Rehbar-I
|
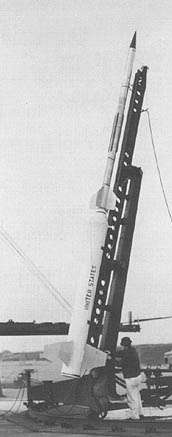
A Rehbar-I Nike-Cajun in launch position in 1962 at Sonmiani | |
| Function | Sounding Rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer |
SUPARCO NASA |
| Country of origin |
|
| Size | |
| Height | 7.70 m (130 Km) |
| Diameter | 42 cm (42.45 cm) |
| Stages | 2 |
| Associated rockets | |
| Derivatives | Dragon Rocket Series, Shahpar Rocket Series |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | Sonmiani Satellite Launch Center |
| Total launches | 4 |
| Successes | 4 |
| Failures | None |
| Partial failures | None |
| First flight |
I: 7 June 1962 IIA: 11 June 1962 III: 18 March 1964 |
| Last flight |
XX: 13 February 1969 XXIII: 7 April 1972 XXIV: 8 April 1972 |
| Notable payloads | Weather Observatory |
| Boosters (Rehbar-I) | |
| No. boosters | 2 |
| Engines | 1 Solid |
| Thrust | 246.3 kN (107,530 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 3.0 sec |
| Burn time | 2.8 seconds |
| Fuel | Solid |
| Boosters | |
| No. boosters | 1 |
| Fuel | LOX/RP-1 |
| First stage | |
| Engines | 1 RS-58-OSA |
| Thrust | 249 kN |
| Specific impulse | 3 sec |
| Burn time | 2 seconds |
| Fuel | RP-1/LOX |
| Second stage - Nike Cajun | |
| Engines | 2 RL-10A |
| Thrust | 147 kN (41,592 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 4 sec |
| Burn time | 3 seconds |
| Fuel | LH2/LOX |
Rehbar was series of sounding rocket launches into the upper atmosphere and the edge of space. Rehbar-I was the first rocket launched by Pakistan's Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO), on 7 June 1962.[1][2] Rehbar-I was a two-staged Solid fuel rocket.
Various sounding rocket models were launched by Pakistan approximately 200 times between 1962 and 1972. Twenty-four of those flights were in the Rehbar series.[3][4] The Rehbar series of flights utilized no less than three and possibly four different sounding rockets. The rockets used were Centaure,[5] Judy-Dart,[6] Nike-Cajun,[7] and according to one source Nike-Apache.[3][8] Other sounding rockets used by Pakistan were Dragon 2B,[9] Petrel,[10] and Skua.[4][11] The Rehbar Sounding Rockets are no longer in services of SUPARCO. Rehbar is an Urdu Language word which literary means "One who leads the way".
Description
In 1960, President John F. Kennedy challenged US scientists to land Americans on the moon and bring them back safely to earth, before the decade was out. NASA rose to the occasion and achieved this staggering task with the landing of Apollo 11 on the moon in 1969.
In 1961, NASA realized that the Indian Ocean region was a black hole of data relating to the wind structure of the upper atmosphere which was badly needed for NASA's satellite/Apollo programs. NASA offered all countries on the littoral of the Indian Ocean help to establish rocket ranges in order to obtain such data on condition of fully sharing it with NASA. President Ayub Khan accompanied by his Chief Scientific Advisor Prof. Abdus Salam were on a state visit in the U.S at the time. Pakistan seized the offer and Prof. Abdus Salam invited Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission's (PAEC) senior engineer Tariq Mustafa to join him in meeting with NASA officials in September 1961 to finalize the arrangement and Pakistan was the first country to take up the offer.
The Rehbar sounding rocket program was built around the U.S Nike-Cajun/Apache rockets carrying sodium vapor and experiments to measure the wind velocities and wind shears in the upper atmosphere. The 5-member team responsible for this pioneering program was led by Tariq Mustafa and included Salim Mehmud and Sikander Zaman both of whom later became Chairmen of SUPARCO.
Rehbar-1 was launched on 7 June 1962. In a period of nine months; the Pakistani team was established, their training completed in US facilities, the rocket range equipment and instrumentation procured, the scientific payloads selected, construction of the rocket range at Sonmiani completed and the first rocket successfully launched. This was a unique achievement that even surprised NASA's specialists. Pakistan was the first amongst all developing (including Brazil, China and India) and Islamic countries to carry out a scientific rocketry program.
The Rehbar-I successful launch carried a payload of 80 pounds of sodium and it streaked up about 130 km into the atmosphere. The Rehbar-I was a two-stage rocket with all solid-propellant motors. The first launch of the Rehbar-I took place in Sonmiani on 7 June 1962.
Achievements
The Rehbar rocket series was an experimental rocket program which later played an important role in Pakistan's development of a missile program. Throughout the 1960s till early 1970s, the SUPARCO launched more than 200 rockets using the different payloads of an experimental satellite. With the launching of Rehbar-1, Pakistan became the third country in Asia, first country in South Asia, and the tenth in the world to launch a vessel into outer space. It was followed by the successful launch of the Rehbar-II in 1962. The last launch of the Rehbar Rocket Program took place on 8 April 1972.
Partial Launch log
| Version | Date of Launch | Launch Location | Launch Pad | Payload | Mission Status |
| 1 Nike Cajun Rehbar-I | 7 June 1962 | SSLC, Sonmiani Beach | 1 | Rehbar-1A Experimental Technology mission, 80 kg of Sodium | Successful, developmental Flight. |
| 2 Nike Cajune Rehbar-II | 11 June 1962 | SSLC, Sonmiani Beach | 1 | Rehbar-2B RS-1 Experimental Technology mission, 130 kg | Success, Developmental Flight with a small pay load of small weather satellite. |
| 23 Nike Cajun Rehbar- XXIII | 27 March 1970 | SSLC, Sonmiani Beach | 1 | Rehbar-23 RS-1 Experimental Rocket Technology mission, 38 kg | Successful, Developmental Flight. |
| 24 Nike Cajun Rehbar- IIIV | 28 March 1971 | SSLC, Sonmiani Beach | 1 | Rehbar-24 Nike Cajune Experimental Rocket Technology mission, 141.5 kg | Success, Developmental Flight. |
See also
- Nike Cajun
- Judi-Dart
- Centaure
- Satellite Launch Vehicle
- SUPARCO
- Chronology of Pakistan's rocket tests
- Solid-fuel rocket
References
- ↑ "SIPARCO History". Pakistan Space & Upper Atmosphere Research Commission. Retrieved 2015-08-11.
- ↑ "Pakistan's first rocket soars 80 miles high". Dawn. 8 June 1962.
- 1 2 "Sonmiani". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-11.
- 1 2 "Pakistan". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-11.
- ↑ "Centaure". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Judy-Dart". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Nike Apache". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Nike Cajun". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-11.
- ↑ "Dragon 2B". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-11.
- ↑ "Petrel". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Skua". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2015-08-05.