Wormhole switching
Wormhole flow control, also called wormhole switching or wormhole routing is a system of simple flow control in computer networking based on known fixed links. It is a subset of flow control methods called Flit-Buffer Flow Control.[1]:Chapter 13.2.1
Switching is a more appropriate term than routing, as "routing" defines the route or path taken to reach the destination.[2] The wormhole technique does not dictate the route to the destination but decides when the packet moves forward from a router.
Mechanism principle
In the wormhole flow control, each packet is broken into small pieces called FLITs (flow control digits).
Commonly, the first flits, called the header flits, holds information about this packet's route (for example, the destination address) and sets up the routing behavior for all subsequent flits associated with the packet. The header flits are followed by zero or more body flits which contain the actual payload of data. Some final flits, called the tail flits, perform some bookkeeping to close the connection between the two nodes.
In wormhole switching, each buffer is either idle, or allocated to one packet. An header flit can be forwarded to a buffer if this buffer is idle. This allocates the buffer to the packet. A body or trailer flit can be forwarded to a buffer if this buffer is allocated to its packet and is not full. The last flit frees the buffer. If the header flit is blocked in the network, the buffer fills up, and once full, no more flit can be send: this effect called "back-pressure" and can be propagated back to the source.
The name "wormhole" plays on the way packets are sent over the links: the address is so short that it can be translated before the message itself arrives. This allows the router to quickly set up the routing of the actual message and then "bow out" of the rest of the conversation. Since a packet is transmitted flit by flit, it may occupy several flit buffers along its path, creating a worm-like image.
This behaviour is quite similar to cut-through switching,[3] commonly called "virtual cut-through," the major difference being that cut-through flow control allocates buffers and channel bandwidth on a packet level, while wormhole flow control does this on the flit level.
In case of circular dependency, this back-pressure can lead to deadlock.
In most respects, wormhole is very similar to ATM or MPLS forwarding, with the exception that the cell does not have to be queued.
One thing special about wormhole flow control is the implementation of virtual channels:
A virtual channel holds the state needed to coordinate the handling of the flits of a packet over a channel. At a minimum, this state identifies the output channel of the current node for the next hop of the route and the state of the virtual channel (idle, waiting for resources, or active). The virtual channel may also include pointers to the flits of the packet that are buffered on the current node and the number of flit buffers available on the next node.[1]:237
Example
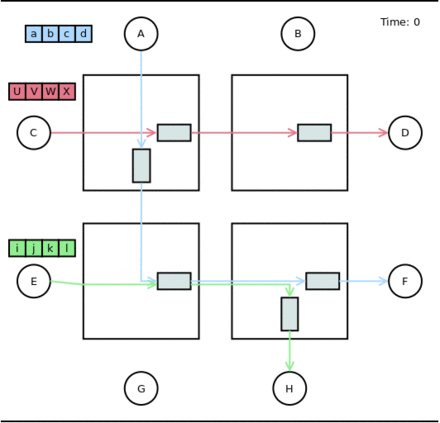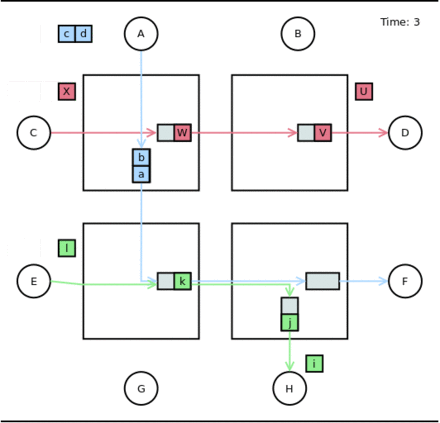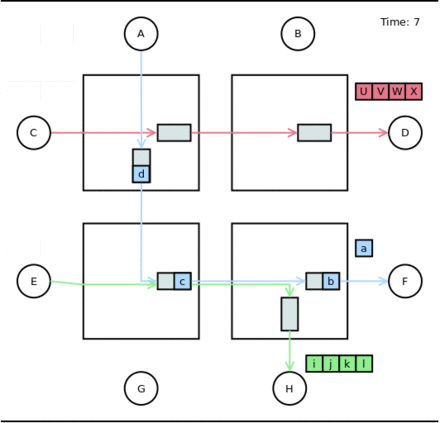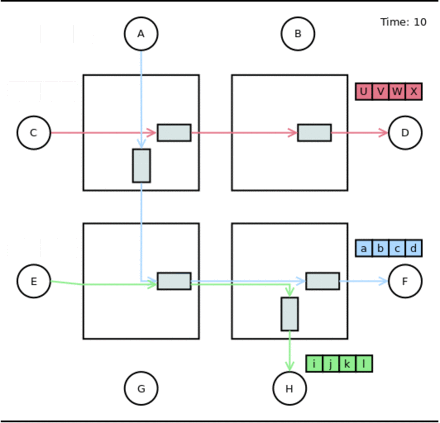
Consider the 2x2 network of the figure on the right, with 3 packets to be send: a pink one, made of 4 flits, 'UVWX', from C to D; a blue one, made of 4 flits 'abcd', from A to F; and a green one, made of 4 flits 'ijkl', from E to H. We assume that the routing has been computed, as drawn, and implies a conflict of a buffer, in the bottom-left router. The throughput is of one flit per time unit.
First, consider the pink flow: at time 1, the flit 'U' is sent to the first buffer; at time 2, the flit 'U' goes through the next buffer (assuming the computation of the route takes no time), and the flit 'V' is sent to the first buffer, and so on.
The blue and green flows requires a step by step presentation:
- Time 1: Both the blue and green flows send theirs first flits, 'i' and 'a'.
- Time 2: The flit 'i' can go on into the next buffer. But a buffer is dedicated to a packet from its first to its last flit, and so, the 'a' flit can not be forwarded. This is the start of a back-pressure effect. The 'j' flit can replace the 'i' flit. The 'b' flit can be sent.
- Time 3: The green packet goes on. The 'c' flit can not be forwarded (the buffer is empty): this back-pressure effect reaches the packet source.
- Time 4: As in time 3
- Time 5: The green packet no longer uses the left-down buffer. The blue packet is unblocked and can be forwarded (assuming that the 'unblocked' information can be forwarded in null time)
- Time 6-10: The blue packet goes through the network.
Advantages
- Wormhole flow control makes more efficient use of buffers than cut-through. Where cut-through requires many packets worth of buffer space, the wormhole method needs very few flit buffers (comparatively).
- An entire packet need not be buffered to move on to the next node, decreasing network latency compared to store-and-forward switching.
- Bandwidth and channel allocation are decoupled
Usage
Wormhole techniques are primarily used in multiprocessor systems, notably hypercubes. In a hypercube computer each CPU is attached to several neighbours in a fixed pattern, which reduces the number of hops from one CPU to another. Each CPU is given a number (typically only 8-bit to 16-bit), which is its network address, and packets to CPUs are sent with this number in the header. When the packet arrives at an intermediate router for forwarding, the router examines the header (very quickly), sets up a circuit to the next router, and then bows out of the conversation. This reduces latency (delay) noticeably compared to store-and-forward switching that waits for the whole packet before forwarding. More recently, wormhole flow control has found its way to applications in Network On Chip systems (NOCs), of which multi-core processors are one flavor. Here, many processor cores, or on a lower level, even functional units can be connected in a network on a single IC package. As wire delays and many other non-scalable constraints on linked processing elements become the dominating factor for design, engineers are looking to simplify organized interconnection networks, in which flow control methods play an important role.
The IEEE 1355 and SpaceWire technologies use wormhole.
Virtual channels
An extension of worm-hole flow control is Virtual-Channel flow control, where several virtual channels may be multiplexed across one physical channel. Each unidirectional virtual channel is realized by an independently managed pair of (flit) buffers. Different packets can then share the physical channel on a flit-by-flit basis. Virtual channels were originally introduced to solve the deadlock avoidance problem, but they can be also used to reduce wormhole blocking, improving network latency and throughput. Wormhole blocking occurs when a packet acquires a channel, thus preventing other packets from using the channel and forcing them to stall. Suppose a packet P0 has acquired the channel between two routers. In absence of virtual channels, a packet P1 arriving later would be blocked until the transmission of P0 has been completed. If virtual channels are implemented, the following improvements are possible:
- Upon arrival of P1, the physical channel can be multiplexed between them on a flit-by-flit bases, so that both packets proceed with half speed (depending on the arbitration scheme).
- If P0 is a full-length packet whereas P1 is only a small control packet of size of few flits, then this scheme allows P1 pass through both routers while P0 is slowed down for a short time corresponding to the transmission of few packets. This reduces latency for P1.
- Assume that P0 is temporarily blocked downstream from the current router. Throughput is increased by allowing P1 to proceed at the full speed of the physical channel. Without virtual channels, P0 would be occupying the channel, without actually using the available bandwidth (since it is being blocked).[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 William James Dally; Brian Towles (2004). "13.2.1". Principles and Practices of Interconnection Networks. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc. ISBN 978-0-12-200751-4.
- ↑ John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson (2006). "Appendix E.5". Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach (Fourth ed.). Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc. ISBN 978-0-12-370490-0.
- ↑ Stefan Haas. "The IEEE 1355 Standard: Developments, Performance and Application in High Energy Physics". 1998. p. 59.
- ↑ http://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~tvrdik/8/html/Section8.html