Strombolian eruption

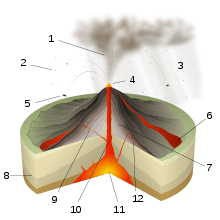
Strombolian eruptions are relatively mildly explosive, with a volcanic explosivity index of about 2 to 3. They are named for the Italian volcano Stromboli, which is the eponym for the type. Strombolian eruptions consist of ejection of incandescent cinder, lapilli, and lava bombs, to altitudes of tens to a few hundreds of metres. The eruptions are small to medium in volume, with sporadic violence.
The Italian vulcanologist Giuseppe Mercalli studied eruptions at Stromboli and Vulcano in 1888-1890, and observed that the characteristic features of eruptions were different between the two. To distinguish between them, Mercalli defined Strombolian eruptions as "...Mildly explosive at discrete but fairly regular intervals of seconds to minutes..."
The tephra typically glows red when leaving the vent, but its surface cools and assumes a dark to black colour and may significantly solidify before impact. The tephra accumulates in the vicinity of the vent, forming a cinder cone. Cinder is the most common product; the amount of volcanic ash is typically rather minor.
The lava flows are more viscous, and therefore shorter and thicker, than the corresponding Hawaiian eruptions; it may or may not be accompanied by production of pyroclastic rock.
Instead the gas coalesces into bubbles, called gas slugs, that grow large enough to rise through the magma column, bursting near the top due to the decrease in pressure and throwing magma into the air. Each episode thus releases volcanic gases, sometimes as frequently as a few minutes apart. Gas slugs can form as deep as 3 kilometers, making them difficult to predict.[1][2]
Strombolian eruptive activity can be very long-lasting because the conduit system is not strongly affected by the eruptive activity, so that the eruptive system can repeatedly reset itself.
Monogenetic cones usually erupt in the Strombolian style. For example, the Parícutin volcano erupted continuously between 1943-1952, Mount Erebus, Antarctica has produced Strombolian eruptions for at least many decades, and Stromboli itself has been producing Strombolian eruptions for over two thousand years. The Romans referred to Stromboli as the "Lighthouse of the Mediterranean."
See also
References
External links
- explanation with photos on academic site
- comparison of volcanic blast types
- USGS Photo Glossary
- Modelling of Volcano for CG/CFD Papers with abstracts, images, and PDFs of modelling of Strombolian (explosive) volcano for computer graphics (CG) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). The main entrance page is here.