British West Florida
| West Florida | |||||
| Colony of Great Britain | |||||
| |||||
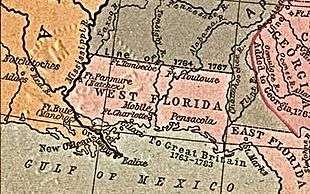 | |||||
| Capital | Pensacola (1763) | ||||
| Governor | |||||
| • | 1763 | George Johnstone | |||
| History | |||||
| • | Treaty of Paris (1763) | 10 February 1763 | |||
| • | Peace of Paris (1783) | 1783 | |||
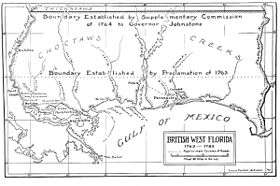
West Florida was a colony of the Kingdom of Great Britain from 1763 until 1783 when it was ceded to Spain as part of the Peace of Paris.
British West Florida comprised parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Florida. Effective British control ended in 1781 when Spain captured Pensacola. The territory subsequently became a colony of Spain, parts of which were gradually annexed piecemeal by the United States beginning in 1810.
Creation
In 1762 during the Seven Years' War a British expedition attacked and occupied Havana, the capital of Cuba. To secure the return of this valuable city, Spain agreed to cede its territory of La Florida to Great Britain under the 1763 Treaty of Paris. France also ceded a large segment of New France to Great Britain, including everything on the east bank of the Mississippi River, except for the city of New Orleans. The British divided these new territories into two separate colonies East Florida, with its capital in St Augustine and West Florida, with the former Spanish settlement of Pensacola as its capital. By a separate treaty Spain was given the western side of the Mississippi, which formed Spanish Louisiana with its capital at New Orleans at the mouth of the river. Many of the existing Spanish inhabitants of Florida were evacuated to Cuba, and new British and American settlers arrived to take over the land.
British era
In 1763 British troops arrived and took possession of Pensacola. George Johnstone was appointed as the first British Governor, and in 1764 a colonial assembly was established.[1][2] The structure of the colony was modeled after the existing British colonies in America, as opposed to Quebec, which was based on a different structure. In contrast to East Florida, where there was little development and population growth, West Florida began to boom in the years following the British takeover, and thousands of new arrivals came to take advantage of the favorable conditions there.
West Florida was invited to send delegates to the First Continental Congress which was convened to present colonial grievances against the British Parliament to George III, but along with several other colonies, including East Florida, they declined the invitation. Once the American War of Independence had broken out, the colonists remained overwhelmingly loyal to the Crown. In 1778 the Willing Expedition proceeded with a small force down the Mississippi, ransacking estates and plantations, until they were eventually defeated by a local militia. In the wake of this, the area received a small number of British reinforcements.
Spanish conquest

Following an agreement signed at Aranjuez, Spain entered the American Revolutionary War on the side of France but not the Thirteen Colonies.[3] Spanish troops under Bernardo de Galvez advanced and seized Baton Rouge and Mobile. In 1781 Spain captured Pensacola and its garrison. As part of the 1783 Peace of Paris, Great Britain ceded the territories of West Florida and East Florida back to Spain. When Spain acquired West Florida in 1783, the eastern British boundary was the Apalachicola River, but Spain in 1785 moved it eastward to the Suwannee River.[4][5] The purpose was to transfer San Marcos and the district of Apalachee from East Florida to West Florida.[6][7]
See also
References
- ↑ John Richard Alden (1957). The South in the Revolution, 1763–1789. Louisiana State University Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-8071-0013-4.
- ↑ Coker, William S; Shofner, Jerrell H.; Morris, Joan Perry; Malone, Myrtle Davidson (1991). Florida from the Beginning to 1992 : a Columbus Jubilee Commemorative. Houston: Pioneer Publications. p. 4. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ↑ Spencer Tucker; James R. Arnold; Roberta Wiener (30 September 2011). The Encyclopedia of North American Indian Wars, 1607–1890: A Political, Social, and Military History. ABC-CLIO. p. 751. ISBN 978-1-85109-697-8.
- ↑ Wright, J. Leitch (1972). "Research Opportunities in the Spanish Borderlands: West Florida, 1781-1821". Latin American Research Review. Latin American Studies Association. 7 (2): 24–34. JSTOR 2502623. Wright also notes, "It was some time after 1785 before it was clearly established that Suwannee was the new eastern boundary of the province of Apalachee."
- ↑ Weber, David J. (1992). The Spanish Frontier in North America. New Haven, Connecticut, USA: Yale University Press. p. 275.
Spain never drew a clear line to separate the two Floridas, but West Florida extended easterly to include Apalachee Bay, which Spain shifted from the jurisdiction of St. Augustine to more accessible Pensacola.
- ↑ "The Evolution of a State, Map of Florida Counties - 1820". 10th Circuit Court of Florida. Retrieved 2016-01-26.
Under Spanish rule, Florida was divided by the natural separation of the Suwanee River into West Florida and East Florida.
- ↑ Klein, Hank. "History Mystery: Was Destin Once in Walton County?". The Destin Log. Retrieved 2016-01-26.
On July 21, 1821 all of what had been West Florida was named Escambia County, after the Escambia River. It stretched from the Perdido River to the Suwanee River with its county seat at Pensacola.
Bibliography
- Calloway, Colin Gordon. The Scratch of a Pen: 1763 and the Transformation of North America. Oxford University Press, 2006.
- Chavez, Thomas E. Spain and the Independence of the United States: An Intrinsic Gift. University of New Mexico Press, 2003.