, Which is the Foundation of the Science Which is called Physiognomy 1775
- Mocan, Naci; Tekin, Erdal (February 2010). "Ugly Criminals". Review of Economics and Statistics. 92 (1): 15–30. doi:10.1162/rest.2009.11757.
- Selected images from: Della Porta, Giambattista: De humana physiognomonia libri IIII (Vico Equense, 1586). Historical Anatomies on the Web. National Library of Medicine.
- Women's traits 'written on face' (BBC News Wednesday, 11 February 2009)
- "On Physiognomy" – An Essay by Arthur Schopenhauer
- "Composite Portraits", by Francis Galton, 1878 (as published in the Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, volume 8).
- "Enquiries into Human Faculty and its Development", book by Francis Galton, 1883.
- French Society for Morphopsychology

