Royal Standard of Thailand

The Royal Standard of Thailand (Thai: ธงมหาราช) is the official flag of the King of Thailand. The standard was adopted in its present form in 1910 under King Vajiravudh (Rama VI). In 1979 the designs were codified in the law; specifically in Article 2 of the Flag Act of 1979 (พระราชบัญญัติธง พ.ศ. ๒๕๒๒), which also regulated Thailand's other flags. However the first Royal Standard was created in 1855 by King Mongkut. The standard is currently used by King Maha Vajiralongkorn or Rama X, since 2016.
The Royal Standard of Thailand or the 'Thong Maharaj' consists of a bright yellow square with a red Royal Garuda at the center. The mythical Hindu and Buddhist beast: the Garuda is the national emblem of Thailand and the official symbol or 'arms' of the King of Thailand. The Garuda has been the symbol of the monarchy since the time of the Kingdom of Ayutthaya. Readopted in 1910, King Vajiravudh decided to replace all of the Royal Standards (for the King and other members of the Royal Family) to feature the Garuda.
Uses
The standards are usually hoisted at the King's palace of residence, sea or land vehicles and as an emblem on the side of the royal aircraft. The standard is also used on ceremonial occasions and official business by the King. The use of these standards are reserved exclusively to the monarchy and are not commonly seen. Unlike the King's personal flag which are commonly seen all over Thailand, usually flying alongside the National flag.
Other members of the royal family
The Law also adopted flags for other members of the Royal Family as well as the Regent of Thailand.
| Standard | Dates | Use | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1911 - | Standard of the Queen of Thailand (ธงราชินี: Thong Rajini) | Similar to the Royal Standard in the ratio of 2:3 with swallow-tail end. Currently used by Queen Mother Sirikit. |
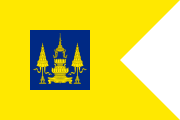 | 1979 - | Standard for Senior members of the Royal Family (usually the mother of the King, most recently used by the Princess Mother) (ธงบรมราชวงศ์: Thong Boromrajawong) | Equal in ratio to the Standard of the Queen in the ratio of 2:3 with swallow-tail end. The blue middle square depicts the Royal Crown atop two bowls on a table flanked by two five-tiered royal umbrellas. Currently not in use. |
 | 1911 - | Standard of the Crown Prince of Thailand (ธงเยาวราชฝ่ายหน้า: Thong Yaowarat Fai Na) | A dark blue square flag with the smaller Royal Standard in the center. Currently not in use. |
 | 1911 - | Standard for the Royal Consort of the Crown Prince of Thailand (ธงเยาวราชฝ่ายใน: Thong Yaowarat Fai Nai) | Dark blue rectangle with the ratio of 2:3 defaced with the Royal Standard. The flag is swallow-tail. Currently not in use. |
 | 1911 - | Standard for the King's sons and brothers (ธงราชวงศ์ฝ่ายหน้า: Thong Rajawong Fai Na) | Dark blue square defaced with yellow circle. The circle features the red Garuda. Currently not in use. |
 | 1911 - | Standard for the King's daughters and sisters (ธงราชวงศ์ฝ่ายใน: Thong Rajawong Fai Nai) | Similar to the Standard for the male royalty in the ratio of 2:3 with swallow-tail end. Currently used by Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn and other princesses. |
 | 1936 - | Standard for the Regent of Thailand (ธงผู้สำเร็จราชการแทนพระองค์: Thong Phu Samret Rajakarnthan Phra Ong) | A white plain square flag with the Garuda on top of a shield depicting the National Flag in the center. |
 | .jpg) |
| The royal standard at King Bhumibol Adulyadej's car in his 83rd birthday anniversary ceremony, December 5, 2010. | The Standard for the Princess of Thailand was carried by royal guards during the funeral procession of Princess Galyani Vadhana, the elder sister of King Bhumibol Adulyadej (Rama IX), in 2008. |
Historical standards
Fourth reign
King Mongkut (Rama IV) felt the need to create a Royal standard to distinguish his royal barge from other vessels during his many travels around the Kingdom and to fly above the Grand Palace in Bangkok when he is in residence. In 1855 a Royal Standard was created called the 'Thong Chom Klao' (ธงจอมเกล้า).
The standard featured a red rectangular flag with a smaller dark blue rectangle inside. Within the dark blue rectangle depicts the Great Crown of Victory on a stand flanked by two seven-tiered Royal Umbrellas. The Crown itself is derived from the King's personal seal, which in itself is a canting of both his given name and ceremonial name: Mongkut (มงกุฎ) and Chom Klao (จอมเกล้า) both meaning 'Crown' in Thai. The crown and the umbrellas are situated on a golden platform.
However the sight of an empty flagpole when the King was not in residence at the palace was considered inauspicious, therefore a second flag was ordered to be hoisted during the King's absence. This Flag is called the 'Thong Airapot' (ธงไอยราพต), the rectangular red flag depicts a mythical three-headed white elephant (Airavata) in full regalia standing on a golden base with a golden pavilion on its back. Within the pavilion is the Thai symbol for Aum or Unalom. The elephant is then flanked on two sides are two seven-tiered Royal Umbrellas.
.svg.png) 'Thong Chom Klao' (ธงจอมเกล้า), Standard of King Mongkut |
_(Rama_IV).svg.png) 'Thong Airapot' (ธงไอยราพต), 'Absence' standard (used when the King is not in residence). |
Fifth reign
In 1891, King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) decided to promulgate a new law to reform the Royal Standard and create for the first time ranks flags for members of the Royal Family. The Royal Standard was changed by adding the new Arms of Dominion, which is a golden shield divided into three parts. The first in yellow depicts a three-headed mythical elephant representing Siam, the second quarter in red depicts a single white elephant for Laos (Lan Xang) and the third quarter in pink depicts two crossed Krisses for the Malay suzerainty (Siam was later forced to relinquish these territories by the French and British, respectively). Inside the crown the symbol for the Chakri Dynasty is added; it depicts an intertwined Chakra and Trisula. The flag ratio is 5:6 The name of the Royal Standard was then changed to 'Thong Boromrajathawat Maha Siaminthra' (ธงบรมราชธวัชมหาสยามินทร์), A few years later in 1897 the name was permanently changed to 'Thong Maharaj'.
The King retained the second colours by replacing the Unalom with his own Royal cypher (จ ป ร, derive from "จุฬาลงกรณ์ ปรมราชาธิราช": Chulalongkorn Paramarajadhiraja; equivalent to Chulalongkorn Rex), which in turn is topped by the Royal Coronet or Phra Kiao (พระเกี้ยว). The name of this flag was also changed to the 'Thong Chudhathipathai' (ธงจุฑาธิปไตย).
.svg.png) 'Thong Boromrajathawat Maha Siaminthra' (ธงบรมราชธวัชมหาสยามินทร์), the King;'s standard in 1891-1897. |
.svg.png) 'Thong Maharaj' (ธงมหาราช), the King's standard in 1897-1910. |
_(Rama_V).svg.png) 'Thong Chudhathipathai' (ธงจุฑาธิปไตย), 'Absence' standard, with the Royal Cypher of King Rama V |
Other members of the royal family
| Standard | Dates | Use | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1891–1897 | Standard for other members of the Chakri Dynasty (ธงเยาวราชธวัช: Thong Yaowaratthawat) | A red flag with the Royal Shield with the Chakra and Trisula above. |
 | 1897–1910 | Standard of the Queen of Siam | Similar to the Royal Standard in the ratio of 2:3 with swallow-tail end. |
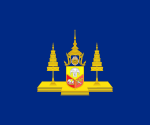 | 1897–1910 | Standard of the Crown Prince of Siam | A dark blue flag with the Royal Arms with the Crown, Chakra and Trisula in the center on a platform with two Royal Five-tiered Umbrellas to the side. |
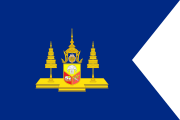 | 1897–1910 | Standard for the Consort of the Crown Prince of Siam | Dark blue rectangle with the ratio of 2:3. Similar to the Crown Prince's Standard, the flag is however swallow-tail. |
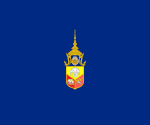 | 1897–1910 | Standard for the King's sons and brothers | Dark blue square with the Royal Arms with the Crown, Chakra and Trisula in the center. |
 | 1899–1910 | Standard for the King's daughters and sisters | Similar to the Standard for the male royalty in the ratio of 2:3 with swallow-tail end. |
Sixth reign
In 1910 King Vajiravudh replaced the Royal Standard and Royal rank flags to mirror the change of the National emblem from the Coat of Arms of Siam to the Royal Garuda. These flags are retained and in use to this day. Six years later he also redesigned the national flag and naval ensigns.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Royal standards of Thailand. |
| Thai Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Royal Flags of Thailand - Personal flags of the various members of the Thai Royal Family
- Emblem of Thailand
- Monarchy of Thailand
- Royal Standard
- List of Thai flags
References
- Flag Act, Article 2 (Thai)
- Royal Standard of Thailand, FOTW page
- Historical Royal Standards, FOTW page
External links
- Siam Flag museum (Thai)
- www.kodmhai.com- Flag Act 1979 (Thai)
- FOTW page
