Ultimaker
 | |
| Industry | 3D printing |
|---|---|
| Founded | 2011 |
| Founder | Martijn Elserman, Erik de Bruijn and Siert Wijnia |
| Headquarters | Geldermalsen, Netherlands |
| Products | Ultimaker Original, Ultimaker Original+, Ultimaker 2, Ultimaker 2+, Ultimaker 2 Go, Ultimaker 2 Extended, Ultimaker 2 Extended+ |
| Website |
www |
Ultimaker is a 3D printer manufacturer. Their product line includes the Ultimaker 2 family, ultimaker 3 family and the Ultimaker Original. The company started out as an open-source printer company.
History
Ultimaker BV is a Dutch 3D printer company which was founded in 2011 by Martijn Elserman, Erik de Bruijn, and Siert Wijnia.[1] Ultimaker started selling their products in May 2011. The company's foundation was laid at ProtoSpace Utrecht where Siert Wijnia organised two workshops to build the RepRap Darwin 3D printer. Erik de Bruin and Martijn Elserman assisted at those workshops. Frustration from their inability to get the Darwin design to work led to the inspiration to create their own design. Instead of sticking to the RepRap principle that their printer should be able to print its own parts, they designed their printer to be built mostly of lasercut plywood parts, that could be produced orders of magnitude faster than printed parts at the time. Their first prototypes bore the name "Ultimaker protobox" but newer prototypes were just titled "Ultimaker". Two Beta-workshops were organised at ProtoSpace Utrecht starting in September and December 2010, each consisting of 10 Monday evenings. In March 2011, Ultimaker ltd. released their first complete product, the "Ultimaker" (renamed in 2013 to "Ultimaker Original") under a Creative Commons BY-NC license.
Their first software ran under a modified version of Replicator-G. They changed this later to Cura due to the fact that more and more users started using this software in favor of Replicator-G, which was originally produced with Makerbot in mind.[2] When the lead developer for Cura started working for Ultimaker, Cura became the lead software product for Ultimaker.[3]
Products
Contrary to the RepRap project founded By Adrian Bowyer, Ultimaker is not focused on an end-goal of self-replication. Their product is designed to make high quality prints. Ultimaker currently sells the Ultimaker Original family as a DIY kit and the Ultimaker 2 family pre-assembled.
Ultimaker's 3D printers currently print using acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polylactic acid (PLA). Ultimaker's printers also can print with other thermoplastics such as Nylon and Acrylic (PMMA), but this is not recommended.
Ultimaker Original
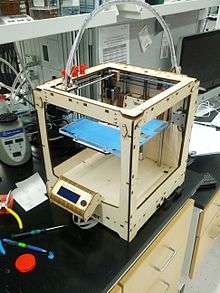
Ultimaker Original is a predecessor of Ultimaker 2 and was released a few months after the company was founded. Ultimaker Original can be modified to the user preference. In 2012, the Ultimaker Original was awarded Fastest and Most Accurate 3D printer available by MAKE Magazine.[4]
Ultimaker 2
Ultimaker 2 is the successor to the Ultimaker Original and was released in September 2013. MAKE magazine classified the Ultimaker 2 as the "best open-architecture 3D printer of 2014" and named it runner-up in the category "Prosumer FFF".[5][6]
Ultimaker 2 Go
The Ultimaker 2 Go is a compact and portable design that comes with a travel case for easy transportation. Released date April 2015.[7] This printer along with the Ultimaker 2 Extended are the newest additions to the Ultimaker family of printers. Recently awarded 2nd place in the Most Portable category in MAKE Magazine's Digital Fabrication Shootout[8] 2015.
Ultimaker 2 Extended
Released date April 2015.[7] Awarded 1st place in the Best Large Format category in MAKE Magazine's Digital Fabrication Shootout[8] 2015. Rated as a top 5 3D printer by 3DForged.com.[9]
Specifications
| Variant | Ultimaker Original | Ultimaker 2 | Ultimaker 2 Go | Ultimaker 2 Extended | Ultimaker 3 | Ultimaker 3 Extended |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release Date | March 2011 | September 2013 | April 2015 | April 2015 | October 2016 | October 2016 |
| Build volume | 21 cm × 21 cm × 20.5 cm | 23 cm × 22.5 cm × 20.5 cm | 12 cm × 12 cm × 11.5 cm | 22.3 cm × 22.3 cm × 30.5 cm | 21.5 cm x 21.5 cm x 20.0 cm | 21.5 cm x 21.5 cm x 30.0 cm |
| Dual extrusion build volume | ? | 19.7 cm x 21.5 cm x 20.0 cm | 19.7 cm x 21.5 cm x 30.0 cm | |||
| Layer Resolution | up to 20 microns | |||||
| Print Speed | 30 mm - 300 mm/s | |||||
| Travel Speed | 30 mm - 350 mm/s | |||||
| Filament Diameter | 2.85 mm recommended | |||||
| Nozzle Diameter | 0.4 mm swappable | 0.4 mm print core | ||||
| Operating Nozzle Temperature | 180°C - 260°C | 180°C - 280°C | ||||
| Operating Heated Bed Temperature | - | 50°C - 100°C | - | 50°C - 100°C | 20°C - 100°C | |
| Frame Dimensions | 35.7 cm × 34.2 cm × 38.8 cm | 35.7 cm × 34.2 cm × 38.8 cm | 25.8 cm × 25.0 cm × 28.75 cm | 49.3 cm × 34.2 cm × 68.8 cm | 34.2 cm x 38.0 cm x 38.9 cm | 34.2 cm x 38.0 cm x 48.9 cm |
| Printer Technology | Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) | |||||
| Software | Cura (Supplied) | |||||
See also
References
- ↑ About us Ultimaker
- ↑ http://replicat.org
- ↑ Developed software Cura
- ↑ magazine, Make (2012). MAKE : ultimate guide to 3D printing (MAKE special issue ed.). Sebastopol, CALIF: O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-1449357375.
- ↑ http://makezine.com/magazine/guide-to-3d-printing-2014/3d-printer-overview-how-they-compare/
- ↑ "Ultimaker komt met nieuwe 3d-printer". Tweakers (in Dutch). Retrieved 2015-10-12.
- 1 2 "Ultimaker is proud to reveal the Ultimaker 2 Go and Ultimaker 2 Extended at CES Las Vegas | Ultimaker". Ultimaker.com. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- 1 2 "The Winners from Make:'s Digital Fabrication Shootout | Make:". Make: DIY Projects, How-Tos, Electronics, Crafts and Ideas for Makers. Retrieved 2015-11-05.
- ↑ "The Best 3D Printers for 2016 | 3D Forged". 3D Forged. Retrieved 2016-02-17.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ultimaker. |