Saharan languages
| Saharan | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: | Chad, Nigeria, Niger, Sudan, Cameroon |
| Linguistic classification: |
|
| Subdivisions: |
|
| Glottolog: | saha1256[1] |
|
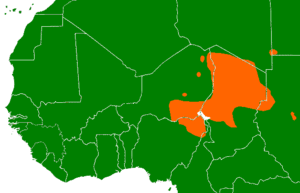
Range of the Saharan languages | |
The Saharan languages are a small family of languages spoken across parts of the eastern Sahara, extending from northwestern Darfur to southern Libya, north and central Chad, eastern Niger and northeastern Nigeria. Noted Saharan languages include Kanuri (4 million speakers, around Lake Chad in Chad, Nigeria, Niger, and Cameroon), Daza (330,000 speakers, Chad), Teda (49,000 speakers, northern Chad), and Zaghawa (170,000 speakers, eastern Chad and Darfur). They are a part of the proposed Nilo-Saharan family.
Internal classification
| Saharan |
| ||||||||||||
| |
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Saharan". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- 1 2 http://www.rogerblench.info/Language/Nilo-Saharan/General/Saharan%20Songhay%20branch.pdf
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/17/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.