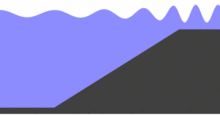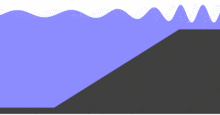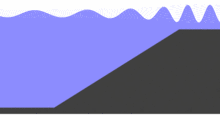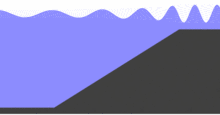
Wave shoaling

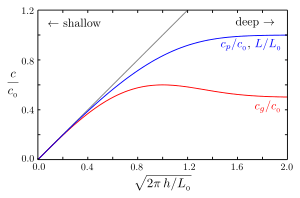
Quantities have been made dimensionless using the gravitational acceleration g and period T, with the deep-water wavelength given by L0 = gT2/(2π) and the deep-water phase speed c0 = L0/T. The grey line corresponds with the shallow-water limit cp =cg = √(gh).
The phase speed – and thus also the wavelength L = cpT – decreases monotonically with decreasing depth. However, the group velocity first increases by 20% with respect to its deep-water value (of cg = 1/2c0 = gT/(4π)) before decreasing in shallower depths.[1]
In fluid dynamics, wave shoaling is the effect by which surface waves entering shallower water change in wave height. It is caused by the fact that the group velocity, which is also the wave-energy transport velocity, changes with water depth. Under stationary conditions, a decrease in transport speed must be compensated by an increase in energy density in order to maintain a constant energy flux.[2] Shoaling waves will also exhibit a reduction in wavelength while the frequency remains constant.
In shallow water and parallel depth contours, non-breaking waves will increase in wave height as the wave packet enters shallower water.[3] This is particularly evident for tsunamis as they wax in height when approaching a coastline, with devastating results.
Mathematics
Wave shoaling
For non-breaking waves, the energy flux associated with the wave motion, which is the product of the wave energy density with the group velocity, between two wave rays is a conserved quantity (i.e. a constant when following the energy of a wave packet from one location to another). Under stationary conditions the total energy transport must be constant along the wave ray – as first shown by William Burnside in 1915:[4]
where is the co-ordinate along the wave ray and is the energy flux per unit crest length. A decrease in group speed must be compensated by an increase in energy density . This can be formulated as a shoaling coefficient relative to the wave height in deep water.[5][6]
For shallow water, when the wavelength is much larger than the water depth, wave shoaling satisfies Green's law:
with the mean water depth, the wave height and the fourth root of
Refraction effects
Following Phillips (1977) and Mei (1989),[7][8] denote the phase of a wave ray as
- .
The local wave number vector is the gradient of the phase function,
- ,
and the angular frequency is proportional to its local rate of change,
- .
Simplifying to one dimension and cross-differentiating it is now easily seen that the above definitions indicate simply that the rate of change of wavenumber is balanced by the convergence of the frequency along a ray;
- .
Assuming stationary conditions (), this implies that wave crests are conserved and the frequency must remain constant along a wave ray as . As waves enter shallower waters, the decrease in group velocity caused by the reduction in water depth leads to a reduction in wave length because the nondispersive shallow water limit of the dispersion relation for the wave phase speed,
dictates that
- ,
i.e., a steady increase in k (decrease in ) as the phase speed decreases under constant .
See also
Notes
- ↑ Wiegel, R.L. (2013). Oceanographical Engineering. Dover Publications. p. 17, Figure 2.4. ISBN 0-486-16019-X.
- ↑ Longuet-Higgins, M.S.; Stewart, R.W. (1964). "Radiation stresses in water waves; a physical discussion, with applications" (PDF). Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts. 11 (4): 529–562.
- ↑ WMO (1998). Guide to Wave Analysis and Forecasting (PDF). 702 (2 ed.). World Meteorological Organization. ISBN 92-63-12702-6.
- ↑ Burnside, W. (1915). "On the modification of a train of waves as it advances into shallow water". Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. Series 2. 14: 131–133. doi:10.1112/plms/s2_14.1.131.
- ↑ Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. (1991). Water wave mechanics for engineers and scientists. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering. 2. Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-02-0420-4.
- ↑ Goda, Y. (2000). Random Seas and Design of Maritime Structures. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering. 15 (2 ed.). Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-02-3256-6.
- ↑ Phillips, Owen M. (1977). The dynamics of the upper ocean (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-29801-6.
- ↑ Mei, Chiang C. (1989). The Applied Dynamics of Ocean Surface Waves. Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 9971-5-0773-0.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ocean surface waves. |