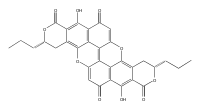
Xylindein
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
8,16-Dihydroxy-3,11-dipropyl-3,4,11,12-tetrahydro-pyrano[4,3-h]pyrano[4',3';5,6]xantheno[2,1,9,8-klmna]xanthene-1,7,9,15-tetraone | |
| Other names
Xylindene (3S,11S)-3,4,11,12-Tetrahydro-8,16-dihydroxy-3,11-dipropyl-1H,7H-dipyrano[4,3-a:4',3'-j]-peri-xanthenoxanthene-1,7,9,15-tetrone peri-xanthenoxanthene-2,8-dicarboxy-lic acid 4,10-dihydro-3,9-dihydroxy-1,7-bis(2 S-hydroxy-pentyl)-4,10-dioxo-di δ-lactone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3779-11-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 23078574 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H24O10 | |
| Molar mass | 568.53 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Xylindein is a quinone pigment, a dimeric naphthoquinone derivative. It is produced by fungi from genus Chlorociboria. This pigment causes green staining of wood infected by the fungi.
Etymology
This pigment was firstly extracted in 1868 by Paul Thénard from wood and resembled indigo, so he called it xylindéine. Combination of xyl- (wood) and indé (indigo) + -ine.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Xylindein at Merriam-Webster dictionary
- ↑ Thenard, Paul; Alphonse Rommier (1868). "Sur un nouvelle matière colorante appelée xylindeine et extraite de certains bois morts". Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l’Académie des sciences (in French). Paris. 66: 108–109. ISSN 0001-4036.
- Xylindein on Chemicalize.org
- Xylindein on eBuyChem.com
- Xylindein on ChemicalBook.com
- Saikawa, Yoko; Watanabe, Takashi; Hashimoto, Kimiko; Nakata, Masaya (October 2000). "Absolute configuration and tautomeric structure of xylindein, a blue-green pigment of Chlorociboria species". Phytochemistry. Elsevier. 55 (3): 237–240. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)00282-X.
- Donner, Christopher; Cuzzupe, Anthony; Falzon, Cheryl; Gill, Melvyn (April 2012). "Investigations towards the synthesis of xylindein, a blue-green pigment from the fungus Chlorociboria aeruginosa". Tetrahedron. Elsevier. 68 (13): 2799–2805. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2012.02.009.
- Robinson, Sara; Tudor, Daniela; Snider, Hilary; Cooper, Paul (March 2012). "Stimulating growth and xylindein production of Chlorociboria aeruginascens in agar-based systems". AMB Express. Springer. 2: 15. doi:10.1186/2191-0855-2-15.
External links
-
 Media related to Xylindein at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Xylindein at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.