Alternatives to animal testing
Alternatives to animal testing are the development and implementation of test methods that avoid the use of live animals.
There is widespread agreement that a reduction in the number of animals used and the refinement of testing to reduce suffering should be important goals for the industries involved.[1] Two major alternatives to in vivo animal testing are in vitro cell culture techniques and in silico computer simulation. However, some claim they are not true alternatives because simulations use data from prior animal experiments and cell cultures often require animal derived products, such as serum or cells. Others say that they cannot replace animals completely as they are unlikely to ever provide enough information about the complex interactions of living systems.[2] Other alternatives include the use of humans for skin irritancy tests and donated human blood for pyrogenicity studies. Another alternative is so-called microdosing, in which the basic behaviour of drugs is assessed using human volunteers receiving doses well below those expected to produce whole-body effects.[3] While microdosing produces important information about pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics it does not reveal information about toxicity or toxicology.[4] Furthermore, it was noted by the Fund for the Replacement of Animals in Medical Experiments that despite the use of microdosing, "animal studies will still be required".[5]
Guiding principles for more ethical use of animals in testing are the Three Rs (3Rs) first described by Russell and Burch in 1959.[6] These principles are now followed in many testing establishments worldwide.
- Replacement refers to the preferred use of non-animal methods over animal methods whenever it is possible to achieve the same scientific aim.
- Reduction refers to methods that enable researchers to obtain comparable levels of information from fewer animals, or to obtain more information from the same number of animals.
- Refinement refers to methods that alleviate or minimize potential pain, suffering, or distress, and enhance animal welfare for the animals used.
Types
Cell culture and tissue engineering
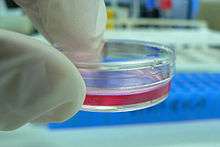
Cell culture can be an alternative to animal use in some cases. For example, cultured cells have been developed to create monoclonal antibodies; prior to this, production required animals to undergo a procedure likely to cause pain and distress.[7] However, even though cell or tissue culture methods may reduce the number of experiments performed on intact animals, the maintenance of cells in culture normally requires the use of animal-derived serum. Although exact figures are difficult to obtain, some have estimated that one million fetal cows are sacrificed each year to obtain the world's supply of fetal bovine serum, used to grow cultured cells.[8]
Skin corrosion and skin irritation
Skin irritation and skin corrosion refer to localized toxic effects resulting from a topical exposure of the skin to a substance. Human skin equivalent tests can be used to replace animal-based corrosive and irritative studies. EpiDerm from Mattek[9] and EpiSkin[10] and SkinEthic RHE model[11] are derived from human skin cells which have been cultured to produce a model of human skin. These methods are currently accepted replacements in Canada and the European Union (EU).[12] In August 2010, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) published the Test Guideline 439 which describes the new procedure for in vitro hazard identification of irritant chemicals.[13]
Another synthetic replacement uses a protein membrane to simulate a skin barrier and is approved as a partial replacement by the US Department of Transportation and European Union.[14]
Skin absorption
Several tissue culture methods which measure the rate of chemical absorption by the skin have been approved by the OECD.
Phototoxicity
Phototoxicity is a rash, swelling or inflammation, like a severe sunburn, caused by exposure to light following exposure to a chemical. The 3T3 Neutral Red Uptake (NRU) Phototoxicity Test, approved by the OECD, detects the viability of 3T3 cells after exposure to a chemical in the presence or absence of light.[15] Although originally derived from a mouse embryo, the 3T3 cell line was developed in 1962.
Human-based
Skin irritation
A skinpatch test has been designed and is used in Canada to measure development of rashes, inflammation, swelling or abnormal tissue growth on human volunteers. Unlike corrosives, substances defined as irritants cause only reversible skin damage.
Another approach has been the development of test methods that use cultured human cells. Human epidermal keratinocytes have been cultured to mimic the human epidermis, and are used to measure skin irritation and dermal corrosion. This method has been accepted by the EU and is intended to replace the Draize rabbit skin irritation test.[16]
Pyrogenicity
Pyrogens are most often pharmaceutical products or intravenous drugs that may cause inflammation or fever when they interact with immune system cells. This interaction can be quickly and accurately tested in vitro.
Modular immune in vitro construct
The modular immune in vitro construct (MIMIC) uses human cells to create a model of the human immune system on which the efficacy of new vaccines and other compounds may be tested, replacing some steps of the vaccine development process that would otherwise be performed on animals. This process is faster and more flexible than previous methods but critics worry that it may be too simple to be useful on a large scale.[17]
Computer simulation

Examples of computer simulations available include models of asthma,[18] though potential new medicines identified using these techniques are currently still required to be verified in animal and human tests before licensing.
Computer operated mannequins, also known as crash test dummies, complete with internal sensors and video, have replaced live animal trauma testing for automobile crash testing. The first of these was "Sierra Sam" built in 1949 by Alderson Research Labs (ARL) Sierra Engineering. These dummies continue to be refined.[19] Prior to this, live pigs were used as test subjects for crash testing.[20]
Other non-animal simulators have been developed for military use to mimic battlefield induced traumas. TraumaMan[21] and the Combat Trauma Patient Simulator can be used to simulate hemorrhaging, fractures, amputations and burns. Previously, animals were intentionally subjected to various traumas to provide military training. TraumaMan is also now used for training medical students.[22]
Computer models have been constructed to model human metabolism, to study plaque build-up and cardiovascular risk, and to evaluate toxicity of drugs, tasks for which animals are also used.[23] In 2007, US researchers using the world's fastest computer at the time, BlueGene L, modeled half a mouse's brain for just 10 seconds. However, due to limitations in computing power, the simulation could only be run at 1/10th the speed of an actual mouse brain.[24] Although this was an advance in science, its representative power as a model was limited and the researchers were quoted as saying that "although the simulation shared some similarities with a mouse's mental make-up in terms of nerves and connections it lacked the structures seen in real mice brains."[24]
For pharmacology and toxicology, physiologically based pharmacokinetic models are much used for in vitro to in vivo extrapolation of alternative testing.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is able to demonstrate to researchers both how drugs are metabolized by use of microdosing, and the detailed condition of organ tissue.[25]
Microfluidic Chip
Microfluidic chip, which is just 2 cm wide, have engraved into a series of small chambers, each containing a sample of tissue from different parts of the body. A substitute of blood flows through micro-channels where the compartments of chips linked by. When injected, test drug circulates around the device, mimicking what goes in the body on a micro scale. Sensors in the chip transfer information for computer analysis.[26]
The choice of the material for chips is still challenging. One of the major materials that can be possibly used in chips is known as Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). However, due to lack of facilities for mass production and drug clearance issue, the use of PDMS is still being speculated, even though it has great properties as microfluidic chip. Also, the biological process involved in proliferation and metabolism might be modified when compared to larger scales, because the materials have micro-structured scales comparable in size to cells.[27]
Fungal model for mammalian drug metabolism
Fungi like Cunninghamella elegans can be used as a microbial model of mammalian drug metabolism[28][29][30][31] thereby reducing the need for laboratory animals.[32]
Future alternatives
Organs on a chip
The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering (US) intends to develop in-vitro organs for drug screening and thereby eliminate the use of animals for this type of testing. One model is the "lung-on-a-chip".[33] This combines microfabrication techniques with modern tissue engineering and mimics the complicated mechanical and biochemical behaviours of a human lung.
Human toxome
Toxicity testing typically involves studying adverse health outcomes in animals subjected to high doses of toxicants with subsequent extrapolation to expected human responses at lower doses. The system relies on the use of a 40+year-old patchwork of animal tests that are expensive (costing more than $3B per year), time-consuming, low-throughput and often provide results of limited predictive value for human health effects. The low-throughput of current toxicity testing approaches (which are largely the same for industrial chemicals, pesticides and drugs) has led to a backlog of more than 80,000 chemicals to which humans are potentially exposed whose potential toxicity remains largely unknown. In 2007, the National Research Council (NRC) released the report "Toxicity Testing in the 21st Century: A Vision and a Strategy",[34] that charted a long-range strategic plan for transforming toxicity testing. The major components of the plan include the use of predictive, high-throughput cell-based assays (of human origin) to evaluate perturbations in key toxicity pathways, and to conduct targeted testing against those pathways. This approach will greatly accelerate our ability to test the vast "storehouses" of chemical compounds using a rational, risk-based approach to chemical prioritization, and provide test results that are hopefully far more predictive of human toxicity than current methods. Although a number of toxicity pathways have already been identified, most are only partially known and no common annotation exists. Mapping the entirety of these pathways (i.e. the Human Toxome[35] ) will be a large-scale effort, perhaps on the order of the Human Genome Project.
Research initiatives
SEURAT-1
SEURAT-1 is a long term strategic target for "Safety Evaluation Ultimately Replacing Animal Testing".[36] It is called "SEURAT-1" to indicate that more steps have to be taken before the final goal will be reached. SEURAT-1 will develop knowledge and technology building blocks required for the development of solutions for the replacement of current repeated dose systemic toxicity testing in vivo used for the assessment of human safety. SEURAT-1 is composed of six research projects, which started on January 1, 2011 and will run for five years. These projects will closely cooperate with a common goal and combine the research efforts of over 70 European universities, public research institutes and companies. The collaboration between these six research projects, the dissemination of results, the cooperation with other international research teams, and the continuous updating on research priorities will be facilitated by the coordination and support action project "COACH".
SEURAT-1 was developed through the Framework Programme 7 (FP7) research initiative and was created through a call for proposals by the European Commission (EC) that was published in June 2009. The Cosmetics Europe industry offered to match the EC's funds to make a total of EUR 50 million available to try to fill current gaps in scientific knowledge and accelerate the development of non-animal test methods.
Euroecotox
Laboratory animals are not restricted to rats, mice, dogs, and rabbits, but also include fish, frogs and birds. Research into alternatives to replace these species is often neglected, although fish are the third most widely used laboratory animal used for scientific purposes in the EU.[37] This is also the field where until now only two alternative tests exist worldwide: One guideline, OECD TG 236,[38] and one guidance (OECD series on testing and assessment 126)[39] are so far available.
Euroecotox[40] is a European network for alternative testing strategies in ecotoxicology. It was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission Environment Programme. The main objectives of the Euroecotox network are: To contribute to the advancement of alternative methods of ecotoxicity testing in Europe. To promote the validation and regulatory acceptance of new alternative ecotoxicity methods. To facilitate the networking of research groups working in the field of alternative ecotoxicology. To provide a gathering point for all stakeholders involved in the development, validation, regulatory acceptance and final use of alternative ecotoxicity testing strategies. To act as the one voice for alternative ecotoxicity testing in Europe.
AXLR8
AXLR8 is a coordination action funded by the European Commission Directorate General for Research & Innovation under the 7 Framework Programme 7 (FP7) Health Theme. The European Commission is currently funding a number of research consortia to develop new 3Rs (replacement, reduction and refinement) test methods and strategies as potential alternatives to the use of animals in safety testing. Monitoring of these 3Rs activities at pan-European, national, and international levels is vital to facilitate swift progress. AXLR8 aims to fulfill this growing need by providing a focal point for dialogue and collaboration.[41] Humane Society International is part of the consortium.
Scientific congresses
The European Society for Alternatives to Animal Testing (EUSAAT)[42] organises an annual conference in Linz (Austria) for
- Dissemination and validation of alternative methods to animal testing
- Promotion of research in the field of the 3Rs
- Reduction of the use of animals for tests in the field of education and continuing education
- Reduction of suffering and stress of laboratory animals by better breeding, keeping, test planning and other accompanying measures
- Experts' guidance and referees' opinion for public and private organizations, companies, universities
- Suitable information for the public and the media
The World Congress on Alternatives and Animal Use in the Life Sciences takes place every three years. The next conference (10th) will be held in September 2017 in Seattle.[43]
The 1st Latino-Americano Congress on Alternative to Animal Testing took place in 2012. Colama (I Congresso Latino-Americano De Metodos Alternativos Ao Uso De Animais No Ensino, Pesquisa E Industria).[44]
Industry and corporate initiatives
- Cosmetics Europe: Represents the interests of more than 4000 companies in the cosmetic, toiletry and perfumery industry since 1962.[45]
- Unilever: "We do not test finished products on animals unless demanded by the regulatory authorities in the few countries where this is the law. In such cases, we try to convince the local authorities to change the law. Where some testing of ingredients is required by law or currently unavoidable, we aim to minimise the number of animals used."[46]
- BASF: "Systematic screening investigations provide information about important toxicological properties of substances at an early stage of development. ... We replace animal experiments whenever an alternative method is available that complies with an OECD Test Guideline and is recognized by the authorities."[47]
Legislation
EU Directive 2010/63/EU
On January 1, 2013, EU Directive 2010/63/EU "on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes" entered into force for the EU Member States (MS),[48] repealing Directive 86/609/EEC.[49] Because it is a Directive, it allows Member States certain flexibility in transposition of national rules. The status of the implementation of the new Directive in the EU is described by the EC General Environment Directorate.[50]
- Article 1.3: The new EU Directive applies to the following animals: (a) live non-human vertebrate animals, including: (i) independently feeding larval forms; and (ii) foetal forms of mammals from the last third of their normal development; (b) live cephalopods.
- Article 4: The Directive refers directly to the 3Rs:[6] "Principle of replacement, reduction and refinement".
- Article 47-2: Member States shall assist the Commission in identifying and nominating suitable specialised and qualified laboratories to carry out such validation studies.
In July 2013, the Commission announced the creation of NETVAL [51] (European Union Network of Laboratories for the Validation of Alternative Methods). EU-NETVAL's primary role is to provide support for EURL ECVAM validation projects, including aspects of training and dissemination, and the identification of methods that have a potential to reduce, refine or replace animals used for scientific purposes.[52] Currently there are 13 test facilities in 9 Member States: Germany (3), The Netherlands (2), Spain (2), Belgium (1), Czech Republic (1), Finland (1), France (1), Italy (1) and Sweden (1).[51]
EU cosmetic regulation
The Cosmetics Directive provides the regulatory framework for the phasing out of animal testing for cosmetics purposes. It establishes prohibitions against (a) testing finished cosmetic products and cosmetic ingredients on animals (testing ban), and (b) marketing in the EU finished cosmetic products and ingredients included in cosmetic products which were tested on animals for cosmetics purposes (marketing ban). The same provisions are contained in Cosmetics Regulation EU 1223/2009, which replaces the Cosmetics Directive as of July 11, 2013.[53]
EU chemical policy: REACH
In 2007, EU legislation on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH EC 1907/2006) came into force, relating to chemicals and their safe use.[54] The aim of REACH is to improve the protection of human health and the environment through the better and earlier identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances. It promotes the use of alternative methods for animal testing, but does not oblige the test performer to do so; Article 25.1 - In order to avoid animal testing, testing on vertebrate animals for the purposes of this Regulation shall be undertaken only as a last resort. It is also necessary to take measures limiting duplication of other tests.
EU test methods regulation
In parallel to the adoption of REACH, the EC published standardised and accepted methods for testing hazardous properties of chemicals. These were written into the "Test Methods Regulation".[55] All the alternative test methods among the in vivo studies are included in PART B; "The European Union is committed to promoting the development and validation of alternative techniques which can provide the same level of information as current animal tests, but which use fewer animals, cause less suffering or avoid the use of animals completely. Such methods, as they become available, must be considered wherever possible for hazard characterisation and consequent classification and labeling for intrinsic hazards and chemical safety assessment."
EU Regulation for Food Additives, Food Enzymes, and Food Flavourings
EU philosophy on food additives, food enzymes, and food flavourings and ingredients intended for human consumption is that none should be put on the market unless they are included on a published Community list of authorised substances, in accordance with the conditions laid down in relevant food law. This approach is intended to bring food producers into compliance with the provisions of Regulation (EC) 1334/2008 that pertain to the safety of food flavourings. As part of the approval process, the EC will require full disclosure of study data, safety issues, and toxicological findings for all such additives.[56]
Within the EU animal welfare law (2010/63/EU), the principles of the 3Rs are invoked whenever toxicological test methods are necessary.[57]
Animal welfare and animal rights organizations
Europe
- Eurogroup for Animals: "An estimated 12.1 million animals – including dogs, rabbits and even our closest genetic relatives, primates – are used in laboratory research throughout Europe every year. Eurogroup focusses on ensuring their protection and works with legislators, experts and industry with the aim of ultimately replacing all animal experiments with viable alternatives. We continue to actively promote the replacement, reduction and refinement of animal tests and do all we can to improve the lives of those animals currently used for research."[58]
Austria
- Vier Pfoten (Four Paws) [59]
France
- Antidote: "When it is about assessing drug safety, humans are not 70kg rats! It is about time to move on from the actual paradigm on assessing drug safety. The first step would be to eliminate all the regulatory requirements for animal testing and replace these tests by 21st century methods."[60]
Germany
- Deutscher Tierschutzbund:[61]
Italy
- Lega Anti Vivisezione [62]
Monaco
- The ALEXANDRA Association: "... aims at stimulating research and development (R&D) in the area of alternative methods to animal experimentation by providing political, technical and educational support to researchers and entrepreneurs worldwide. In particular alternative methods based on 'Open Source' concepts i.e. non-patent protected core technologies for human tissue reconstruction and cell culture technologies will be actively promoted."[63]
United Kingdom
- British Union for the Abolition of Vivisection (BUAV): "For over 100 years the BUAV has been campaigning peacefully to create a world where nobody wants or believes we need to experiment on animals."[64]
United States
- New England Anti-Vivisection Society (NEAVS): "Recognition of the inadequacy of animal toxicity testing has resulted in the development of better techniques ... NEAVS and its programs will help hasten the inevitable and necessary transition away from animal-based experimentation, testing, and teaching, toward science and science education governed by progressive scientific thought and compassionate ethics."[65]
Joint
- Humane Society International (HSI) in the US and UK: "Today, scientific and government authorities worldwide are acknowledging the deficiencies of "animal models" and calling for a new approach to safety testing and health research using state-of-the-art techniques. Advances in biology, genetics, computer science and robotics have given scientists new tools to help identify the root causes of human toxicity and disease."[66]
- People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) in the US and UK: "We teamed up with CeeTox, Inc. to fund work on a new humane skin test that could replace painful tests on mice and guinea pigs."[67]
Public campaigns and awards
- Petition to the European Parliament for the abolition of vivisection as a European Citizen Initiative.[68] The threshold of 1 million signatures was reached for the deadline (1 November 2013). The European Commission is currently checking the authenticity of each signature.
- "Go cruelty free"[69]
- HSI's report "Advancing Safety Science and Health Research with Innovative, Non-Animal Tools"[70]
- The Lush Prize: "The Lush Prize is a major initiative which will use resources to bring forward the day when safety testing takes place without the use of animals. The Lush Prize will focus pressure on toxicity testing for consumer products and ingredients in a way which complements the many projects already addressing the use of animals in medical testing."[71]
- EPAA (European Partnership for Alternative Approaches to Animal Testing) will grant a €3000 prize to a laboratory technician involved in implementing and raising awareness of Replacement, Reduction and Refinement of animal testing.[72]
- The Alternatives Research and Development Foundation (ARDF) provides grants to advance the use of non-animal methods in the fields of biomedical testing, research, and education.[73]
- The international NC3Rs 3Rs Prize is awarded to highlight an outstanding original contribution to scientific and technological advances in the 3Rs in medical, biological or veterinary sciences published within the last three years.[74]
- The American Fund for Alternatives to Animal Research (AFAAR) funds a wide and encompassing range of research involving the use, development, or validation of alternatives.[75]
Education and training
- IIVS: The Institute for In Vitro Sciences, Inc. is a non-profit research and testing laboratory dedicated to the advancement of in vitro (non-animal) methods worldwide. Founded in 1997, IIVS has worked with industry and government agencies to implement in vitro testing strategies that limit animal use while supplying key information for product safety and efficacy decisions.[76]
- NORINA is a database containing details of products which may be used as alternatives or supplements to the use of animals in education and training.[77] NORINA's search engine is linked to those of two other databases: TextBase, which provides information on textbooks and other written material of relevance to laboratory animal science and alternatives, and 3R Guide which gives details of guidelines, information centres, databases, journals and email lists within the field of replacement, reduction and refinement of animal experimentation. The three databases are hosted by Norecopa.[78]
- InterNICHE is the International Network for Humane Education. It has been developed to meet the needs of teachers and trainers, students, ethics committees, alternatives producers and campaigners internationally.[79]
- "Tierschutz macht Schule" - the Association for Animal Welfare Education - was founded in the course of the implementation of Austria's nationwide animal welfare law. The animal welfare education association aims to improve the living conditions of pets, farm animals, laboratory animals and wild animals through providing knowledge about their needs and behaviour to children, youth and the public.[80] The association offers a teaching magazine about research animals and animal tests suitable for secondary schools and college, which can be ordered on their website. It aims at explaining alternatives to animal testing in a youth appropriate language and can be used in lessons straight away.
- XCellR8's mission is to support, develop and implement the use of scientifically advanced and ethically sound alternatives to animal testing. They are an exclusively in vitro company, with commitment to promoting non-animal testing strategies at the core of all of their activities.[81]
Institutes and national or international organizations
Institutes and organizations that research or fund alternatives to animal testing include:
Asia - Oceania
Australia
- Medical Advances Without Animals Trust[82]
India
- Alternatives to Animal Experimentation Laboratory, Department of Pharmacology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh.[83]
- Mahatma Gandhi-Doerenkamp Center for Alternatives to Use of Animals in Life Science, Bharathidasan university, Trichy, Tamil Nadu, India Education[84]
Japan
- Japanese Center for the Validation of Alternative Methods (JACVAM), since 2005[85]
South Korea
- The Korean Center for the Validation of Alternative Methods (KOCVAM), since 2009[86]
South America
Brazil
- BraCVAM as the Brazilian Center for the Validation of Alternatives Methods. It was established in 2011.[87][88]
North America
Canada
- Canadian Council on Animal Care[89]
- Health Canada, which does not have a formal validation center, but coordinates health related test method validation and acceptance issues[90]
United States of America
- American Fund for Alternatives to Animal Research (AFAAR): "Over the years, AFAAR has funded alternatives worldwide, including more than 200 human tissue culture tests to replace toxicity and other testing on animals ... Today, AFAAR funds a wide and encompassing range of research involving the use, development, or validation of alternatives."[75]
- Interagency Coordinating Committee on the Validation of Alternative Methods (ICCVAM), since 1994;[91]
- Johns Hopkins University Center for Alternatives to Animal Testing[92]
- Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine
- UC Davis Center for Animal Alternatives
Europe
- The EC's involvement in activities targeted to the validation of alternative approaches to animal testing started in 1991, with the launch of ECVAM (European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods), hosted by the Joint Research Centre, Institute for Health and Consumer Protection (IHCP). As from 2011, ECVAM's tasks are assigned to EURL ECVAM.[93] Official bodies such as the EURL ECVAM,[93] hosts an online database of toxicological, non-animal alternative test methods DB-ALM,.[94]
- Under the Framework Programmes 6 and 7, the EC funded a significant number of large integrated research projects aiming to develop alternatives to animal testing for about EUR 330 million based on the Review of REACH from February 2013 (the European Chemical Program).[95]
- The European Partnership for Alternative Approaches to Animal Testing (EPAA) as a liaison between the EC and industries.[96]
- The European Consensus Platform for Alternatives (ECOPA) coordinates efforts amongst EU member states.[97]
Austria
- Zentrum fuer Ersatz[98]
Finland
- Finish Center for Alternative Methods (FICAM), since 2008[99]
France
- FRANCOPA is the French platform dedicated to development, validation, and dissemination of alternative methods in animal testing. It was created in November 16, 2007 [100]
Germany
- Zentralstelle zur Erfassung und Bewertung von Ersatz- und Ergänzungsmethoden (ZEBET), since 1989[101][102]
Norway
- Norecopa is the Norwegian consensus platform for the replacement, reduction and refinement of animal experiments. It was founded on October 10, 2007 [103]
Romania
- Romanian Center for Alternative Test Methods (ROCAM) promotes the application of alternative methods in industry and their acceptance by regulators in Romania and also the development of new methods and approaches. ROCAM was established in June 2015 with the main goal to support and promote the 3Rs principles in Romania and regionally.
United Kingdom
- Dr Hadwen Trust
- Fund for the Replacement of Animals in Medical Experiments[104]
- National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (NC3Rs), since 2004[105]
International
ICATM
International Cooperation on Alternative Test Methods (ICATM): On April 27, 2009 the United States, Canada, Japan and EU signed a memorandum of cooperation that could reduce the number of animals required for consumer product safety testing worldwide. The agreement will yield globally coordinated scientific recommendations on alternative toxicity testing methods that should speed their adoption in each of these countries, thus reducing the number of animals needed for product safety testing.[106]
.jpg)
OECD
The OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) is a forum for discussion where governments express their points of view, share their experiences, and search for common ground, as opposed to a supranational organization.[110] OECD is a forum where alternative test methods also undergo validation and are therereafter accepted for regulatory purposes in more than 35 member countries worldwide.[111] NGOs are represented at the technical level at the OECD, under the ICOPA International Council on Animal Protection in OECD program.[112]
The testing of chemicals is labor-intensive and expensive. Often the same chemical is tested in several countries simultaneously, which means that redundant animal tests are performed. To relieve some of this burden, the OECD Council adopted a decision in 1981, stating that data generated in a member country, in accordance with OECD Test Guidelines and Principles of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), shall be accepted in other member countries for assessment purposes and other uses relating to the protection of human health and the environment. This principle is referred to using the acronym MAD, for the Mutual Acceptance of Data.[110]
See also
References
- ↑ R E Hester R M Harrison et al. Alternatives To Animal Testing (Issues in Environmental Science and Technology) Royal Society of Chemistry; 1 edition (June 7, 2006) ISBN 978-0-85404-211-1
- ↑ Lipinski, Christopher; Hopkins, A (16 December 2004). "Navigating chemical space for biology and medicine". Nature. 432 (7019): 855–61. doi:10.1038/nature03193. PMID 15602551.
- ↑ Malcolm Rowland (February 2006). "Microdosing and the 3Rs". National Center for the Replacement, Refinement, and Reduction of Animals in Research ( NC3Rs ). Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ↑ "Alternatives?". Speaking of Research. 2009-07-31. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ FRAME (2005). "Human microdosing reduces the number of animals required for pre-clinical pharmaceutical research". Alternatives to Laboratory Animals. 33 (439).
- 1 2 Russell, W.M.S. and Burch, R.L., (1959). The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique, Methuen, London. ISBN 0-900767-78-2
- ↑ "Special section: Monoclonal antibodies". Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Archived from the original on 2007-08-20. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ Brunner, D., Jürgen Frank, Helmut App, Harald Schöffl, Walter Pfaller and Gerhard Gstraunthaler. 2010 Serum-free Cell Culture: The Serum-free Media Interactive Online Database. Altex 27:53–62.
- ↑ "EpiDermTM Tissue Model". MatTek Corporation. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "L'Oréal cutaneous tissue engineering platform". Invitroskin. 2007-04-30. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "News - Congress - Workshops - SkinEthic Laboratories - SkinEthic Reconstructed Human Epidermis RHE validated in Europe". Skinethic.com. 2008-12-19. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Alternatives In Testing". Neaves Humane Science is Superior Science. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "Test No. 439: In Vitro Skin Irritation - Books - OECD iLibrary". OECD I-Library. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ Stobbe JL, Drake KD, Maier KJ (2003). "Comparison of in vivo (Draize method) and in vitro (Corrositex assay) dermal corrosion values for selected industrial chemicals". International Journal of Toxicology. 22 (2): 99–107. doi:10.1080/10915810305094. PMID 12745991. INIST:14763182.
- ↑ "Background - 3T3 Neutral Red Uptake Phototoxicity Assay - MB Research Labs". 3t3nru.mbresearchlabs.com. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "The use of reconstructed human epidermis for skin absorption testing: Results of the validation study". PubMed.gov. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ Guthrie, Catharine (2008-03-27). "Putting Immunity in a Test Tube". TIME. Retrieved 2009-12-22.
- ↑ "Asthma". entelos.com. Archived from the original on 2005-04-15. Retrieved 2007-10-05. (from internet archive)
- ↑ "Using test dummy experiments to investigate pediatric injury risk in simulated short-distance falls". PubMed.gov. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "I was a human crash-test dummy - Salon.com". Archive.salon.com. 1999-11-19. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "About the TraumaMan System | Simulab Corporation". Simulab.com. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "TraumaMan Offers Lifelike Practice for Med Students". NPR. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Game of Hearts". Portfolio.com. 2008-07-16. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- 1 2 "Technology | Mouse brain simulated on computer". BBC News. 2007-04-27. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "alternatives to animal testing". Peta
- ↑ Robert C. R. Wootton, and Andrew J. Demello. "Microfluidics: Analog-to-digital Drug Screening." Nature 483.7387 (2012): 43. Web.
- ↑ Prot, Jean, and Eric Leclerc. "The Current Status of Alternatives to Animal Testing and Predictive Toxicology Methods Using Liver Microfluidic Biochips." Annals of Biomedical Engineering 40.6 (2012): 1228-243. Web.
- ↑ Kristian Björnstad; Anders Helander; Peter Hultén; Olof Beck (2009). "Bioanalytical investigation of asarone in connection with Acorus calamus oil intoxications". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 33 (9): 604–609. doi:10.1093/jat/33.9.604. PMID 20040135.
- ↑ Joanna D. Moody; Donglu Zhang; Thomas M. Heinze; Carl E. Cerniglia (2000). "Transformation of amoxapine by Cunninghamella elegans". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 66 (8): 3646–3649. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.8.3646-3649.2000. PMC 92200
 . PMID 10919836.
. PMID 10919836. - ↑ A. Jaworski; L. Sedlaczek; J. Dlugoński; Ewa Zajaczkowska (1985). "Inducible nature of the steroid 11-hydroxylases in spores of Cunninghamella elegans (Lendner)". Journal of Basic Microbiology. 25 (7): 423–427. doi:10.1002/jobm.3620250703.
- ↑ Hezari, M.; Davis, P. J. (1993). "Microbial models of mammalian metabolism. Furosemide glucoside formation using the fungus Cunninghamella elegans". Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals. 21 (2): 259–267. PMID 8097695.
- ↑ Sharma, KK; Mehta, T; Joshi, V; Mehta, N; Rathor, AK; Mediratta, KD; Sharma, PK (2011). "Substitute of animals in drug research: An approach towards fulfillment of 4R's". Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 73 (1): 1–6. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.89750. PMC 3224398
 . PMID 22131615.
. PMID 22131615. - ↑ "Lung-on-a-chip". Hansjorg Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering. Retrieved 27 January 2014.
- ↑ Committee on Toxicity Testing and Assessment of Environmental Agents, National Research Council (2007). "Toxicity testing in the 21st century: A vision and a strategy". Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ↑ "The Human Toxome Project". The Human Toxome Project. Retrieved 27 January 2014.
- ↑ "SEURAT-1 - Towards the Replacement of in vivo Repeated Dose Systemic Toxicity Testing". Seurat-1.eu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Sixth Report from the Commission to the Council and the European Parliament on the Statistics on the number of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes in the member states of the European Union COM(2010) 511/final 2" (PDF). European Commission. 2010. Retrieved August 20, 2013.
- ↑ 20 February 2015. "Comparing the LAL Method with the Pyrogen Test on Rabbits". Wako Pyrostar. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ↑ "SHORT GUIDANCE ON THE THRESHOLD APPROACH FOR ACUTE FISH TOXICITY". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 27 January 2014.
- ↑ "euroecotox.eu". euroecotox.eu. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Home| AXLR8". Axlr8.eu. 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Home". Eusaat.org. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "World Congress flyer" (PDF). ALTEX. ALTEX.
- ↑ "COLAMA 2012". Uff.br. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Cosmetics Europe - Alternative Methods". Cosmeticseurope.eu. 2011-08-25. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Developing alternative approaches to animal testing | Sustainable living | Unilever Global". Unilever.com. 2013-07-17. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Alternative Methods in Use - BASF - The Chemical Company - Corporate Website". BASF. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2010). Directive 2010/63/EU "Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council" Check
|url=value (help). Retrieved August 12, 2013. - ↑ "EUR-Lex - 31986L0609 - EN - EUR-Lex". Eur Lex. 11 Apr 2014. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "Animals used for scientific purposes - Environment - European Commission". European Commission. 11 Apr 2014. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- 1 2 "EURL ECVAM's" (PDF). Ihcp.jrc.ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "EU-NETVAL (European Union Network of Laboratories for the Validation of Alternative Methods) — Institute for Health and Consumer Protection – (JRC-IHCP), European Commission". Ihcp.jrc.ec.europa.eu. 2014-01-20. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2006). "Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH)". Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- ↑ European Union (31 May 2008). "Acts adopted under the EC Treaty/Euratom Treaty whose publication is obligatory". Official Journal of the European Union. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "Regulations: No 1331/2008". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Guidance for Submission for Food Additive Evaluations" (PDF). European Food Safety Authority. 16 Aug 2012. Retrieved 23 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "Animal Testing | What We Do". Eurogroup For Animals. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Medical research on animals: facts and fiction". Vier-pfoten.org. 2012-11-13. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Antidote Europe". Antidote Europe. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Tierschutzbund". Tierschutzbund.de. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "LAV - Diritti agli animali - LAV". Lav.it. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "R&D on Alternative Methods to Animal Experimentation". AlexandraProject.org. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "About US". Buav.org. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "NEAVS". Neavs.org. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Advancing Humane Science : Humane Society International". Hsi.org. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Home". PETA.org.uk. 2012-01-10. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "stopvivisezione.net". stopvivisezione.net. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Welcome". Go Cruelty Free. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "End Animal Testing : Humane Society International". Hsi.org. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "About the £250,000 Lush Prize". Lushprize.org. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Enterprise and Industry - European Commission". Ec.europa.eu. 2011-01-01. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "Alternatives Research Grants | Alternatives Research & Development Foundation (ARDF)". Ardf-online.org. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "3Rs Prize 2013". NC3Rs. 2013-12-11. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- 1 2 "About Us | AFAAR". Alternativestoanimalresearch.org. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
- ↑ "IIVS". Iivs.org. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ NORINA
- ↑ "Norecopa". norecopa.no. Retrieved 2014-11-12.
- ↑ "Welcome". InterNICHE. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "Mission statement :: Tierschutz macht Schule". Tierschutzmachtschule.at. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "Cell Culture Technology". XCellR8. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "MAWA Trust". MAWA Trust. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ A Guide to the Alternatives of Animal Experimentation (2009; revised edition 2010). Eds. Syed Ziaur Rahman and Mohd Tariq Salman, Ibn Sina Academy of Medieval Medicine and Sciences, Aligarh, India (ISBN 978-81-906070-4-9)
- ↑ Akbarsha, MA; Pereira, Shiranee (Nov–Dec 2010). "Mahatma Gandhi-Doerenkamp Center for Alternatives to Use of Animals in Life Science Education". Pharmacol Pharmacother. 1 (2): 108–10. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.72353. PMC 3043344
 . PMID 21350619. Archived from the original on July 13, 2011.
. PMID 21350619. Archived from the original on July 13, 2011. - ↑ "JaCVAM". Jacvam.jp. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "International Cooperation > KoCVAM". Nifds.go.kr. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "BRA : Brazilian Center for Validation of Alternative Methods established" (PDF). Altex.ch. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ Presgrave OA (December 2008). "The need for the establishment of a Brazilian Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods (BraCVAM)". Alternatives to Laboratory Animals. 36 (6): 705–8. PMID 19154096.
- ↑ "Three Rs". Ccac.ca. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Framework for International Cooperation on Alternative Test Methods (ICATM) - Consumer and Personal Care Products - Health Canada". Hc-sc.gc.ca. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "NTP Interagency Center for the Evaluation of Alternative Toxicological Methods - National Toxicology Program". Iccvam.niehs.nih.gov. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Center for Alternatives to Animal Testing - Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health". Caat.jhsph.edu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- 1 2 "European Union Reference Laboratory for alternatives to animal testing (EURL ECVAM) — Institute for Health and Consumer Protection – (JRC-IHCP), European Commission". Ihcp.jrc.ec.europa.eu. 2014-01-24. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Home page". Evcam Database Service on Alternative methods to Animal Experimentation).
- ↑ "Review of REACH - Chemicals - Enterprise and Industry". Ec.europa.eu. 2013-06-28. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "European Partnership for Alternatives Approaches to Animal Testing - European Commission". Ec.europa.eu. 2014-02-20. Archived from the original on 2013-11-01. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "ecopa - european consensus-platform for alternatives". Ecopa.eu. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Zentrum für Ersatz- und Ergänzungsmethoden zu Tierversuchen". zet. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "FICAM front page". Ficam.fi. 2012-09-26. Retrieved 2014-06-02.
- ↑ "FRANCOPA: Accueil". Francopa.fr. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "ZEBET database on alternatives to animal experiments on the Internet (AnimAlt-ZEBET)". BfR. 2004-09-30. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Mission". BfR. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Norwegian consensus platform for the replacement, reduction and refinement of animal experiments". Retrieved 2014-11-12.
- ↑ "Fund for the Replacement of Animals in Medical Experiments". Frame.org.uk. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "NC3RS". Nc3rs.org.uk. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ NIH. "Reducing the Number of Animals in Research Testing" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 27, 2013. Retrieved 24 Apr 2014.
- ↑ "Official web site". ICH. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "Testing of chemicals". OECD. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- ↑ "International Cooperation on Cosmetic Regulation (ICCR)". Fda.gov. Retrieved 2014-02-26.
- 1 2 "Testing of chemicals". OECD. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "Members and partners". OECD. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "Welcome to ICAPO". Icapo.org. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
External links
| Wikiversity has learning materials about Alternatives to animal testing |
- National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research
- Alternatives to Animals: The Latest: Tracks news stories about scientific developments in alternatives to animal use
- International Network for Humane Education
- Go3R: semantic search to avoid animal experiments
- The Use of Databases, Information Centers and Guidelines When Planning Research that May Involve Animals, Animal Welfare Information Center Bulletin, National Agricultural Library. Provides an overview of databases, bibliographies and guidelines that provide useful information on alternative methods when planning research that may involve animals.
- CADASTER Seventh Framework Programme project aimed to develop computational methods to minimize number of experimental tests for REACH – Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals
